Available with Production Mapping license.
A straight line diagram depicts a linear feature, such as a road, as a straight line. Such diagrams are usually produced by a highway department and display features along the road, including bridges and intersecting roads. Rows in the diagram show data about the road, which can include speed limits, the number of lanes, bridge numbers, and historical data.
Straight line diagrams have two primary purposes. The first purpose is data production. When there are many types of events you are managing for a linear referencing route feature, it becomes difficult to visualize and edit this information when you are working with a view of the data that represents the true geometry of the route. By creating a straight line diagram, each aspect of the data appears as a separate line, which allows easy access to the information for editing. The second purpose is for creating a hard-copy map book where each page displays a different route or section of a route.
The Generate Straight Line Diagram tool allows you to create a straight line diagram that includes all the events for all the routes in a transportation network or for selected routes. The wizard that guides you through the process allows you to choose the routes.
Choosing the routes for the straight line diagram
The first step in creating a straight line diagram is to choose the routes on which the straight line diagram is going to be based. You can choose to create a straight line diagram for the route that is currently selected in the map, or you can create straight line diagrams for all the routes in the map.
- Start ArcMap.
- Load your route and the events you want to include in the straight line diagram.
- Add the Generate Straight Line Diagram tool by doing the following:
- Click Customize > Customize Mode on the main menu.
The Customize dialog box appears.
- Click the Commands tab.
- In the Categories list, click Production Editing.
- Click and drag the Generate Straight Line Diagram button
 to a toolbar.
to a toolbar. - Click Close.
- Click Customize > Customize Mode on the main menu.
- On the main menu, click View > Layout View.
- Click the Generate Straight Line Diagram button
 .
.The Generate Straight Line Diagram Dataset dialog box appears.

- Click the Choose Route Layer drop-down arrow and choose the route layer that contains the routes for which you want to create the straight line diagram.
- Choose an option in the Features area for the routes you want to include in the straight line diagram.
- To only use the selected routes, choose the Selected Feature(s) option.
- To use all the routes in the layer, choose the All Features option.
- Optionally, to divide the routes into sections and create straight line diagrams for each one, check the Divide Route Layer for Straight Line Diagrams check box.
- Click Next.
The Generate Straight Line Diagram Dataset dialog box appears.
If you have chosen to divide the routes, proceed to Configuring sections for divided routes.
If you are not going to divide the routes into sections, proceed to Choosing a template for the straight line diagram.
Configuring sections for divided routes
In this part of the wizard, you can configure the way the routes are divided into sections. You can choose to divide the routes using one of the following options:
- Divide Routes Evenly—This option allows you to choose the number of sections that each route will be divided into. This option produces a fixed number of diagrams for each route, regardless of the length of the routes. For example, you have two routes—one that is 10 measure units long and one that is 20 units long. You choose to divide the routes evenly into two sections. The first route will produce two straight line diagrams, one from measure 0 to 5 and one from 5 to 10. The second route will produce two straight line diagrams, from measure 0 to 10 and 10 to 20.
Divide Routes every X measure units—This option allows you to specify the length, in the measure units, where each route feature will be divided. This option produces a varying number of diagrams for each route; however, each diagram displays the same length of each route.
For example, you have two routes—one that is 10 measure units long and one that is 20 units long. You choose to divide the routes every 10 measure units. The first route will produce one straight line diagram from measure 0 to 10. The second route will produce two straight line diagrams, from measure 0 to 10 and 10 to 20.
You can also choose to create a separate feature class for the divided routes, then customize the name and location for it. This feature class contains the geometry of the original routes; however, the features are divided to match the straight line diagram. Creating this feature class allows you to create map books that show the same section of a route in both the data view and the straight line diagram view.
- Choose an option for dividing the routes in the Straight Line Diagram Divisions area.
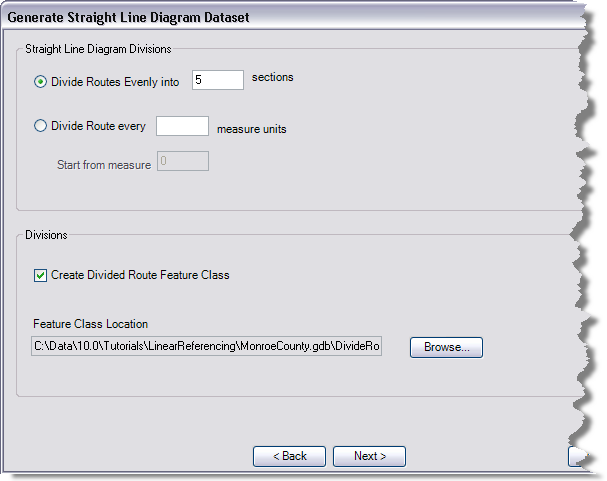
To divide the routes into a specific number of sections
Choose the Divide Routes Evenly into option, then type the number of sections you want to create for each route in the sections text box.
To divide the routes based on a number of measure values
Choose the Divide Routes every option, then type the number of measure units each section is going to contain in the measure units text box. Optionally, you can specify the starting measure value in the Start from measure text box if the starting measure value is not zero.
- To create a separate feature class for the divided routes, check the Create Divided Route Feature Class check box.
By default, the feature class is stored in the same workspace as the route and event tables. The default name of the feature class is Divide Route.
- Optionally, to change the name of the divided route feature class, do the following:
- Click Browse.
The Generate Straight Line Diagram dialog box appears.
- Type a new name for the feature class in the Name text box.
- Click Save.
The Generate Straight Line Diagram Dataset dialog box appears.
- Click Browse.
- Click Next.
The Generate Straight Line Diagram Dataset dialog box appears.
Choosing a template for the straight line diagram
In this part of the wizard, you define a template to use for the straight line diagram and the data frame that is going to contain the dataset for the straight line diagram. You can also choose which data frame is going to contain the base data and how the layers are included.
When pointing to a template .mxd, you can use any .mxd with at least two data frames.
- Click Browse next to the Choose template mxd with field.
The Generate Straight Line Diagram dialog box appears.
- Choose the map document (.mxd) or map template (.mxt) file you want to use as the template for the straight line diagram.
- Click Open.
The Generate Straight Line Diagram Dataset dialog box appears.
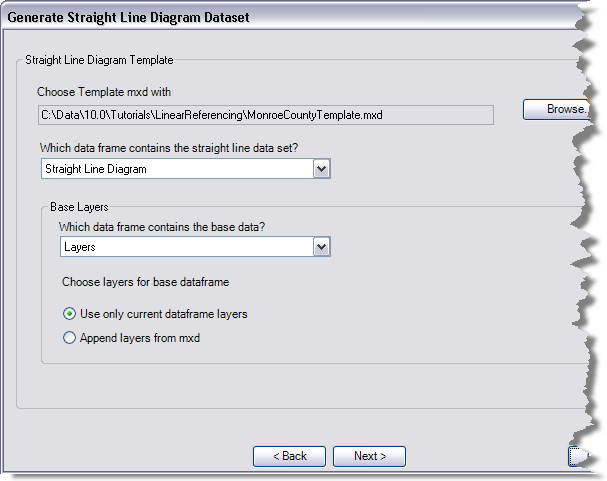
- Click the Which data frame contains the straight line data set drop-down arrow and choose the data frame that contains the dataset for the straight line diagram.
- Click the Which data frame contains the base data drop-down arrow and choose the data frame that contains the source data for the straight line diagram.
- Choose a method for determining which layers are included in the straight line diagram.
- To only include layers loaded in the data frame, choose the Use only current dataframe layers option.
- To include additional layers that are not in the current map document but are in the template map document, choose the Append layers from mxd option.
- Click Next.
The Generate Straight Line Diagram Dataset dialog box appears.
Choosing the events to include in the straight line diagram
In this part of the wizard, you are going to choose the events that are going to be depicted in the straight line diagram. By default, the event layers from the map and template .mxd file are included. You can also append other event layers as needed.
In the list, there is always an item called Reference Layer. This item is always checked and cannot be changed. The reference layer is a line that is created by default in the diagram without any events on it. The reference layer can be used in multiple ways. For example, the reference layer can be used to symbolize the location where other routes intersect the route that is the focus of the current diagram. You can choose to display events above and/or below this reference layer.
Learn more about choosing events for the straight line diagram
- In the Choose Event Layers and Order list, check the check boxes next to the event layers you want to include in the straight line diagram.

- To add event layers to the list, do the following:
- Click the Add button
 .
.The Add Route Events dialog box appears.
- Create the event layer you want to add to the straight line diagram.
- Click the Add button
- To change the order of the event layers, do the following:
- Choose the event layer in the Choose Event Layers and Order list.
- To move the layer up in the list, click the Move Up button
 .
. - To move the layer down in the list, click the Move Down button
 .
.
- Click Next when you are finished choosing and arranging event layers.
The Generate Straight Line Diagram Dataset dialog box appears.
Configuring the spacing for the straight line diagram
In this part of the wizard, you can customize the amount of space allocated for each part of the straight line diagram on the page layout. The straight line diagram itself spans the entire width of the data frame and has options for spacing for different parts of the diagram.
- Header and Footer—The features are created in a square area; however, the dimensions of the data frame where you want to add the events may not be square. Enter values for the header and footer to make the diagram in an area that is wider than it is high.
- Reference—The space that you give to the reference parameter is the amount of space that is used for the reference layer. The reference layer is created in the middle of this space.
- Events—There may be one or two of these properties based on the location of the events in relation to the reference layer. This property defines how much of the diagram is going to be filled with the event layers. The percentage of space for the event layers is evenly divided based on the number of events that have been selected.
- Gap—There may be one or two of these properties based on the location of the events in relation to the reference layer. The gap allows you to specify extra space that may appear between the reference layer and the events. For example, perhaps you place the reference layer with events above and below and you want to display the measures along the route below the reference layer. In this case, you might want to have a larger gap at the bottom of the reference layer than at the top.
- Type a value in the Header text box that represents the amount of space the header uses in the straight line diagram data frame.
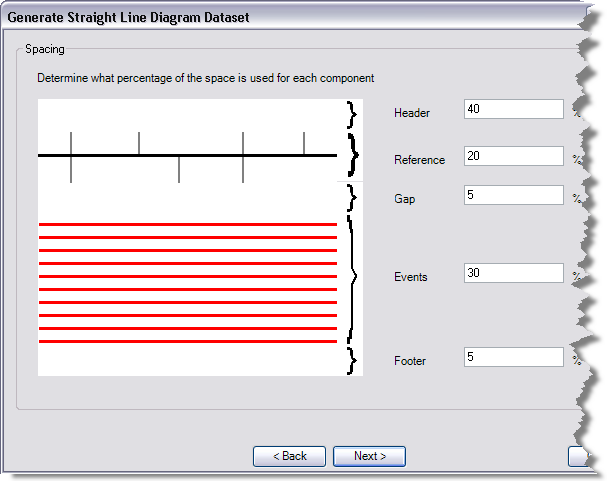
- Type a value in the Reference text box that represents the amount of space the reference layer has in the straight line diagram data frame.
- Type a value in each Gap text box that represents the amount of empty space that exists between the reference layer and the events in the straight line diagram data frame.
- Type a value in each Events text box that represents the amount of space the events have in the straight line diagram data frame.
- Type a value in the Footer text box that represents the amount of space the header can use in the straight line diagram data frame.
- Click Next.
The Generate Straight Line Diagram Dataset dialog box appears.
Choosing the workspace
The final task that must be completed before the straight line diagram can be generated is to choose the workspace that is going to store the straight line diagram dataset. This is usually the same workspace that contains the route features.
- Click Browse on the Generate Straight Line Diagram Dataset dialog box.
The Database location for SLD dialog box appears.
- Navigate to the workspace where you want to store the straight line diagram dataset.
- Click OK.
The Generate Straight Line Diagram Dataset dialog box appears.
- Click Finish.
One straight line diagram is generated for each route that has been selected.
