Summary
Computes the intersection of multipatch features to produce closed multipatches encompassing the overlapping volumes, open multipatch features from the common surface areas, or lines from the intersecting edges.
Illustration
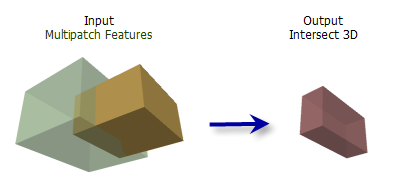
Usage
Exercise caution when determining the data used for this analysis. Highly detailed features may produce extremely complex geometries that could exhibit display performance issues on account of their total number of vertices and orientation.
If one input is given, the intersection of features in that multipatch dataset will be computed, whereas if two were given, the intersection of features from both datasets will be determined and intersections found in only one input get ignored.
Syntax
Intersect3D_3d (in_feature_class_1, {in_feature_class_2}, out_feature_class, {output_geometry_type})| Parameter | Explanation | Data Type |
in_feature_class_1 | The multipatch features that will be intersected. When only one input feature layer or feature class is provided, the output will indicate the intersection of its own features. | Feature Layer |
in_feature_class_2 (Optional) | The optional second multipatch feature layer or feature class to be intersected with the first. | Feature Layer |
out_feature_class | The feature class that will be produced by this tool. | Feature Class |
output_geometry_type (Optional) | Determines the type of intersection geometry created.
| String |
Code Sample
Intersect3D example 1 (Python window)
The following sample demonstrates the use of this tool in the Python window.
import arcpy
from arcpy import env
env.workspace = 'C:/data'
arcpy.Intersect3D_3d('inMultipatch1.shp', 'outMultipatch.shp',
'inMultipatch2.shp')
Intersect3D example 2 (stand-alone script)
The following sample demonstrates the use of this tool in a stand-alone Python script.
'''****************************************************************************
Name: Intersect3D Example
Description: This script demonstrates how to use the
Intersect3D tool
****************************************************************************'''
# Import system modules
import arcpy
import exceptions, sys, traceback
from arcpy import env
try:
# Obtain a license for the ArcGIS 3D Analyst extension
arcpy.CheckOutExtension('3D')
# Set environment settings
env.workspace = 'C:/data'
# Set Local Variables
inMP1 = 'Boston_MP_Small.shp'
inMP2 = 'Boston_MP.shp'
# Ensure output has a unique name
outMP = arcpy.CreateUniqueName('Intersect.shp')
# Execute Intersect 3D
arcpy.Intersect3D_3d(inMP1, outMP, inMP2)
except arcpy.ExecuteError:
print arcpy.GetMessages()
except:
# Get the traceback object
tb = sys.exc_info()[2]
tbinfo = traceback.format_tb(tb)[0]
# Concatenate error information into message string
pymsg = 'PYTHON ERRORS:\nTraceback info:\n{0}\nError Info:\n{1}'\
.format(tbinfo, str(sys.exc_info()[1]))
msgs = 'ArcPy ERRORS:\n {0}\n'.format(arcpy.GetMessages(2))
# Return python error messages for script tool or Python Window
arcpy.AddError(pymsg)
arcpy.AddError(msgs)
Environments
Licensing Information
- ArcGIS for Desktop Basic: Requires 3D Analyst
- ArcGIS for Desktop Standard: Requires 3D Analyst
- ArcGIS for Desktop Advanced: Requires 3D Analyst