Available with 3D Analyst license.
Summary
Converts a raster to a triangulated irregular network (TIN) dataset.
Illustration
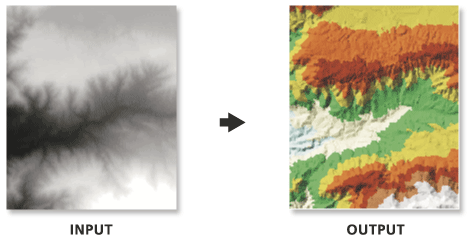
Usage
Converting a raster to a TIN will not, in and of itself, produce a better surface. You need ancillary data that's compatible with, and improves, the surface definition. Such data could be added to the TIN using the Edit TIN tool.
The default maximum allowable difference between the height of the input raster and the height of the output TIN is 1/10 of the z range of the input raster.
While the maximum size of a TIN that can be used under Win32 is between 15 to 20 million nodes, it's recommended to cap the size at a few million. Large input rasters, and small z-tolerance settings, may exceed this. If size is an issue, consider processing subsets.
Syntax
RasterTin_3d (in_raster, out_tin, {z_tolerance}, {max_points}, {z_factor})| Parameter | Explanation | Data Type |
in_raster | The raster to process. | Raster Layer |
out_tin | The TIN dataset that will be generated. | TIN |
z_tolerance (Optional) | The maximum allowable difference in (z units) between the height of the input raster and the height of the output TIN. By default, the z tolerance is 1/10 of the z range of the input raster. | Double |
max_points (Optional) | The maximum number of points that will be added to the TIN before the process is terminated. By default, the process will continue until all the points are added. | Long |
z_factor (Optional) | The factor that the height values of the raster will be multiplied by in the resulting TIN dataset. This is typically used to convert Z units to match XY units. | Double |
Code Sample
RasterTin example 1 (Python window)
The following sample demonstrates the use of this tool in the Python window.
import arcpy
from arcpy import env
arcpy.CheckOutExtension("3D")
env.workspace = "C:/data"
arcpy.RasterTin_3d("vermont_ele.tif", "C:/output/TIN_VT", "2", "1000", "1")
RasterTin example 2 (stand-alone script)
The following sample demonstrates the use of this tool in a stand-alone Python script.
'''*********************************************************************
Name: RasterTin Example
Description: This script demonstrates how to use the
RasterTin tool to create a TIN for each IMG raster in the
target workspace.
**********************************************************************'''
# Import system modules
import arcpy
from arcpy import env
# Obtain a license for the ArcGIS 3D Analyst extension
arcpy.CheckOutExtension("3D")
# Set environment settings
env.workspace = "C:/data"
try:
# Create the list of IMG rasters
rasterList = arcpy.ListRasters("*", "IMG")
# Loop the process for each raster
if rasterList:
for raster in rasterList:
# Set Local Variables
zTol = 2
maxPts = 1500000
zFactor = 1
# [:-4] strips the last 4 characters (.img) from the raster name
outTin = "C:/Output/TIN_" + raster[:-4]
print "Creating TIN from " + raster + "."
#Execute RasterTin
arcpy.RasterTin_3d(raster, outTIN, zTol, maxPts, zFactor)
print "Finished."
else:
"There are no IMG rasters in the " + env.workspace + " directory."
except Exception as e:
# Returns any other error messages
print e.message
Environments
Licensing Information
- ArcGIS for Desktop Basic: Requires 3D Analyst
- ArcGIS for Desktop Standard: Requires 3D Analyst
- ArcGIS for Desktop Advanced: Requires 3D Analyst