Concurrent routes in ArcGIS Roads and Highways are routes that share the same centerline features; that is, they travel the same physical medium but are modeled with different measures. This relationship may have been created to model two separate routes with different directions of calibration to model different directions of travel on the highway, or to model locations on route where multiple routes converge into a common roadway for a subset of their paths.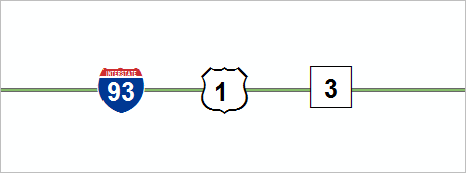
In the figure above, there is a concurrent route where Interstate Route 93, US Route 1, and Massachusetts Route 3 coexist on the same pavement. Let's imagine that the events, such as speed limits, are registered to Interstate Route 93. Now, in the case where a segment of the interstate is retired or realigned, the existing speed limit event records on that segment need to be assigned to either US Route 1 or Massachusetts Route 3 (if snap event measure behavior is assigned to the speed limit event layer). By configuring the route dominance, we provide a set of rules that decide which of the two routes will be the new parent route for the speed limit event.
You can set up route dominance rules using attribute fields in the network or the internal event layers that are registered to the network.
In the following example, we'll set up route dominance using the functional class event such that the lower the functional class value (from interstates, 1, to local roads, 7), higher dominance is assigned.
-
In ArcCatalog, right-click
your LRS and click Properties.
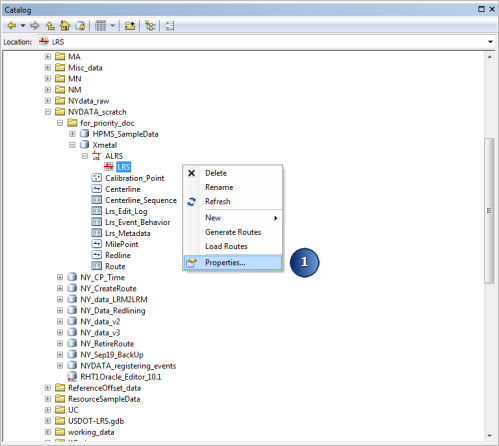
The LRS Network Properties dialog box appears.
- On the Route Dominance tab, click Add Rule.
A new row is added in the table to add route dominance rules.
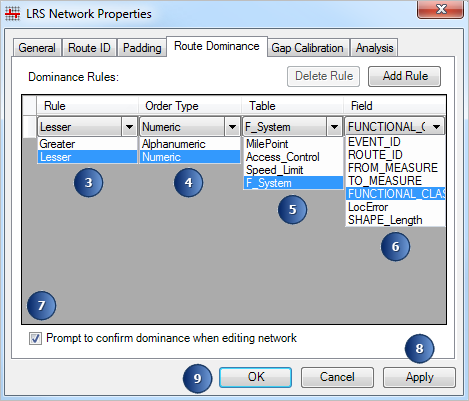
- Click the Rule drop-down arrow and choose Lesser.
- Click the Order Type drop-down arrow and choose Numeric.
The Numeric option only supports numbers, such as 1,2,11,22. The Alphanumeric option supports both numbers and text, such as 1,2,11,22 and 1,11A,22A,22B.
- Click the Table drop-down arrow and choose the functional class event (F_System, in this case).
- Click the Field drop-down arrow and choose the field from the F_System table that contains the functional class values.
- Check the Prompt to confirm dominance when editing network check box.
- Click Apply.
- Click OK.
A rule has been configured to give dominance to the route with the lower functional class value in case of a realignment or retirement of a concurrent route. You can set up multiple dominance rules using this method.