ArcMap 10.8 through 10.8.2 introduce new features and capabilities in mapping, geoprocessing, publishing, and data management.
For information about bugs that were fixed, see the 10.8 issues addressed, 10.8.1 issues addressed, and 10.8.2 issues addressed lists.
General (10.8.2)
ArcGIS Server 10.9.1 can be installed on the same machine as ArcGIS Desktop, ArcReader, and ArcGIS Engine 10.8.2 clients.
Geoprocessing (10.8)
The following new and improved functionality is available in geoprocessing tools in ArcMap 10.8:
Cartography toolbox
The following functionality is new in 10.8:
- You can now choose to partition data based on vertex count, in addition to the previously available method of feature count, in the Create Cartographic Partitions tool. With the Partition Method parameter set to Vertices, partitioning is dictated by the number and density of vertices rather than the number of features. Use this method when input data contains a relatively small number of complex features, such as high-resolution country polygons, or where long features are likely to cross multiple partition boundaries, such as contour lines.
- The Simplify Building tool has a new parameter called Input barrier layers. Use this parameter to identify one or more layers that contain features that must not be crossed by simplified lines. Barrier features can be points, lines, or polygons.
- The Smooth Line and Smooth Polygon tools have a parameter called Handling Topographical Errors that was previously hidden from the tools' user interfaces. This parameter specifies how topological errors, possibly introduced by processing, are handled. Previously, the parameter was available only through scripting for legacy compatibility and was ignored. The parameter is fully functional in this release and provides a new, third option to resolve the errors in addition to just flagging them.
Spatial Analyst toolbox
In the Distance toolset for ArcMap 10.8, the Cost Path and Cost Path As Polyline tools have been updated with a new parameter, Force flow direction convention for backlink raster. When checked, this parameter forces the tool to treat the input backlink raster as a flow direction raster. Flow direction rasters can have integers with values ranging from 0 to 255.
Data (10.8, 10.8.1, and 10.8.2)
The following functionality changes have been made to data management in ArcMap 10.8, 10.8.1, and 10.8.2:
Publishing
At 10.8, when you author a map to publish a feature service, the field order you define is now preserved when you publish the feature service to a GIS Server.
Databases and geodatabases
The following are changes in database and geodatabase support for 10.8:
- ArcGIS now supports Oracle 19c.
- Support for IBM Db2 V12 for z/OS is added in ArcGIS 10.8.
- The Desktop and Workgroup database server setup files that you download from My Esri now include Microsoft SQL Server 2017 Express. This is a 64-bit installation, as ArcGIS no longer supports 32-bit installations of SQL Server Express. If you still have a 32-bit SQL Server Express instance, you can detach and attach databases or backup and restore them to move geodatabases from a 32-bit SQL Server Express instance database server to a 64-bit SQL Server Express instance database server.
Support for the following databases is added at 10.8.1:
- PostgreSQL 12.2 and PostGIS 3.0.1 are supported.
- SQLite 3.31.1 is supported.
- IBM Db2 11.5 is supported.
- Dameng 8.1.0.147 is supported.
- Amazon Relational Database Service (RDS) for Oracle is supported when you connect to the database service from clients running in the same Amazon Web Services region as the Amazon RDS instance.
A new SQL function—ST_Perimeter—is available in 10.8.1 that allows you to find the perimeter of a polygon or multipolygon in an ST_Geometry feature class in an Oracle, PostgreSQL, or SQLite database.
Beginning with ArcGIS Desktop 10.8.2, you cannot upgrade user-schema geodatabases in Oracle. Before you can upgrade the sde schema geodatabase, you must move user-schema geodatabase content out of the datbase and delete the user-schema geodatabases from the database.
Mapping (10.8, 10.8.1, and 10.8.2)
The following are changes to map projections at 10.8:
- An unknown coordinate system warning message now appears when data is added to the project without a projection defined. Similarly, a transformation warning message now appears when the data is automatically transformed to the geographic coordinate system of the map or scene.
Three new map projections have been added.
The Adams square II projection depicts the world in a square. It is a conformal map projection, except in the four corners of the square. The projection was developed by Oscar S. Adams in 1925. In his original design, the projection displays the equator and central meridian as diagonals of the square in a diamond orientation. The Esri implementation of this projection maintains its conformal property on ellipsoids such as WGS 1984.
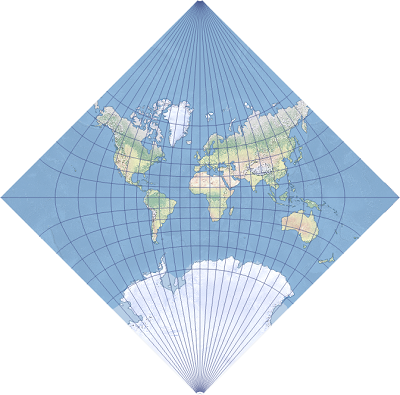
The Adams square II projection is shown in normal aspect. Adams square II can also be configured into a form that is almost identical to the Spilhaus world ocean map.
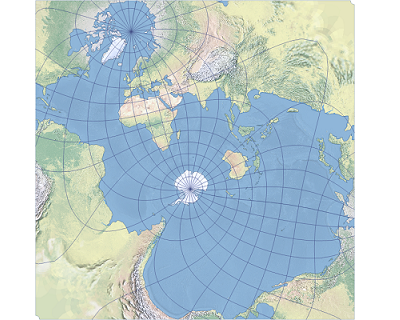
The Adams square II projection is shown with the Spilhaus configuration. Tobler cylindrical I and Tobler cylindrical II are two compromise cylindrical map projections. They were developed and introduced by Waldo Tobler in 1997 as alternatives to the Miller cylindrical projection. These projections were implemented in ArcGIS as the 100th and 101st map projection algorithms in Waldo Tobler's honor.
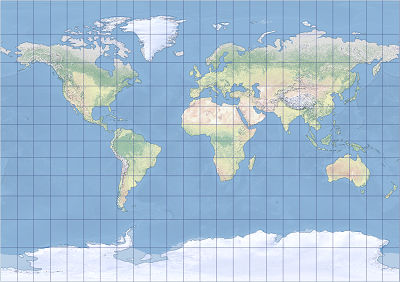
The Tobler cylindrical I map projection is shown. 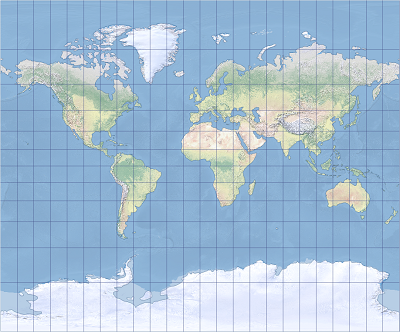
The Tobler cylindrical II map projection is shown.
- Help topics have been added for all map projections supported in ArcGIS. See the list of supported map projections. Click the links to open each topic.
- The perspective cylindrical map projection has been added at 10.8.1. It is a cylindrical map projection, which can be constructed geometrically by projecting the globe onto a tangent (or secant) cylinder from the point on the equatorial plane opposite a given meridian.

The central cylindrical projection, a special case of the perspective cylindrical projection, is shown. - Two new variants were added to the Lambert conformal conic projection at 10.8.1:
- The Lambert conformal conic 1SP variant only supports definitions with one standard parallel and scale factor but uses the same algorithm as the Lambert conformal conic variant.
- The Lambert conformal conic 2SP variant only supports definitions with two standard parallels but uses the same algorithm as the Lambert conformal conic variant.
- The plate carrée projection now supports an oblique variation starting at 10.8.2.