You can open Microsoft Excel tables directly in ArcGIS and work with them in the same way as other tabular data sources. For example, you can add them to ArcMap, preview them in ArcCatalog, and use them as inputs to geoprocessing tools.
Excel files are added to ArcMap in the same way as other data, through the Add Data dialog box. When you browse to an Excel file, you will need to choose which table you want to open. For example, if you have an Excel workbook called Sales_Figures.xls that contains three worksheets—Sales, Month, and Year to Date—each worksheet is a separate table in ArcGIS. Any name references to cells or ranges defined in Excel are preserved in ArcGIS.
When accessed from ArcGIS, a worksheet is shown as a table with a dollar sign ($) at the end of its name, but a named range does not have a dollar sign. Worksheets or named ranges with names containing spaces have single quotation marks placed around the table name.
Once added to ArcMap, you can open the table from the Source view of the table of contents. However, you will not be able to edit the table or export records to an Excel format.
The following example contrasts how a multisheet document is exposed in Microsoft Excel and on the ArcMap Add Data dialog box.
- Three worksheets as they appear on the Sheet tab bar at the bottom of the Excel window
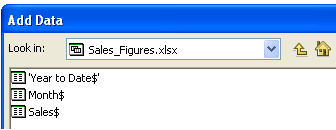
- Available worksheets inside the Sales_Figures workbook on the ArcMap Add Data dialog box
When working with Microsoft Excel files, keep the following in mind:
- ArcGIS supports both .xls files, and .xlsx files. One advantage of .xlsx files is that it allows much larger worksheets (1,048,576 rows by 16,384 columns) than you can have in the .xls format (65,536 rows by 256 columns).
- ArcGIS does not require that Microsoft Excel or Microsoft Office be installed to open an .xlsx file within ArcGIS, however you will need to download and install the correct Microsoft Access Database Engine driver that is compatible with ArcMap and Microsoft. Download and install the Microsoft Access Database Engine 2016 Redistributable driver that is compatible with your configuration.
- Excel tables are read-only in ArcGIS as well as in Excel when you have a workbook open in ArcGIS.
- Field names are derived from the first row in each column of the worksheet. You can view the properties, set aliases for the field names, and set field visibility on the Fields tab of the table's Properties dialog box.
- Excel does not enforce field types for values during data entry as standard databases do. Therefore, the field type specified in Excel is not used in determining the field type exposed in ArcGIS. Instead, field type in ArcGIS is determined by a scan of the values in the first eight rows for that field. If the scan finds mixed data types in a single field, that field will be returned as a string field, and the values will be converted to strings.
- Numeric fields are converted to the double data type in ArcGIS.
- Excel tables behave in the same way as other tables that don't have an ObjectID field. This means you cannot edit, perform relates, or make selections on the map.
- Excel file support in ArcGIS uses Microsoft OLE DB Provider for Jet 4.0 and its supporting Excel Indexed Sequential Access Method (ISAM) driver. For more information on the Microsoft OLE DB Provider for Jet 4.0 and its supporting Excel ISAM, visit Microsoft Support.
- You can directly export to Excel by using Table to Excel from the Geoprocessing Model & Script Tool Gallery. You can also export tabular data to dBASE format, which can be opened in Excel 97/2003 and saved as an .xls file. Microsoft discontinued support for .dbf files in Office 2007.
- You can still open an Excel file through an OLE DB database connection.