Summary
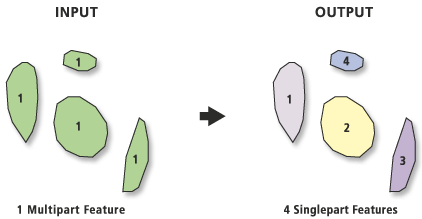
Creates a feature class containing singlepart features generated by separating multipart input features.
Illustration
Usage
The attributes of the input features will be maintained in the output feature class. A new field, ORIG_FID, will be added to the output feature class and set to the input feature IDs.
Each part of a multipart feature will be separated into individual features in the output feature class. Features that are already singlepart will not be affected.
Most of the output feature types will be the same as input (input polygons remain polygons; input lines remain lines). The one exception is if the input features are type multipoint, the output feature class will be type point.
To reconstruct multipart features from singlepart features based on a common field value, such as ORIG_FID, use the Dissolve tool.
A multipatch feature will be separated into its constituent geometry parts. Each part can be defined by a collection of vertices containing X, Y, and Z coordinates that are arranged as:
- Individual triangles that reference 3 vertices.
- Triangle strips that are defined by multiple triangles which successively share one common edge.
- Triangle fans that are defined by multiple triangles with a common point of origin.
- Rings that represent a co-planar region whose boundary is defined by 4 or more vertices.
Syntax
arcpy.management.MultipartToSinglepart(in_features, out_feature_class)
| Parameter | Explanation | Data Type |
in_features | The input features that can be any feature type. | Feature Layer |
out_feature_class | The output feature class containing features that vary with input feature type. | Feature Class |
Code sample
MultipartToSinglepart Example 1 (Python window)
The following Python window script demonstrates how to use the MultipartToSinglepart function in immediate mode.
import arcpy
arcpy.env.workspace = "C:/data"
arcpy.MultipartToSinglepart_management("landuse.shp",
"c:/output/output.gdb/landuse_singlepart")
MultipartToSinglepart Example 2 (stand-alone script)
The following stand-alone script is a simple example of how to apply the MultipartToSinglepart function in a scripting environment.
# Name: MultipartToSinglepart_Example2.py
# Description: Break all multipart features into singlepart features,
# and report which features were separated.
# Import system modules
import arcpy
# Create variables for the input and output feature classes
inFeatureClass = "c:/data/gdb.gdb/vegetation"
outFeatureClass = "c:/data/gdb.gdb/vegetation_singlepart"
try:
# Create list of all fields in inFeatureClass
fieldNameList = [field.name for field in arcpy.ListFields(inFeatureClass)]
# Add a field to the input this will be used as a unique identifier
arcpy.AddField_management(inFeatureClass, "tmpUID", "double")
# Determine what the name of the Object ID is
OIDFieldName = arcpy.Describe(inFeatureClass).OIDFieldName
# Calculate the tmpUID to the OID
arcpy.CalculateField_management(inFeatureClass, "tmpUID",
"!" + OIDFieldName + "!", "PYTHON")
# Run the tool to create a new fc with only singlepart features
arcpy.MultipartToSinglepart_management(inFeatureClass, outFeatureClass)
# Check if there is a different number of features in the output
# than there was in the input
inCount = int(arcpy.GetCount_management(inFeatureClass).getOutput(0))
outCount = int(arcpy.GetCount_management(outFeatureClass).getOutput(0))
if inCount != outCount:
# If there is a difference, print out the FID of the input
# features which were multipart
arcpy.Frequency_analysis(outFeatureClass,
outFeatureClass + "_freq", "tmpUID")
# Use a search cursor to go through the table, and print the tmpUID
print("Multipart features from {0}".format(inFeatureClass))
for row in arcpy.da.SearchCursor(outFeatureClass + "_freq",
["tmpUID"], "FREQUENCY > 1"):
print(int(row[0]))
else:
print("No multipart features were found")
except arcpy.ExecuteError:
print(arcpy.GetMessages())
except Exception as err:
print(err.args[0])
Environments
Licensing information
- Basic: Yes
- Standard: Yes
- Advanced: Yes