Available with Spatial Analyst license.
Summary
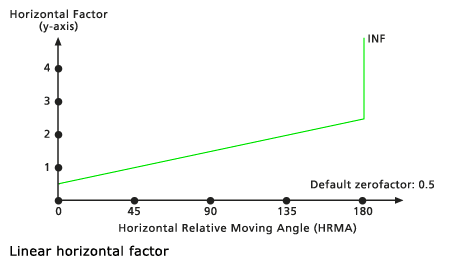
Defines the relationship between the horizontal cost factor and the horizontal relative moving angle through a linear function.The function specifies that the horizontal factor has a linear relationship with the horizontal relative moving angle.
Illustration
Discussion
The HfLinear object is used in the Spatial Analyst tools Path Distance, Path Distance Allocation, and Path Distance Back Link.
The horizontal factors (HFs) are determined by a straight line in the horizontal relative moving angle (HRMA)-HF coordinate system. The line intercepts the y-axis, equitable to the HF factor, at the value associated with the zerofactor. The slope of the line can be specified using the slope modifier. If no slope is identified, the default is 0.5/45 or 1/90 (specified as 0.01111).
Syntax
HfLinear ({zeroFactor}, {cutAngle}, {slope})| Parameter | Explanation | Data Type |
zeroFactor | The zeroFactor will be used to position the y-intercept of the linear function. (The default value is 0.5) | Double |
cutAngle | The cutAngle establishes the HRMA degree threshold beyond which the HFs are set to infinity. (The default value is 181.0) | Double |
slope | Identifies the slope of the straight line in the HRMA-HF coordinate system. Slope is specified as the rise over the run. For example, a 30-degree slope is 1/30, specified as 0.03333 (rise/run: 1 HF on the y axis / 30 degrees on the x axis). (The default value is 0.011111) | Double |
Properties
| Property | Explanation | Data Type |
| zeroFactor (Read and Write) | The zeroFactor will be used to position the y-intercept of the function. The zeroFactor is assigned as the horizontal factor when HRMA is less then the cut angle. | Double |
| cutAngle (Read and Write) | The cutAngle establishes the HRMA degree threshold beyond which the HFs are set to infinity. When the HRMA is less than the cut angle then the zero factor is assigned and when the HRMA is greater than the cut angle, infinity is assigned. | Double |
| slope (Read and Write) | Identifies the slope of the straight line in the HRMA-HF coordinate system. Slope is specified as the rise over the run. For example, a 30-degree slope is 1/30, specified as 0.03333 (rise/run: 1 HF on the y axis / 30 degrees on the x axis). | Double |
Code Sample
HfLinear example 1 (Python window)
Demonstrates how to create an HFLinear class and use it in the PathDistance tool within the Python window.
import arcpy
from arcpy import env
from arcpy.sa import *
env.workspace = "C:/sapyexamples/data"
myHorizFactor = HfLinear(0.5, 181.0, 0.01111)
outPathDist = PathDistance("source.shp", "costraster", "", "", myHorizFactor)
outPathDist.save("C:/sapyexamples/output/pathdisthfl")
HfLinear example 2 (stand-alone script)
Performs a PathDistance analysis using the HFLinear class.
# Name: HfLinear_Ex_02.py
# Description: Uses the HfLinear object to execute the PathDistance tool
# Requirements: Spatial Analyst Extension
# Import system modules
import arcpy
from arcpy import env
from arcpy.sa import *
# Set environment settings
env.workspace = "C:/sapyexamples/data"
# Set local variables
inSourceData = "source.shp"
inCostRaster = "costraster"
# Create the HfLinear Object
zeroFactor = 0.5
cutAngle = 181.0
slope = 0.01111
myHorizFactor = HfLinear(zeroFactor, cutAngle, slope)
# Check out the ArcGIS Spatial Analyst extension license
arcpy.CheckOutExtension("Spatial")
# Execute PathDistance
outPathDist = PathDistance(inSourceData, inCostRaster, "", "", myHorizFactor)
# Save the output
outPathDist.save("C:/sapyexamples/output/pathdisthfl2")