Available with Data Reviewer license.
In a map display, it is likely that you will find features that spatially relate to each other, whether they are a road on a land feature or a lake surrounded by grassland. It is also possible for features from the same feature class to overlap one another and share attributes.
The Geometry on Geometry check searches for features from either the same or two different feature classes that share a spatial relationship and returns them as results. If the check is configured to use the intersects or touches spatial relationship, the check will create results with point geometries. The check can be used with the entire feature class, a subtype, or a set of features selected using a SQL query. When features that meet the specified condition are found, they are written to the Reviewer table for further evaluation.
Learn more about the types of spatial relationships that can be evaluatedOnce you have defined the criteria for the check, you can configure the notes and a severity rating. The notes allow you to provide a more specific description for the feature that has been written to the Reviewer table and are copied to the Notes field in the Reviewer table. The severity rating allows you to indicate how important the results from a check are in terms of your quality assurance/quality-control processes. The lower the number, the greater the priority the check's results have.
- Start ArcMap.
- On the main menu, click Customize > Toolbars > Data Reviewer.
- Click the Select Data Check drop-down arrow on the Data Reviewer toolbar, click the plus sign (+) next to Feature on Feature Checks, then click Geometry on Geometry Check.
The Geometry on Geometry Check Properties dialog box appears.
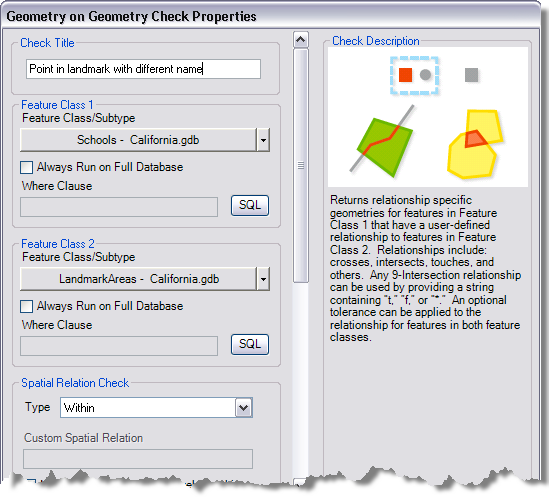
- If necessary, type a unique name for the check in the Check Title text box.
- Click the Feature Class/Subtype drop-down arrow in the Feature Class 1 area to choose the feature class and subtype on which to run the check.
- To run the check on the entire feature class and save this setting, check the Always Run on Full Database check box.
- To run the check on specific features in a feature class, click SQL to construct a SQL query.
- Repeat steps 5–7 in the Feature Class 2 area.
- Click the Type drop-down arrow and choose the type of spatial relationship to use with the check.
- Touches—A part of the feature from feature class 1 comes into contact with the boundary of a feature from feature class 2. The interiors of the features do not intersect.
- Contains—A feature from feature class 1 completely encloses a feature from feature class 2.
- Intersects—Any part of a feature from feature class 1 comes into contact with any part of a feature from feature class 2.
- Relation—A custom spatial relationship is defined based on the interior, boundary, and exterior of features from both feature classes.
- Within—A feature from feature class 2 completely encloses a feature from feature class 1.
- Crosses—The interior of a feature from feature class 1 comes into contact with the interior or boundary (if a polygon) of a feature from feature class 2 at a point.
- Overlaps—The interior of a feature from feature class 1 partly covers a feature from feature class 2. Only features of the same geometry can be compared.
If you choose Relation from the Type drop-down list, the Custom Spatial Relation text box becomes available.
- If necessary, type the custom spatial relation parameter in the Custom Spatial Relation text box.
- To invert the spatial relationship, check the Not - find features not in this relationship check box.
- If you want to union features from feature class 2 that have a spatial relationship with features from feature class 1, check the Merge features from feature class 2 check box.
When the Merge features from feature class 2 check box is checked, the check finds features from feature class 1 that have a relationship with multiple features in feature class 2. For example, a road that crosses two or more counties would be returned as a result when you want to find roads that are within counties.
- Type the number of units to use for the tolerance in the Tolerance text box.
- Click the Tolerance drop-down arrow and choose the units of measurement to use with the tolerance.
- To check for identical matches in attributes between features, choose an option in the Attributes area.
- None—No attributes are checked, in addition to the spatial relationship between the features.
If you choose this option, proceed to step 18.
- Compare All Attributes—All the attributes from both feature class 1 and feature class 2 are checked for identical matches with each other, in addition to the spatial relationship between the features.
If you choose this option, proceed to step 16.
- Compare Attributes—Only the attributes selected on the Compare Attributes dialog box have their values compared, in addition to the spatial relationship between the features.
If you choose this option, proceed to step 17.
- None—No attributes are checked, in addition to the spatial relationship between the features.
- If you have chosen the Compare All Attributes option and want to ignore certain attributes, do the following:
- Check the Attributes to Ignore (Feature Level Metadata) check box.
- Click Select Attributes.
The Attributes To Ignore dialog box appears.
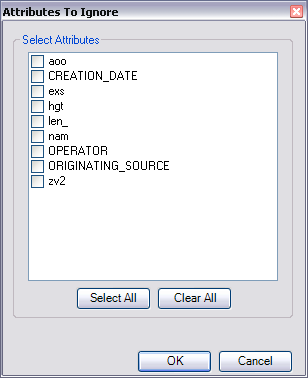
- Check the check boxes next to the names of the attributes you want to ignore when finding spatial relationships.
- Click OK.
The Geometry on Geometry Check Properties dialog box appears.
- Proceed to step 18.
- If you have chosen the Compare Attributes option, do the following:
- Click Select Attributes.
The Compare Attributes dialog box appears. Feature classes 1 and 2 automatically populate the Data Source 1 and Data Source 2 fields.
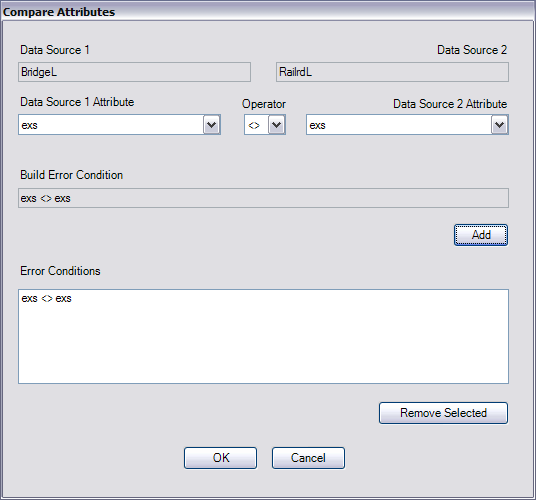
- Click the Data Source 1 Attribute drop-down arrow and choose a field to use in the comparison.
- Click the Data Source 2 Attribute drop-down arrow and choose a field to use in the comparison.
- Click the Operator drop-down arrow and choose an operator to use in the comparison.
- Click Add.
The condition is added to the Error Conditions list.
- Repeat steps 17b–17e as necessary.
- Click OK.
The Geometry on Geometry Check Properties dialog box appears.
- Proceed to step 18.
- Click Select Attributes.
- If necessary, type descriptive text for the check results in the Notes text box in the Reviewer Remarks area.
- If necessary, click the Severity drop-down arrow and choose a value that indicates the priority of the check's results in the Reviewer Remarks area.
The severity indicates the importance of the check result. The values range from 1 to 5, with 1 being the highest priority and 5 being the lowest.
- Click OK.
- Click the Run Data Check button
 on the Data Reviewer toolbar.
on the Data Reviewer toolbar.
The Features to Validate dialog box appears.
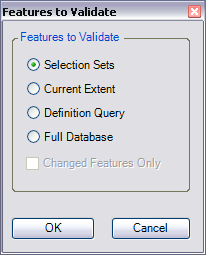
- Choose an option in the Features to Validate area.
- Selection Set—The check is run on the features that are currently selected in the map.
- Current Extent—The check is run on the current map extent, which is controlled by the map scale.
- Definition Query—The check is run on the features that are displayed based on definition queries that have been created for the feature class.
- Full Database—The check is run on all the features in the feature class.
- To run the check only on features that have been edited in a versioned workspace, check the Changed Features Only check box.
- Click OK.
The check is run on the extent specified on the Features to Validate dialog box.
When the check finishes, a check results dialog box appears.
- Do one of the following:
- If you want to browse the results in the Browse Features window, choose the Browse Results option.
- If you have started a Reviewer session and want to record the results in the Reviewer table, choose the Write to Reviewer Table option.
- Click OK.