Description
Also known as simple cylindrical, equidistant cylindrical, rectangular, or Plate Carrée (if the standard parallel is the equator).
This projection is very simple to construct because it forms a grid of equal rectangles. Because of its simple calculations, its usage was more common in the past. In this projection, the polar regions are less distorted in scale and area than they are in the Mercator projection.
Learn more about the Mercator projection
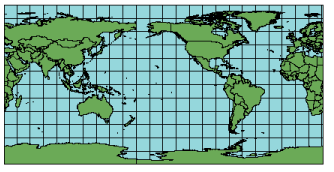
Projection method
This simple cylindrical projection converts the globe into a Cartesian grid. Each rectangular grid cell has the same size, shape, and area. All the graticular intersections are 90 degrees. The central parallel may be any line, but the traditional Plate Carrée projection uses the equator. When the equator is used, the grid cells are perfect squares, but if any other parallel is used, the grids become rectangular. In this projection, the poles are represented as straight lines across the top and bottom of the grid.
Lines of contact
Tangent at the equator or secant at two parallels symmetrical around the equator.
Linear graticules
All meridians and all parallels.
Properties
Shape
Distortion increases as the distance from the standard parallels increases.
Area
Distortion increases as the distance from the standard parallels increases.
Direction
North, south, east, and west directions are accurate. General directions are distorted, except locally along the standard parallels.
Distance
The scale is correct along the meridians and the standard parallels.
Limitations
Noticeable distortion of all properties away from standard parallels.
Uses and applications
Best used for city maps or other small areas with map scales large enough to reduce the obvious distortion.
Used for simple portrayals of the world or regions with minimal geographic data. This makes the projection useful for index maps.
Parameters
Desktop
- Supported on spheres only
Workstation
- Radius of the sphere of reference
- Longitude of Central Meridian
- Latitude of standard parallel
- False Easting (meters)
- False Northing (meters)