- Table of contents
- Getting information about the WMS service layer
- Changing the display of the WMS service layer
- Changing WMS service layer properties
- Displaying the WMS service layer in different coordinate systems
- Querying features from the WMS service layer
- Printing and exporting a map containing a service layer
- How WMS server errors are handled
Web Mapping Service (WMS) services can be used in ArcMap (as well as in ArcScene and ArcGlobe) as map layers. Following are some common tasks for working with WMS service layers.
Table of contents
When added to ArcMap, the WMS service layer's entry in the table of contents is contracted to save space, but you can expand it and its groups to see the individual layers it contains.
A WMS service layer is made up of three entries that are arranged hierarchically in the table of contents. At the top is the name of the WMS service, which holds all the WMS map layers. The next level is WMS group layers, whose only function is to organize WMS sublayers into related groups. There is at least one WMS group layer, but there can be any number of WMS group layers (and even nested groups within groups). WMS group layers do not hold any map layers—it is the third group, WMS sublayers, that actually contains the map layers.
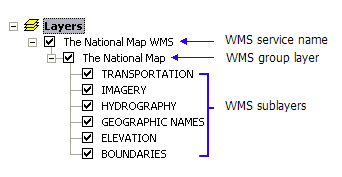
Note the line connecting the sublayers. This line prohibits you from inserting a layer within this service (group) layer or breaking apart the service layer into its constituent sublayers.
Some WMS services do not include legend information about the symbols used by the layers in the service. When legend information is not available, no symbology is shown for the layers in the table of contents. These layers will be listed in the table of contents without expansion controls next to them.
When a WMS service includes legend information, you can view the WMS sublayer's symbology in the table of contents by clicking the expansion control next to a sublayer. The legends for the layers in WMS services are all hidden by default, since accessing a legend for each layer in a WMS service requires sending a separate request to the server. For each additional layer, it is an additional request to the server.
The size of WMS legends can vary greatly. Sometimes the size of the legend specified by the server is too large to be displayed in the ArcMap table of contents. This usually happens when the legend for a layer contains multiple symbols, such as a transportation layer displaying symbology for the different types of roads. With WMS services, the legends for layers are transmitted over the Internet as one image containing all the symbols. Although ArcMap supports legend entries with multiple symbols in its table of contents, ArcMap expects these entries to contain multiple images, one image per symbol. ArcMap also places a limit on the size, height, and width (in pixels) of an image it will display in the table of contents. When the image received for a layer in a WMS service exceeds this limit, no legend is displayed for the layer. These layers are therefore listed in the table of contents without symbology and without expansion controls. When a WMS legend is available but is not displayed in the table of contents, you can view the legend on the Styles tab of the WMS sublayer's Layer Properties dialog box.
Getting information about the WMS service layer
The service layer properties Source tab displays information such as the map extent, data (service) type, URL, service name, and default coordinate system of the service.
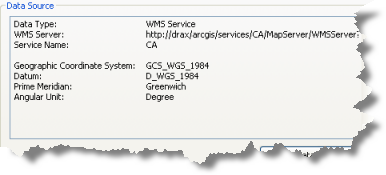
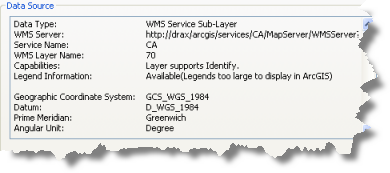
You can get information about each WMS sublayer from the service sublayer properties Source tab. This includes the capabilities of the sublayer (whether the layer supports Identify), whether a legend is available for the sublayer, the default coordinate system, and a list of server-supported coordinate systems for this particular sublayer.
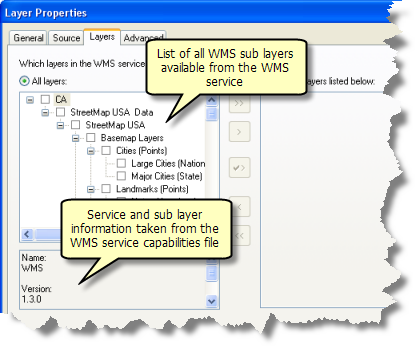
The Layers tab displays all the members of the WMS service. Information provided by the WMS server for each WMS layer is displayed in a box on the lower left of the dialog box.
The Set Data Source button on the Source tab enables you to repair the map service layer if for any reason the connection to the server was interrupted when opening the map. You can tell if the layer needs repairing because it won't be drawn, its check box in the table of contents will be unavailable, and there will be a red exclamation point next to its check box
This also enables you to specify a different WMS service for this layer. You cannot choose a different service type to set the data source. For example, you cannot replace a WMS service with an ArcGIS for Server map service using Set Data Source. If you want to do this, you will need to manually remove the WMS service from the map and manually add the ArcGIS for Server map service.
The application will only repair/replace the data source for the current service layer, even if the data sources of other service layers that need repairing are from the same server. You will need to update these layers separately.
Changing the display of the WMS service layer
There are a number of things you can do to affect the display of a web map layer. These include changing the feature symbology, toggling layer or label visibility, changing the drawing order of service sublayers, setting a background for the service, applying transparency, and (if supported by the server) visualizing the service based on a time parameter.
Depending on how the WMS service is authored, you may be able to change the rendering of a WMS layer. WMS layer rendering is determined by a style. The style consists of the symbols and colors used to represent features in a WMS service. The WMS specification allows a WMS layer to contain any number of styles. You can choose from the available styles using the Styles tab of the WMS service sublayer's Layer Properties dialog box.
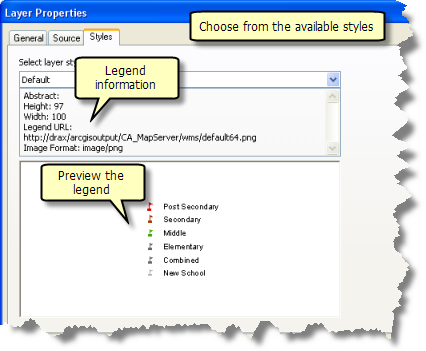
If the WMS service does not support styles, you will see Legend not available in the preview window. As you choose different styles from the drop-down menu, the information in the text box and the image in the preview window change accordingly. You can preview as many of the listed styles as you want. The style is not applied to the layer until you click OK or Apply. Once you do this, ArcMap sends a new GetMap request to the WMS server using the new style.
This tab also includes information describing the given style, the height and width of the legend image in pixels, the URL for the legend image, and the image format.
You can turn the visibility of service and service sublayers on and off using the check boxes in the table of contents. You cannot toggle the visibility of WMS sublayer labels.
When you add a WMS service into ArcMap, all the layers in that service are available for display in the map, even if you only add a single WMS sublayer or a single WMS group layer. Even though the table of contents entry for the service layer only lists the added sublayer, you still have access to the entire list of sublayers through the Layer Properties dialog box of the service layer. In cases where you add an entire WMS service, the table of contents entry for the service layer will include all the layers and groups, using the drawing order defined by the author of the service. Some WMS services contain a large number of layers and are more like data collections than individual maps.
The Layers tab allows you to choose which WMS service sublayers to display in your map. If you want to remove some of the sublayers from the map and the table of contents, simply use the Just the layers listed below option and don't include them in that list. You can also control layer visibility and drawing order.
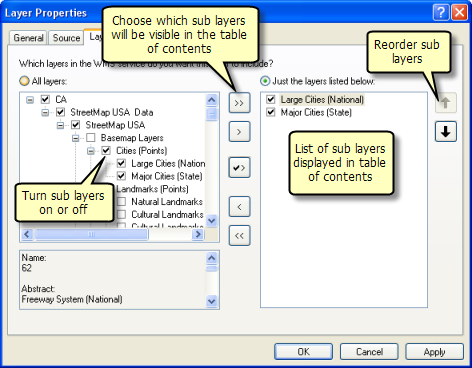
On the left side of this dialog box, you will see all the WMS group layers and WMS sublayers for the service listed. The grouping, naming, and ordering of the layers in this list directly reflect the way the author of this WMS service chose to organize and present the data it contains. Those items can only be changed by the author of the service. However, clicking Just the layers listed below on the right side of the tab allows you to configure which layers in the WMS service will be included in its table of contents entry, add and remove specific WMS layers from your map, and control layer visibility and drawing order. When you use this option, any groups into which the layers have been organized by the publisher of the service are not reflected in the table of contents. The layers you choose appear in a flat, ungrouped list, the same as they appear in the list on the right.
To change the drawing order, click the Just the layers listed below option and move the WMS sublayers you want in your map to the right side of the dialog box. Now, you can select the WMS sublayers and use the arrow buttons to move them up or down the hierarchy to change the drawing order.
Steps
- Right-click the WMS service layer in the table of contents and click Properties.
- Click the Layers tab.
- Click Just the layers listed below.
- Click the layer or layers that you want to list in the table of contents. You can hold down CTRL or SHIFT to choose multiple WMS sublayers.
- Click the Right Arrow
 to add selected layers or the Double Right Arrow
to add selected layers or the Double Right Arrow  to add all WMS sublayers. You can also click the Arrow With Check Mark
to add all WMS sublayers. You can also click the Arrow With Check Mark  to add only the visible layers.
to add only the visible layers. - Use the Left Arrow
 to remove the selected layers or the Double Left Arrow
to remove the selected layers or the Double Left Arrow  to remove all WMS sublayers.
to remove all WMS sublayers. - Click OK.
When you apply these changes, you see the updates in the table of contents, and the new drawing order is reflected in your map. ArcMap sends a new request to the WMS server to account for the new drawing order.
You can change the background color of the service layer, set a specific color as transparent, apply a level of transparency to the service layer, or change the image type received from the server using the options available on the Advanced tab.
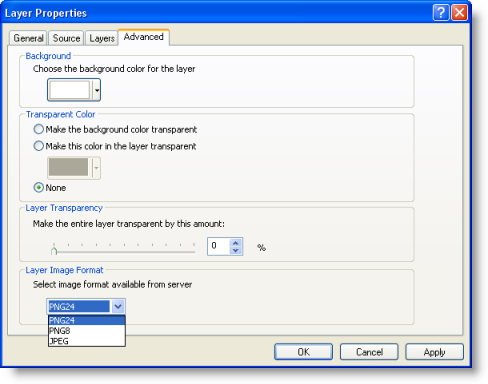
Many web map services support multiple image formats. If the WMS server supports PNG format, ArcMap will, by default, request images in PNG. PNG is a general purpose format that will not reduce image quality; that is why it is the default. PNG returns a high-quality image that supports transparency. However, the file size can be much larger than other formats and slower to download from the server. JPEG is often much faster since its size can be much smaller than a PNG. However, JPEG does not support transparency. JPEG is really only appropriate for imagery data. For example, JPEG would be a good option if you're using a WMS layer based on imagery as a basemap. Also, choosing JPEG from the Layer Image Format drop-down list could improve performance. Of course, the WMS server must support JPEG for it to be available. If you are overlaying the WMS service on top of other layers or want the best, highest-quality image available, you should use PNG (provided the WMS server supports this format).
To choose an available image format, click the Advanced tab on the Layer Properties dialog box and choose the format from the Layer Image Format drop-down list. This list only displays formats supported by the service. You cannot choose a format not supported by the service.
Visualizing temporal data can help you step through your data and see the patterns or trends that emerge over time. In ArcMap, ArcGlobe, or ArcScene, you can enable your temporal data to participate in time and visualize it using a simple time slider that changes the data in the display or in a graph through time. If the service supports time, you will see the Time tab of the Layer Properties dialog box. For more information on visualizing time, see Using the Time Slider window.
Changing WMS service layer properties
There are a couple of properties you can change for a service layer, such as changing the name of the service layer, changing the description, and setting visibility scale ranges or the image format returned by the server.
You can change the name of the service layer either by clicking the service layer in the table of contents and typing a new name or by opening the General tab of the Layer Properties dialog box and entering a new name there. The Description text box is initially populated with an abstract, when one is provided by the service. You can change the description for WMS service layers, but the Description text box for group and WMS sublayers within the WMS service is read-only.
You can set visible scale ranges on the service layer where all the sublayers contained within it are drawn only when the map is within the specified scale range. By setting a scale range on a service layer, you can avoid sending image requests to the server at map scales that are inappropriate for the layer's data. You set scale ranges on the General tab on the Layer Properties dialog box. Scale ranges can only be set at the service level for map services. You cannot set them for service sublayers.
Here are some things to keep in mind when interacting with WMS sublayers at various map scales:
- ArcMap may not draw WMS sublayers precisely at their reported scales. This is due to resolution differences between the WMS server and ArcMap. You may have to adjust the map scale so the sublayer will be drawn.
- A WMS sublayer may act as though it has scale dependency and is not drawn outside a certain scale range, yet no scale range is being reported on the General tab of the sublayer's Layer Properties dialog box. Since reporting the scale range is optional under the OGC WMS specification, some WMS servers omit this information. In such cases, the sublayer is drawn within the correct scale range, but ArcMap won't show the scale range on the General tab. ArcMap cannot determine scale ranges for WMS layers and can only provide the information given to it by the WMS service.
Displaying the WMS service layer in different coordinate systems
When using WMS services, you might want to keep to server-supported coordinate systems for best results. WMS servers may only support a limited set of coordinate systems, depending on how a service has been configured by its author. In addition, each WMS sublayer within the WMS service can potentially support a different set of coordinate systems. Like with other layers, if a WMS service layer is the first layer added to a new, empty data frame, the data frame takes on the WMS service's default coordinate system.
If the data frame is in a coordinate system that is not supported by the WMS server, ArcMap gets an image from the server in a supported coordinate system—in most cases, this will be GCS 1984—and projects this image internally so it will be displayed in your map. In other words, ArcMap will project this image on the fly. Depending on the coordinate system being used by the data frame, there may be some level of distortion in the display of the WMS layer—most noticeably if the layer has text. The benefit of using only coordinate systems supported by the WMS server is that the image returned by the WMS server is not postprocessed to fit into an unsupported coordinate system.
For more information, see How to choose a coordinate system supported by a WMS server.
Querying features from the WMS service layer
Identifying features is the only querying task you can perform on WMS layers, although the format of information you receive can vary depending on the server. ArcMap displays what is returned by the server inside an Internet Explorer control embedded in the Identify window. The result of an identify query may be provided as field-value pairs, HTML, or images.
According to the OGC WMS specification, WMS services are not required to support <GetFeatureInfo>, which is the request ArcMap sends to the server when you query features of a WMS service. If the service supports identifying, like the one in the graphic below, you will see its sublayers listed in the Identify window. If you don't see them listed, you won't be able to identify features from that WMS service.
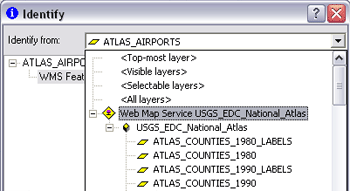
Because there is no concept of a primary display field for a feature identified in a WMS service layer, the node in the Identify tree representing the features in a WMS service layer is always referred to as WMS Feature(s).
When you identify a feature from a WMS service layer, you should either use the <Visible Layers> option, which identifies features in any of the visible layers in the WMS service layer, or choose the particular layer you are interested in identifying. This is because the default option, <Top-most layer>, may not work as you expect. When you use this option and click the map, Identify only works on features from the topmost layer in the WMS service's drawing hierarchy. If there are no features present in the layer at that location, this option does not automatically identify features from layers lower in the drawing hierarchy as it does with other layer types, such as those referencing shapefiles or geodatabase feature classes. Instead, you receive null results. This is a limitation of WMS servers.
In addition, identify tolerance levels are determined by the WMS server, not ArcMap. When identifying WMS point features, you may have to repeat your clicks until you get close enough to the feature to register a positive result.
Printing and exporting a map containing a service layer
You can print and export maps containing service layers. However, you need to be aware of limitations that are inherent to working with image-based services. For more information, see Printing and exporting maps containing service layers.
How WMS server errors are handled
You may sometimes get an error message from particular WMS services when you add them into a map. As with any live web mapping service based on images, when ArcMap attempts to draw a WMS service in a map, it sends a request for an image to the WMS server providing that service. If the server returns an error instead of an image, ArcMap displays that error message. These error messages, which appear each time you redraw the map, reflect problems with the WMS service and normally can't be remedied in ArcMap. ArcMap displays these messages to warn you that something about the WMS service is not working as ArcMap expects and also to provide a basic diagnostic capability. However, because these errors can vary widely between different WMS servers, it is difficult for ArcMap to reveal the exact problem. As a result, the error messages are fairly generic, and what the problem is may not be obvious. For example, the error may be caused by a particular layer belonging to the WMS service or to a particular combination of layers.
If you get an error message, you can stop it from appearing again by simply unchecking the WMS service in the table of contents or removing it from your map. Sometimes, you may be able to tell which layer in the WMS service is causing the problem. In that case, try turning off that particular layer in the table of contents to prevent the error message from appearing.
Note that if you get an error message from a WMS service, it doesn't necessarily mean that you won't be able to draw this service in your map at all. For example, some WMS services may return the error Bounding box has an invalid area when you try to draw them at a very small scale, but the service will draw, and the error message won't appear when you zoom in to larger scales. In this situation, you should specify a scale range for the WMS service layer using the General tab of its Layer Properties dialog box so the layer is not drawn at very small scales. This prevents the error messages from appearing when the layer can't be drawn.