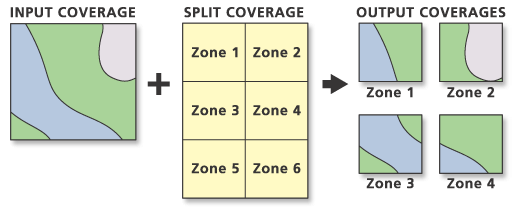
The Split tool creates output coverages by overlaying two sets of features. Split performs a series of Clip operations, one for each output coverage. Each output coverage contains only those portions of input coverage features that are overlapped by the specified polygons of the Split Coverage.
Input Coverage features can be polygons, lines, or points. Split Coverage features must be polygons. The unique values in the Split Item are used to name the output coverages, and the number of unique values in the Split Item determines the maximum number of output coverages.
The final output coverage count is determined by whether there is overlap between the Input Coverage features and the Split Coverage polygons. For example, the Split Coverage may contain six unique values in its Split field, but only four overlap with Input Coverage features. In this case, the result would be four output coverages only.
Split discovers the feature classes in the Input Coverage and offers the available clipping methods:
- Poly—Polygons and region subclasses are split, and a PAT is saved. The label point for each remaining polygon is moved only if its original location falls outside the clipping boundary. Region subclasses are maintained. Route systems are ignored.
- Line—Arcs are split and an AAT is saved. Route systems are maintained.
- Point—Points are copied and a PAT is saved.
- Poly & Line (Net)—Polygons and arcs are clipped, and their PAT and AAT are saved. Route systems are maintained.
- Line & Point (Link)—Arcs and points are split, and their AAT and PAT are saved. Route systems are maintained.
- Geometry—Points, arcs, and annotation in a coverage without topology (no attribute files) are split. Attributes are ignored.
Output coverage features are of the same class as the Input Coverage features. They are clipped to the boundaries of the split polygons in the Split Coverage. Topology is built for the output coverage.
The feature attribute tables for the output coverage contain the same items as the Input Coverage attribute tables. The feature's internal number is used to transfer attribute information from the Input Coverage to each of the output coverages.
Feedback on this topic?