Summary
Measures the degree to which features are concentrated or dispersed around the geometric mean center.
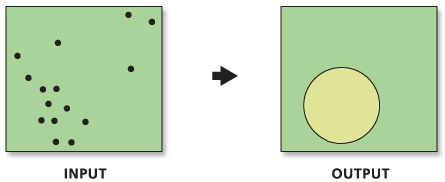
Illustration
Usage
The standard distance is a useful statistic as it provides a single summary measure of feature distribution around their center (similar to the way a standard deviation measures the distribution of data values around the statistical mean).
The Standard Distance tool creates a new feature class containing a circle polygon centered on the mean for each case. Each circle polygon is drawn with a radius equal to the standard distance. The attribute value for each circle polygon is its standard distance value.
The Case Field is used to group features prior to analysis. When a Case Field is specified, the input features are first grouped according to case field values, and then a standard distance circle is computed for each group. The case field can be of integer, date, or string type, and will appear as an attribute in the Output Feature Class. Records with NULL values for the Case Field will be excluded from analysis.
The standard distance calculation may be based on an optional Weight Field (to get the standard distance of businesses weighted by employees, for example). The Weight Field should be numeric.
If the underlying spatial pattern of the input features is concentrated in the center with fewer features toward the periphery (spatial normal distribution), a one standard deviation circle polygon will cover approximately 68 percent of the features; a two standard deviation circle will contain approximately 95 percent of the features; and three standard deviations will cover approximately 99 percent of the features in the cluster.
This tool requires projected data to accurately measure distances.
-
For line and polygon features, feature centroids are used in distance computations. For multipoints, polylines, or polygons with multiple parts, the centroid is computed using the weighted mean center of all feature parts. The weighting for point features is 1, for line features is length, and for polygon features is area.
-
Map layers can be used to define the Input Feature Class. When using a layer with a selection, only the selected features are included in the analysis.
Syntax
StandardDistance_stats (Input_Feature_Class, Output_Standard_Distance_Feature_Class, Circle_Size, {Weight_Field}, {Case_Field})| Parameter | Explanation | Data Type |
Input_Feature_Class | A feature class containing a distribution of features for which the standard distance will be calculated. | Feature Layer |
Output_Standard_Distance_Feature_Class | A polygon feature class that will contain a circle polygon for each input center. These circle polygons graphically portray the standard distance at each center point. | Feature Class |
Circle_Size | The size of output circles in standard deviations. The default circle size is 1; valid choices are 1, 2, or 3 standard deviations.
| String |
Weight_Field (Optional) | The numeric field used to weight locations according to their relative importance. | Field |
Case_Field (Optional) | Field used to group features for separate standard distance calculations. The case field can be of integer, date, or string type. | Field |
Code sample
StandardDistance Example (Python Window)
The following Python Window script demonstrates how to use the StandardDistance tool.
import arcpy
arcpy.env.workspace = r"C:\data"
arcpy.StandardDistance_stats("AutoTheft.shp", "auto_theft_SD.shp", "1_STANDARD_DEVIATION", "#", "#")
StandardDistance Example (stand-alone Python script)
The following stand-alone Python script demonstrates how to use the StandardDistance tool.
# Measure the geographic distribution of auto thefts
# Import system modules
import arcpy
# Local variables...
workspace = "C:/data"
locations = "AutoTheft.shp"
links = "AutoTheft_links.shp"
standardDistance = "auto_theft_SD.shp"
stardardEllipse = "auto_theft_SE.shp"
linearDirectMean = "auto_theft_LDM.shp"
try:
# Set the workspace (to avoid having to type in the full path to the data every time)
arcpy.env.workspace = workspace
# Process: Standard Distance of auto theft locations...
arcpy.StandardDistance_stats(locations, standardDistance, "1_STANDARD_DEVIATION", "#", "#")
# Process: Directional Distribution (Standard Deviational Ellipse) of auto theft locations...
arcpy.DirectionalDistribution_stats(locations, standardEllipse, "1_STANDARD_DEVIATION", "#", "#")
# Process: Linear Directional Mean of auto thefts...
arcpy.DirectionalMean_stats(links, linearDirectMean, "DIRECTION", "#")
except:
# If an error occurred while running a tool, print the messages
print(arcpy.GetMessages())
Environments
Licensing information
- ArcGIS Desktop Basic: Yes
- ArcGIS Desktop Standard: Yes
- ArcGIS Desktop Advanced: Yes