Summary
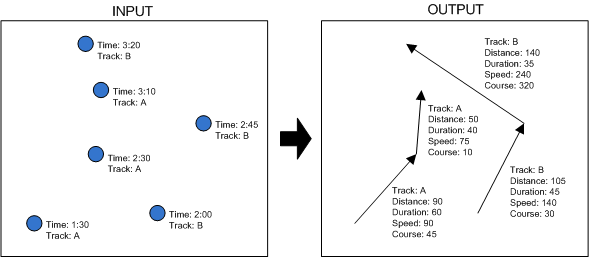
Calculates values that are computed from the difference between successively ordered features in a track. A new line feature class is created to represent the track intervals and store the calculated values (distance, duration, speed, and course).
Illustration
Usage
For this tool to work, the input feature class or layer must have date and time information contained in a single time field of data type text, short, long, float, double, or date. If the time field data type is date, the tool will automatically detect the format. If the time field data type is anything other than date, a time field format (and possibly other information for a time field data type of text) is required to parse the data values correctly.
If the time field selected is text, short, long, float, or double, the time field format can be selected from a list of supported time field formats, or you can define a custom time field format to interpret custom date and/or time values in a text field. For more information about custom formats for text fields, refer to converting string time values into date format.
This tool automatically generates the output field names that store the calculated values in the output feature class, and the autogenerated name includes an abbreviation of the units used.
Syntax
TrackIntervalsToLine_TA (in_features, out_feature_class, time_field, {track_id_field}, {time_field_format}, {locale_id}, {am_designator}, {pm_designator}, {distance_field_units}, {distance_field_name}, {duration_field_units}, {duration_field_name}, {speed_field_units}, {speed_field_name}, {course_field_units}, {course_field_name})| Parameter | Explanation | Data Type |
in_features | The input feature class or layer. | Feature Layer |
out_feature_class | The output line feature class that will be created. | Feature Class |
time_field | The field in the input feature class or layer that contains date and time information. This tool requires date and time information to be contained in the same field, and the data type of the field must be short, long, float, double, text, or date. | Field |
track_id_field (Optional) | The field that contains data values that are used to group the input features into tracks. The data type of the field can be short, long, float, double, text, or OID. | Field |
time_field_format (Optional) | If the data type of the time field is anything other than date, this parameter determines the format that is used to interpret data values in the time field. Some examples of formats are as follows:
If the data type of the time field is text, either a standard Esri text time format can be used, or a custom format can be specified. However, custom formats cannot be used if you specified KEEP_ON_DISK for the storage policy. If the data type of the time field is numeric (short, long, float, or double), only standard Esri numeric time formats can be used. If the data type of the time field is date, this parameter is not needed. | String |
locale_id (Optional) | If the data type of the time field is text, this parameter determines which locale is used to interpret data values in the time field. For all time field data types other than text, this parameter is not needed. If no locale is entered, the current locale of the operating system is used. For a list of available locales supported by your system, open the tool dialog box and expand this drop-down list. When entering the locale as a parameter, it is recommended that you use only the locale ID (LCID) assigned by Microsoft, which can be entered as a long integer such as 1033. You can also enter the full string representation of the locale as a parameter, such as "01033-English_(United_States)", but you must replace spaces with underscore characters. | Long |
am_designator (Optional) | If the time field data type is text and the time format is a 12-hour clock representation including a time marker (t or tt), this parameter determines the character (t) or characters (tt) that designate AM in the time field data values. If nothing is entered, the default AM designator for the selected locale is used. For all time field data types other than text, this parameter is not needed. | String |
pm_designator (Optional) | If the time field data type is text and the time format is a 12-hour clock representation including a time marker (t or tt), this parameter determines the character (t) or characters (tt) that designate PM in the time field data values. If nothing is entered, the default PM designator for the selected locale is used. For all time field data types other than text, this parameter is not needed. | String |
distance_field_units (Optional) | Specifies the distance units that will be used in the output distance field.
| String |
distance_field_name (Optional) | Specifies the name of the distance field that will be added to the input feature class or layer. If no field name is specified, a name is automatically chosen. | String |
duration_field_units (Optional) | Specifies the time units that will be used in the output duration field.
| String |
duration_field_name (Optional) | Specifies the name of the duration field that will be added to the input feature class or layer. If no field name is specified, a name is automatically chosen. | String |
speed_field_units (Optional) | Specifies the speed units that will be used in the output speed field.
| String |
speed_field_name (Optional) | Specifies the name of the speed field that will be added to the input feature class or layer. If no field name is specified, a name is automatically chosen. | String |
course_field_units (Optional) | Specifies the course units that will be used in the output course field.
| String |
course_field_name (Optional) | Specifies the name of the course field that will be added to the input feature class or layer. If no field name is specified, a name is automatically chosen. | String |
Code Sample
TrackIntervalsToLine example using date field and default units and output field names
This sample shows how to run the tool on a feature class with a date field using the default units and output field names.
import arcpy
arcpy.CheckOutExtension("tracking")
in_features = "C:\Data\Vehicles.gdb\Planes"
out_feature_class = "C:\Data\Vehicles.gdb\Plane_Intervals"
time_field = "DATE_TIME"
track_id_field = "ACID"
arcpy.TrackIntervalsToLine_ta(in_features, out_feature_class, time_field, track_id_field)
TrackIntervalsToLine example using text date field, custom units, and custom field names
This sample shows how to run the tool on a feature class with a date field of data type text, specifying custom units and field names.
import arcpy
arcpy.CheckOutExtension("tracking")
in_features = "C:\Data\Vehicles.gdb\Planes"
out_feature_class = "C:\Data\Vehicles.gdb\Plane_Intervals_2"
time_field = "DATE_TEXT"
track_id_field = "ACID"
time_field_format = "MM/dd/yyyy HH:mm:ss"
distance_field_units = "MILES"
distance_field_name = "DISTANCE"
duration_field_units = "SECONDS"
duration_field_name = "DURATION"
speed_field_units = "KILOMETERS_PER_HOUR"
speed_field_name = "SPEED"
course_field_units = "DEGREES"
course_field_name = "HEADING"
arcpy.TrackIntervalsToLine_ta(in_features, out_feature_class, time_field, track_id_field, time_field_format, "", "", "", distance_field_units, distance_field_name, duration_field_units, duration_field_name, speed_field_units, speed_field_name, course_field_units, course_field_name)
Environments
This tool does not use any geoprocessing environments
Licensing Information
- ArcGIS for Desktop Basic: Requires Tracking Analyst
- ArcGIS for Desktop Standard: Requires Tracking Analyst
- ArcGIS for Desktop Advanced: Requires Tracking Analyst