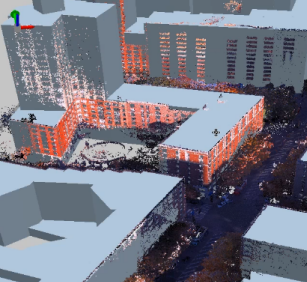
Lidar (light detection and ranging) is a relatively new remote sensing technology allowing us to collect very dense point samples of features in 3D. Lidar technology has evolved to become a common source of geographic data in GIS. These vast collections of real-world points are typically stored in LAS files. Each lidar point can have additional attributes such as intensity, class codes, and RGB color values, which can be leveraged inside ArcGIS.
ArcGIS reads LAS files natively, providing immediate access to lidar data without the need for data conversion or import. LAS attributes can be used to filter out content and symbolize points in 2D and 3D. Also, as lidar data often comes as a group of files, ArcGIS provides the ability to define logical sets of LAS files for working in localized projects.
Using ArcGIS you can:
Quickly view lidar data in 2D and 3D
- Validate your existing GIS data
- Measure heights and distances between points


Import LAS files into multipoint features
- Build and manage a terrain dataset
- Use the multipoint features to build raster DEMs and DSMs
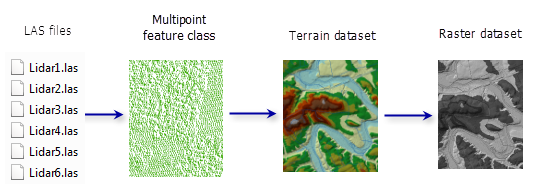
Manage huge volumes of lidar data holdings
- Know where you have (and don't have) lidar data
- Quickly identify source files for an area
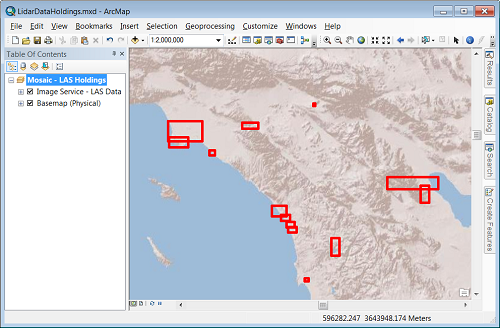
Update lidar class codes
- Manually fix errors in class codes
- Write add-ins to automatically classify lidar points
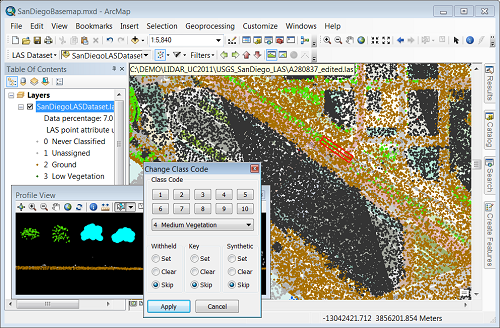
Analyze the lidar as a surface
- Analyze visibility against first-return lidar points
- Run floodplain models against bare-earth lidar points
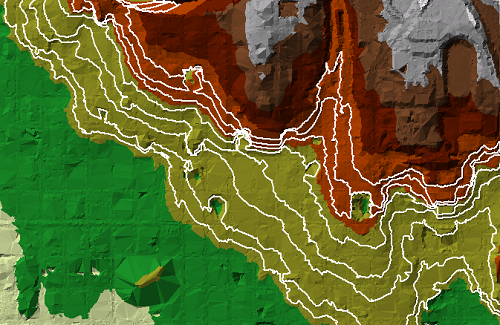
Improve the quality of the lidar surface with constraint features
- Incorporate other 3D features, such as ridgelines, into the lidar surface
- Interactively digitize in new breaklines in 3D
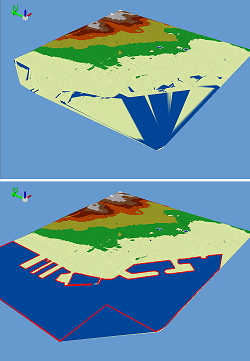
Leverage lidar data for feature extraction
- Digitize new GIS features against the points
- More accurately rotate and reposition existing GIS features