Summary
Adds vertices along line or polygon features. Also replaces curve segments (Bezier, circular arcs, and elliptical arcs) with line segments.
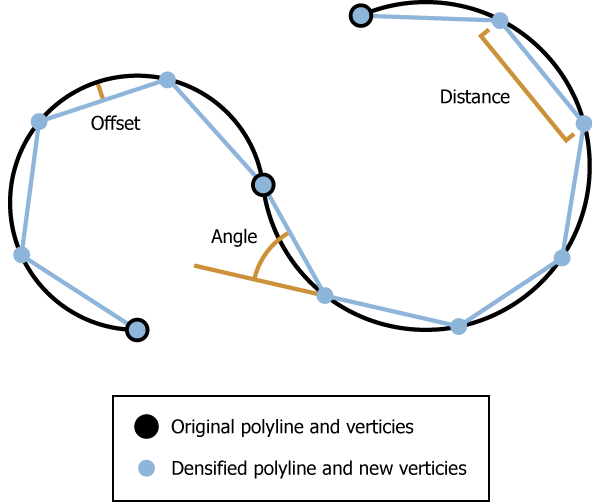
Illustration
Usage
Straight line segments are densified by the Distance parameter. Curve segments are simplified through densification by either the Distance , Maximum Deflection Angle, or Maximum Offset Deviation parameter.
Densification is done segment by segment.
Only one densification method can be selected each time Densify is executed.
The Spatial Reference of the data is very important to the result generated by this tool. Data should be densified in an appropriate coordinate system to maintain the correct shape of the features.
For each vertex of the original feature, including the start and end point, there will be a coincident vertex in the resulting feature.
When densifying by Maximum Offset Deviation, if the input geometry contains circular arcs, then an upper limit on the offset will be enforced such that the angle between two consecutive line segments in the output cannot exceed ten degrees. This angle can be exceeded if you densify by the Maximum Deflection Angle.
Syntax
Densify_edit (in_features, {densification_method}, {distance}, {max_deviation}, {max_angle})| Parameter | Explanation | Data Type |
in_features | The polygon or line feature class to be densified. | Feature Layer |
densification_method (Optional) | The method selected to handle feature densification.
| String |
distance (Optional) | The maximum linear distance between vertices. This distance will always be applied to line segments and to simplify curves. The default value is a function of the data's xy tolerance. | Linear unit |
max_deviation (Optional) | The maximum distance the output segment can be from the original. This parameter only affects curves. The default value is a function of the data's xy tolerance. | Linear unit |
max_angle (Optional) | The maximum angle that the output geometry can be from the input geometry. The valid range is from 0 to 90. The default value is 10. This parameter only affects curves. | Double |
Code sample
Densify example 1 (Python window)
The following Python window script demonstrates how to use the Densify function in immediate mode.
import arcpy
arcpy.Densify_edit("C:/data.gdb/lines", "ANGLE","", "", "0.75")
Densify example 2 (stand-alone script)
The stand-alone script, below, shows the Densify function as part of a workflow which also utilizes the Snap editing tool.
# Name: Snap.py
# Description: Snap climate regions boundary to vegetation layer
# boundary to ensure common boundary is coincident
# import system modules
#
import arcpy
# Set environment settings
#
arcpy.env.workspace = "C:/data"
# Make backup copy of climate regions feature class,
# since modification with the Editing tools below is permanent
#
climateBackup = "backups/climate.shp"
arcpy.CopyFeatures_management('climate.shp', climateBackup)
# Densify climate regions feature class to make sure there are enough
#vertices to match detail of vegetation layer when layers are snapped
#
arcpy.Densify_edit('climate.shp', "DISTANCE", "10 Feet")
# Snap climate regions feature class to vegetation layer vertices and edge
# first, snap climate region vertices to the nearest vegetation vertex within 30 Feet
# second, snap climate region vertices to the nearest vegetation edge within 20 Feet
#
snapEnv1 = ["Habitat_Analysis.gdb/vegtype", "VERTEX", "30 Feet"]
snapEnv2 = ["Habitat_Analysis.gdb/vegtype", "EDGE", "20 Feet"]
arcpy.Snap_edit('climate.shp', [snapEnv1, snapEnv2])
Environments
Licensing information
- ArcGIS Desktop Basic: No
- ArcGIS Desktop Standard: Yes
- ArcGIS Desktop Advanced: Yes