Available with Spatial Analyst license.
Summary
Calculates the base e exponential of the cells in a raster.
Illustration
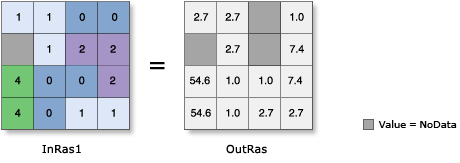
Usage
Input values can be integer or float, and can be negative as well as positive.
You can review some results for both positive and negative floating-point input values in the examples of output values from the Exponential tools.
The base e exponential is the most commonly used exponential function.
Input values less than or equal to -745 will be set to NoData in the output, because these values cannot be accurately represented by 32-bit floating-point numbers.
The output raster from this tool is always floating-point type, regardless of the input value type.
Output values from this tool are always positive.
See Analysis environments and Spatial Analyst for additional details on the geoprocessing environments that apply to this tool.
Syntax
Exp (in_raster_or_constant)
| Parameter | Explanation | Data Type |
in_raster_or_constant | The input values for which to find the base e exponential. In order to use a number as an input for this parameter, the cell size and extent must first be set in the environment. | Raster Layer | Constant |
Return Value
| Name | Explanation | Data Type |
| out_raster | The output raster. The cell values are the base e exponential of the input values. | Raster |
Code sample
Exp example 1 (Python window)
This example calculates the base e exponential of the input raster values, and returns the result as a TIFF raster.
import arcpy
from arcpy import env
from arcpy.sa import *
env.workspace = "C:/sapyexamples/data"
outExp = Exp("landuse")
outExp.save("C:/sapyexamples/output/outexp.tif")
Exp example 2 (stand-alone script)
This example calculates the base e exponential of the input raster values.
# Name: Exp_Ex_02.py
# Description: Calculates the base e exponential of cells in a raster
# Requirements: Spatial Analyst Extension
# Import system modules
import arcpy
from arcpy import env
from arcpy.sa import *
# Set environment settings
env.workspace = "C:/sapyexamples/data"
# Set local variables
inRaster = "landuse"
# Check out the ArcGIS Spatial Analyst extension license
arcpy.CheckOutExtension("Spatial")
# Execute Exp
outExp = Exp(inRaster)
# Save the output
outExp.save("C:/sapyexamples/output/outexp")
Environments
Licensing information
- ArcGIS Desktop Basic: Requires Spatial Analyst
- ArcGIS Desktop Standard: Requires Spatial Analyst
- ArcGIS Desktop Advanced: Requires Spatial Analyst