A number of geoprocessing tools, including Spatial Join, Append, Merge, Feature Class To Feature Class, and Table To Table, have a parameter for controlling how fields from the input datasets are processed and written, or mapped, to the output dataset—the Field Map parameter. In addition to the basic moving of attributes from input to output, field mapping can also be useful for some common tasks such as field concatenation and calculating statistics such as mean, sum, and standard deviation.
The field map is displayed graphically in a tree view. The field map output fields are displayed as the top-level elements in the tree view and their names and field types are shown. These output fields are the set of attribute fields that will be in the output dataset. Fields from the input datasets are seen as subelements in the tree view. Each output field can have zero, one, or many input fields connected to it in the tree. The input fields associated with an output field will determine what attribute values from the input datasets are transferred to the fields in the output dataset. An input field in the field map will show which specific input dataset the field belongs to, and the field name and type.
You can add or delete output fields from the field map, and add or delete input fields from any output field. You can also change a number of properties of an output field such as field name and type as well as a Merge Rule that determines how to process multiple input fields associated with one output field.
Modifying the default field map
To modify the field map control, use the buttons on the control as well as right-click context menus of both output and input fields.
The context menu for an output field has the following options:
- Add Input Field opens a dialog box that lists all input fields. Select one or many input fields and click OK to add them to the output field.
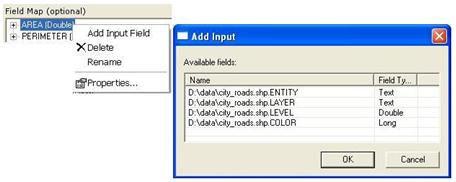
- Delete removes the output field from the field map.
- Rename allows you to modify the name of the output field.
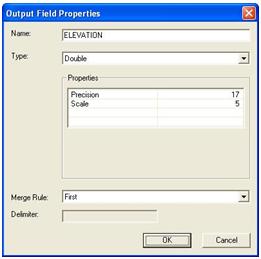
- Properties allows you to modify properties of the output field, such as the name, type, and merge rule.
The context menu for an input field has the following options:
- Delete removes the input field from the field map.
- Format (text fields only) allows you to modify the start and end position of text from the input field to be used in field mapping.
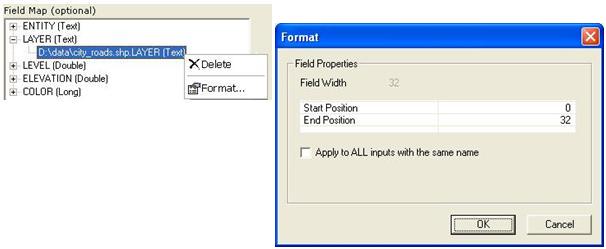
The Start Position value is the start point from which row values will be truncated. Row value widths start at zero.
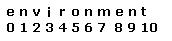
Values that are longer than the End Position value will be truncated at the specified point. For example, if a start position of 3 and an end position of 7 is specified for a text field with the value environment, the value in the output field will be ironm.
The context menu of the whole field map (any white space) has the following options:
- Add Output Field allows you to add a new output field to the field map. A dialog box opens where you can enter the field name, type, merge rule, a delimiter, if the Join merge rule is selected, and other field properties.
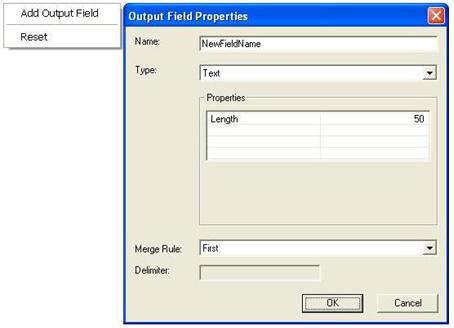
- The Reset option will set the field map, including all output and input field properties, back to the default, resetting any customizations.
Merge rules
The merge rule property of an output field allows you to specify how values from two or more input fields are merged into a single output value. Null values will be excluded from all merge calculations. There are several merge rules that you can use:
| Merge rule | The output value is... |
|---|---|
| First | From the first (top) input field. |
| Last | From the last (bottom) input field. |
| Join | A concatenation of input field values. You can use a delimiter to separate the various input values. If no delimiter is used, all values will be joined into one continuous string. |
| Sum | The sum total of input field values. |
| Mean | The mean (average) of input field values. |
| Median | The median (middle) of input field values. The median is the middle value which separates a total set of values into upper and lower halves; for example, the median of 1,3,5,7,9,11,13 is 7. |
| Mode | The value of input fields that is the most common or has the highest frequency. |
| Min | The minimum (lowest) input field value. |
| Max | The maximum (highest) input field value. |
| Standard deviation | The standard deviation of input field values. Do not use Standard deviation if your output field has only a single input field, as the output value will always be zero. |
| Count | The number of values in the input fields, excluding null values. |
| Range | The absolute difference between the minimum and maximum field values. |
Setting the Field Map parameter in scripting
In scripting, use the FieldMappings object to specify a field map parameter.