Available with Standard or Advanced license.
When new parcels are created, they need to be joined to the parcel fabric parcel fabric layer. A new parcel is not yet connected to the parcel fabric, even if you snapped to existing parcel points to create the parcel. New parcels need to be joined to the parcel fabric to be connected to the parcel fabric network.
Since parcels are created as floating geometries or floating features, this allows data entry without needing coordinates, points of beginning, or spatial references. All that is required to enter a parcel in the parcel fabric are the recorded dimensions from the plan or record of survey.
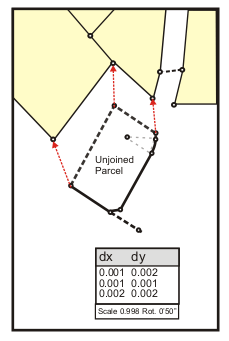
Parcel joining is an interactive process where the parcel points of a floating parcel or group of parcels are matched with their corresponding points in the parcel fabric.
Parcels can be joined to the parcel fabric using the following methods:
- Click Keep And Join
 on the Parcel Details dialog box after entering a new parcel.
on the Parcel Details dialog box after entering a new parcel. - Right-click an unjoined parcel in the Parcel Explorer window and click Join.
- Right-click a parcel in the parcel fabric layer and click Rejoin. You would rejoin a parcel to correct incorrect join links.
- Click Parcel Editor > Append File to append and join parcels stored in a cadastral .xml file.
There are two join methods to choose from on the Join Parcel dialog box when joining parcels:
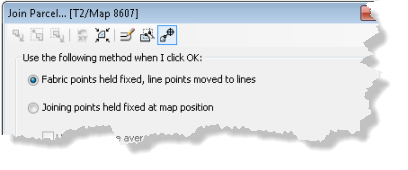
- Fabric points held fixed, line points moved to lines
Use this method to fit parcels cartographically and topologically to the surrounding parcels.
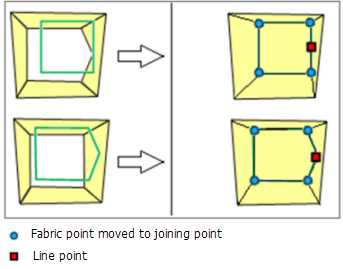
- Joining points held fixed at map position
Use this method to hold the coordinate location of the floating parcels as fixed. The surrounding parcels are fitted cartographically and topologically to the parcels being joined.
Fabric points held fixed
New parcels are fitted to surrounding parcels based on established join lines. The parcels are cartographically fitted such that there are no slivers, gaps, or overlaps. This method is typically used when surrounding parcels are considered equally or more accurate than the parcels being joined.
When using the Fabric points held fixed method, the following join tools are available:
- The Reset X And Y tool
 resets joining parcels to their original map location if you have dragged or moved the parcels during joining.
resets joining parcels to their original map location if you have dragged or moved the parcels during joining. - The Bring Joining Parcel To Map Extent tool
 places join parcels in the visible map extent.
places join parcels in the visible map extent.
Accuracy
Because parcels are fitted cartographically to the surrounding fabric, they may be distorted depending on the data quality. When joining more accurate parcels to less accurate surrounding parcels using the Fabric points held fixed method, it is important to specify the appropriate accuracy levels on the parcels being joined and the surrounding parcels. If the joining parcel's accuracy is set to a higher level than the accuracy level of the surrounding parcels, a parcel fabric adjustment will result in the surrounding parcels adjusting around the more accurate parcel and the more accurate parcel maintaining its data integrity. Parcels with a higher accuracy level have a higher weight in a fabric least-squares adjustment and will adjust less than those parcels with a lower accuracy level and lower weight.
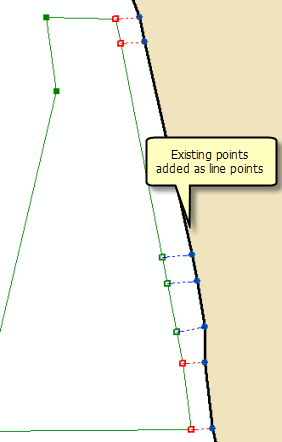
Line points
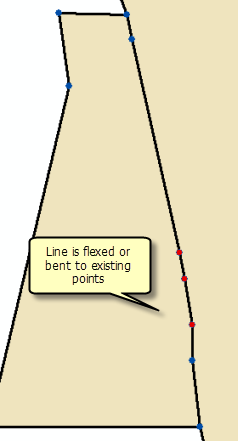
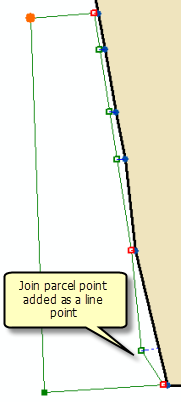
Parcel points that are joined as line points are automatically moved to the existing parcel lines.
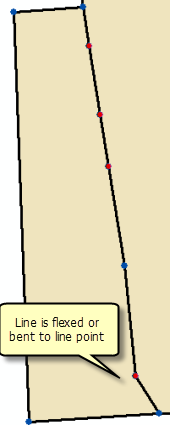
If a straight parcel line is joined to a series of existing lines that are not collinear, the straight line will be bent or flexed to the position of the existing parcel points as long as the existing parcel points have been added as line points. Straight lines are bent or flexed to their line points if they lie closer to their line points than the tolerance specified for Line-point under the Edit Environment tab of the Parcel Fabric Properties dialog box.
Joining points held fixed
Joining parcels are held at a fixed position and surrounding parcels are fitted to the join parcels. This method allows you to preserve the shape of accurate parcels when joining them to less accurate surrounding parcels.
The Joining points held fixed method is recommended for appending parcel data from cadastral XML files. The point coordinates in the cadastral XML file are used to place the parcels in the map extent. If parcels are appended from a different coordinate system or spatial reference, the parcels may not be visible in the map extent when first placed in the map. The Bring Joining Parcel To Map Extent tool  located on the Join Parcel dialog box can be clicked to place the parcels in the visible map extent.
located on the Join Parcel dialog box can be clicked to place the parcels in the visible map extent.
The following tools on the Join Parcel dialog box are also available when using the Joining points held fixed method:
- The Reset X And Y tool
 resets joining parcels to their original coordinates if you have dragged or moved the parcels.
resets joining parcels to their original coordinates if you have dragged or moved the parcels. - Check the Use coordinate averaging check box to calculate an average (mean) between the join parcel coordinates and corresponding parcel fabric coordinates.
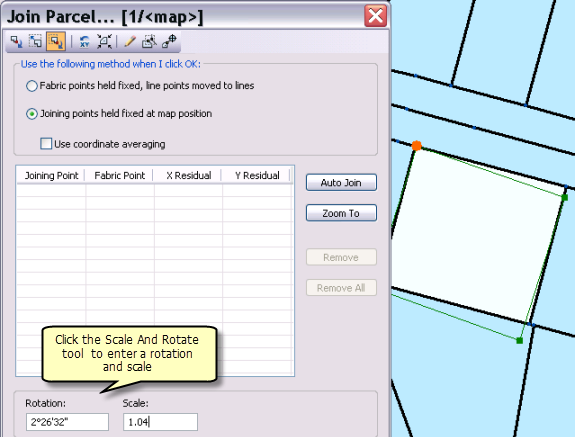
Scale and rotation
Use the Scale And Rotate tool  to scale and rotate the joining parcel. Rotation and scale values can typed into the Join Parcel dialog box.
to scale and rotate the joining parcel. Rotation and scale values can typed into the Join Parcel dialog box.
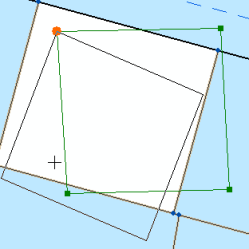
You can also use the mouse cursor to scale and rotate the joining parcels. Click the Scale And Rotate tool and snap to parcel vertices to scale and rotate the parcel. The scale and rotation values on the Join Parcel dialog box will update as you scale and rotate the parcel.
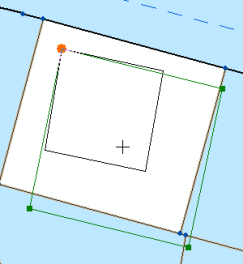
Line points
Points on the join parcel are joined as line points to surrounding parcels if there are no matching parcel points. If necessary, straight lines are bent or flexed to the line point when the parcel is joined.
Join links
Join links are established between the join parcel's points and the corresponding points in the parcel fabric. Failure to establish a join link between a join parcel point and its matching fabric point will result in duplicate points for the same location. Overlapping points can result in gaps and slivers in the parcel fabric.
Join links can be manually created or created by dragging a box around the two points you want to join. To manually create a join link, the Join A Parcel Or Group Of Parcels tool  is used to snap to the joining parcel's point and to the corresponding point in the fabric.
is used to snap to the joining parcel's point and to the corresponding point in the fabric.
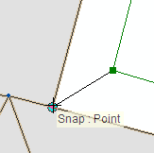
Join links can also be automatically created by dragging a box around the two points you want to join. The Create Join Link tool  is used to drag a box around the points to be joined.
is used to drag a box around the points to be joined.
Establishing join links using the trace link tool
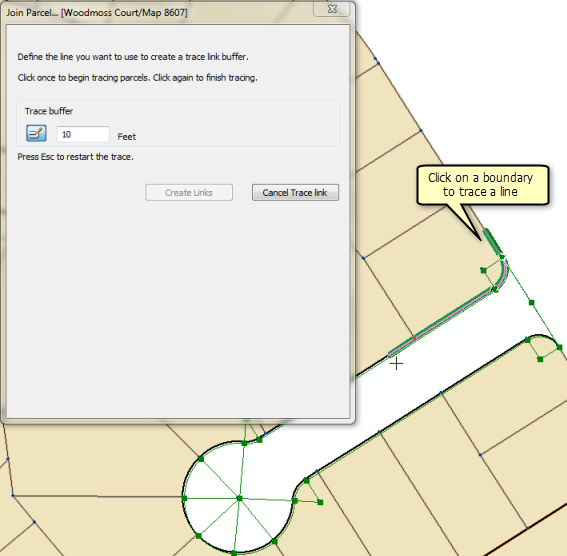
Instead of establishing join links individually point by point, you can use the Trace Fabric To Create Join Links tool  located on the Join Parcel dialog box to detect join links along traced boundaries. The trace link tool will detect join links between the joining parcel line and the traced boundary line if the joining parcel line lies within the specified trace link buffer.
located on the Join Parcel dialog box to detect join links along traced boundaries. The trace link tool will detect join links between the joining parcel line and the traced boundary line if the joining parcel line lies within the specified trace link buffer.
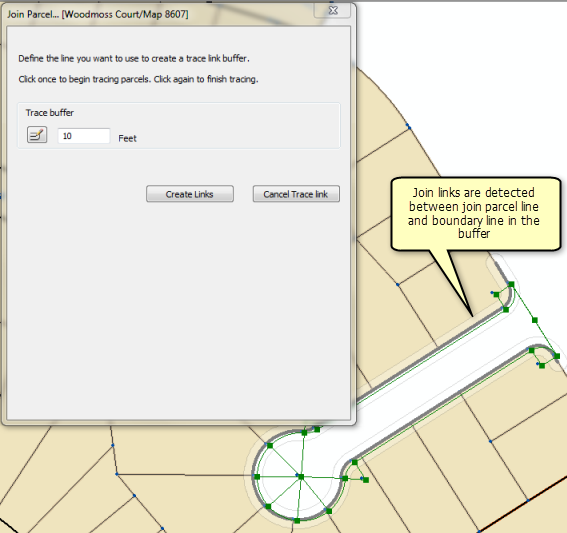
To use the trace link tool, click the Trace Fabric To Create Join Links tool  , specify a trace buffer, and click a parcel boundary to begin tracing a line. Click a parcel boundary to finish tracing the line and click Create Links. Once the links are established, click Auto Join to detect any missing join links or line point links, and then click OK to join the parcel.
, specify a trace buffer, and click a parcel boundary to begin tracing a line. Click a parcel boundary to finish tracing the line and click Create Links. Once the links are established, click Auto Join to detect any missing join links or line point links, and then click OK to join the parcel.
Make sure to set an appropriate join tolerance for detecting line points under Auto-join settings on the Tolerances tab on the Parcel Editor Options dialog box.
Autojoining
After at least two join links have been established, click Auto Join on the Join Parcel dialog box to detect any remaining or missing links.
Auto Join uses the transformation parameters from the existing established join links and applies them to all other points in the parcel group to detect other possible join lines. If there is a large difference in accuracy between the parcels being joined and the surrounding fabric, you may need to establish a few more join lines for Auto Join to correctly detect remaining join links.
Autojoin also detects line point join links. A line point join link occurs when a parcel point is joined to a parcel line.
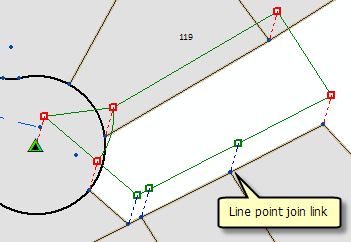
The autojoin process uses the Auto-join settings tolerance located on the Tolerances tab on the Parcel Editor Options dialog box. You can edit this tolerance to suit the quality of your data. For example, a small tolerance of about 0.3 feet can be used if the quality of both the joining parcel and surrounding parcels is good. If the joining parcel is more accurate than the surrounding fabric parcels, a small tolerance will not likely detect all line point links.
Join residuals
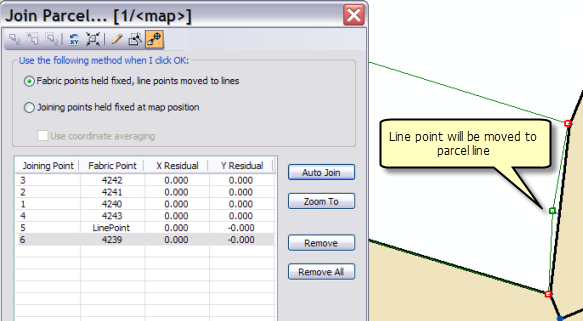
As each parcel point is matched with its corresponding fabric point, a set of join residuals, a scale, and a rotation are recomputed and displayed on the Join Parcel dialog box.
Join residuals are computed from a transformation between the joining parcel's points and the corresponding points in the parcel fabric. If only two points are joined, a Helmert transformation is used. If more than two points are joined, a least-squares transformation is used. Each time another point is joined, join residuals, scale, and rotation are recalculated.
Join residuals are an indication of how well the unjoined parcel fits with the surrounding parcel fabric. Large join residuals may result from a situation where the parcel being joined is more accurate than the surrounding parcel fabric. Large residuals may occur when the surrounding parcel fabric has been migrated from digitized data and the parcel being joined has been entered from the survey record. Large join residuals could also indicate an error in the dimensions of the parcel being joined.