Available with Network Analyst license.
Network datasets are well suited to model transportation networks. They are created from source features, which can include simple features (lines and points) and turns, and store the connectivity of the source features. When you perform an analysis using the ArcGIS Network Analyst, the analysis always happens on a network dataset.
A network dataset models the street network shown in the graphic below. The graphic highlights that one-way streets, turn restrictions, and overpasses/tunnels can be modeled. The analyses that are performed on the network, such as the route from stop 1 to stop 2, respect these and other network dataset properties.
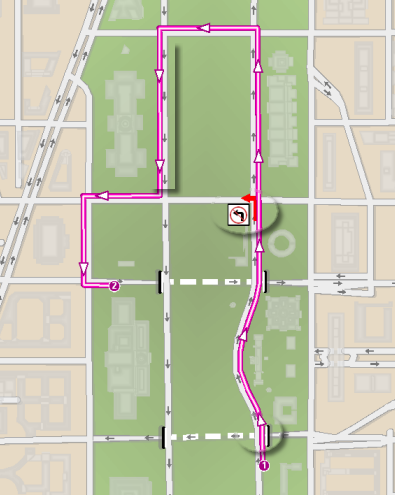
To understand connectivity and why it's important, consider that features are normally unaware of each other. For example, if two line features intersect, neither line is aware of the other. Similarly, a point feature at the end of a line feature doesn't have any inherent information that lets it know about the line. However, the network dataset keeps track of which source features are coincident. It also has a connectivity policy, which you can modify, to further define which coincident features are truly connected. This makes it possible to model overpasses and underpasses without having the roads connect. This way, when a network analysis is performed, the solvers know which paths along the network are feasible.
Multimodal network datasets
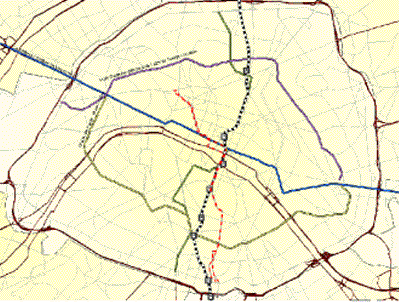
More complex connectivity scenarios, such as multimodal transportation networks, are also possible. The following is an example of a transportation network in downtown Paris displaying road, rail, and bus networks.
The network dataset also possesses a rich network attribute model that helps model impedances, restrictions, and hierarchy for the network.
Workspaces
In ARC/INFO, coverages were used to create networks on the fly. In ArcView GIS, a persistent network was created when a network analysis function was run on a line shapefile for the first time. In ArcGIS, the network dataset stores the persistent network. You can save this network, modify its properties, and model a variety of networks using network datasets.
There are a few options available when creating a network dataset. The best option is to create a network dataset from feature classes in a feature dataset of a geodatabase. Since a feature dataset can store and easily communicate with multiple feature classes, the network dataset can support multiple sources and model a multimodal network. The shapefile-based network dataset provides ArcView GIS users with the opportunity to rapidly migrate their data. The shapefile network dataset is created from a polyline shapefile containing the network source (for instance, a street network) and, optionally, a shapefile turn feature class. Such a network dataset cannot support multiple edge sources and cannot be used to model multimodal networks.
The ArcGIS Network Analyst can also read SDC network datasets. This allows you to perform network analysis on vendor-supplied SDC data, without having to create your own network dataset.