Summary
Converts a raster dataset to polyline features.
Usage
The input raster can have any valid cell size greater than 0, and may be any valid integer raster dataset.
The Field parameter allows you to choose which attribute field of the input raster dataset will become an attribute in the output feature class. If a field is not specified, the cell values of the input raster (the VALUE field) will become a column with the heading Grid_code in the attribute table of the output feature class.
The following graphic illustrates how the input raster is vectorized when it is converted to a polyline feature output. The result is presented for both the settings of the Simplify parameter.
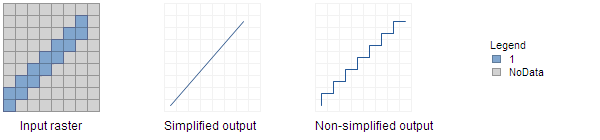
Comparing the output with different simplify options If Extent is specified in the environment setting, and the lower-left corner of the output extent does not match with any cell corner of the input raster, in the processing, a shift of the cell alignment of the input raster will be performed to match the specified extent. This shift will trigger a resampling of the input raster using the Nearest Neighbor method. Consequently, the output features will be shifted as well, and as a result, the output features may not overlay the original input raster exactly. You can avoid this shift by using the input raster as the Snap Raster in the environment.
Syntax
RasterToPolyline_conversion (in_raster, out_polyline_features, {background_value}, {minimum_dangle_length}, {simplify}, {raster_field})| Parameter | Explanation | Data Type |
in_raster | The input raster dataset. The raster must be integer type. | Raster Layer |
out_polyline_features | The output feature class that will contain the converted polylines. | Feature Class |
background_value (Optional) | Specifies the value that will identify the background cells. The raster dataset is viewed as a set of foreground cells and background cells. The linear features are formed from the foreground cells.
| String |
minimum_dangle_length (Optional) | Minimum length of dangling polylines that will be retained. The default is zero. | Double |
simplify (Optional) | Simplifies a line by removing small fluctuations or extraneous bends from it while preserving its essential shape.
| Boolean |
raster_field (Optional) | The field used to assign values from the cells in the input raster to the polyline features in the output dataset. It can be an integer or a string field. | Field |
Code sample
RasterToPolyline example (Python window)
Converts a raster dataset to polyline features.
import arcpy
from arcpy import env
env.workspace = "c:/data"
arcpy.RasterToPolyline_conversion("flowstr", "c:/output/streams.shp", "ZERO",
50, "SIMPLIFY")
RasterToPolyline example (stand-alone script)
Converts a raster dataset to polyline features.
# Name: RasterToPolyline_Ex_02.py
# Description: Converts a raster dataset to polyline features.
# Requirements: None
# Import system modules
import arcpy
from arcpy import env
# Set environment settings
env.workspace = "C:/data"
# Set local variables
inRaster = "flowstr"
outLines = "c:/output/flowstream.shp"
backgrVal = "ZERO"
dangleTolerance = 50
field = "VALUE"
# Execute RasterToPolygon
arcpy.RasterToPolyline_conversion(inRaster, outLines, backgrVal,
dangleTolerance, "SIMPLIFY", field)
Environments
- Auto Commit
- Current Workspace
- Default Output Z Value
- Extent
- Geographic Transformations
- M Resolution
- M Tolerance
- Maintain Spatial Index
- Output CONFIG Keyword
- Output Coordinate System
- Output has M values
- Output has Z values
- Output M Domain
- Output XY Domain
- Output Z Domain
- Scratch Workspace
- Snap Raster
- XY Resolution
- XY Tolerance
- Z Resolution
- Z Tolerance
Licensing information
- ArcGIS Desktop Basic: Yes
- ArcGIS Desktop Standard: Yes
- ArcGIS Desktop Advanced: Yes