Tools that honor the Mask environment will only consider those cells that fall within the analysis mask in the operation.
Illustration
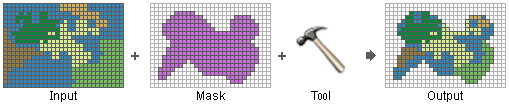
Usage notes
- Setting an analysis mask means that processing will only occur on locations that fall within the mask, and all locations outside of it will be assigned to NoData in the output.
- The mask can be a raster or a feature dataset.
- If the analysis mask is a raster, all cells that have a value will be considered to define the mask. Cells in a mask raster that are NoData will be considered to be outside the mask and will be NoData in the output.
Tools such as Reclassify and Con can help create a raster analysis mask.
- If the analysis mask is a feature dataset, it will internally be converted to a raster on execution. For this reason, you should take care to ensure that the Cell Size and Snap Raster are set appropriately for your analysis.
Dialog syntax
Mask—A dataset that defines which locations in the inputs will be considered in the execution of the tool. If the mask dataset is a raster, all cells with a value will compose the mask. Cells that are NoData in a raster mask will be NoData in the output. If a feature dataset is used as input for the mask, it will be converted internally to a raster on execution.
Scripting syntax
arcpy.env.mask = mask_source
| Parameter | Explanation |
|---|---|
mask_source | The dataset that defines the mask. It can be a raster or a feature dataset. If the dataset is a raster, cells that have a value will constitute the mask, and any cells that are NoData in the mask will be NoData in the output. |
Script example
This example demonstrates how to set the Mask environment before executing a Spatial Analyst extension tool.
import arcpy
# Set environment
arcpy.env.workspace = "C:/workspace"
# Set Mask environment
arcpy.env.mask = "C:/data/maskpoly.shp"
# Set local variables
InZones = "C:/data/parcels.shp"
InZoneField = "Parcel_ID"
InValueRaster = "C:/data/Slope"
# Check out a Spatial Analyst license
arcpy.CheckOutExtension("Spatial")
# Process: Calculate the mean slope of each parcel area.
out = arcpy.sa.ZonalStatistics(InZones, InZoneField, InValueRaster, "MEAN","DATA")
out.save("mean_ParSlp")