Summary
Creates 3D features by interpolating z-values from a surface.
Illustration
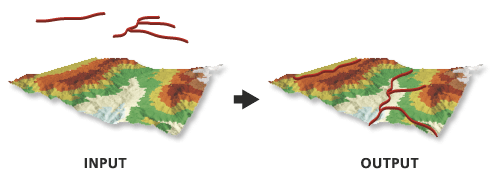
Usage
When using natural neighbors interpolation, consider specifying a sampling distance that's equal to or above half of the average point spacing of the data points in the surface.
When using the Interpolate Vertices Only option, features with vertices that fall outside the data area of the surface will not be part of the output.
Syntax
InterpolateShape_3d (in_surface, in_feature_class, out_feature_class, {sample_distance}, {z_factor}, {method}, {vertices_only}, {pyramid_level_resolution})| Parameter | Explanation | Data Type |
in_surface | The surface to use for interpolating z-values. | LAS Dataset Layer; Mosaic Layer; Raster Layer; Terrain Layer; TIN Layer |
in_feature_class | The input features to process. | Feature Layer |
out_feature_class | The feature class that will be produced by this tool. | Feature Class |
sample_distance (Optional) | The spacing at which z-values will be interpolated. By default, this is a raster dataset's cell size or a triangulated surface's natural densification. | Double |
z_factor (Optional) | The factor by which z-values will be multiplied. This is typically used to convert Z linear units to match XY linear units. The default is 1, which leaves elevation values unchanged. This parameter is disabled if the spatial reference of the input surface has a Z datum with a specified linear unit. | Double |
method (Optional) | Interpolation method used to determine elevation values for the output features. The available options depend on the surface type being used:
| String |
vertices_only (Optional) | Specifies whether the interpolation will only occur along the vertices of an input feature, thereby ignoring the sample distance option.
| Boolean |
pyramid_level_resolution (Optional) | The z-tolerance or window-size resolution of the terrain pyramid level that will be used by this tool. The default is 0, or full resolution. | Double |
Code sample
InterpolateShape example 1 (Python window)
The following sample demonstrates the use of this tool in the Python window.
import arcpy
from arcpy import env
arcpy.CheckOutExtension("3D")
env.workspace = "C:/data"
arcpy.InterpolateShape_3d("my_tin", "roads.shp", "roads_interp.shp")
InterpolateShape example 2 (stand-alone script)
The following sample demonstrates the use of this tool in a stand-alone Python script.
'''*********************************************************************
Name: InterpolateShape Example
Description: This script demonstrates how to use InterpolateShape
on all 2D features in a target workspace.
*********************************************************************'''
# Import system modules
import arcpy
from arcpy import env
import exceptions, sys, traceback
# Set local variables
inWorkspace = arcpy.GetParameterAsText(0)
surface = arcpy.GetParameterAsText(1)
try:
arcpy.CheckOutExtension("3D")
# Set default workspace
env.workspace = inWorkspace
# Create list of feature classes in target workspace
fcList = arcpy.ListFeatureClasses()
if fcList:
for fc in fcList:
desc = arcpy.Describe(fc)
# Find 2D features
if not desc.hasZ:
# Set Local Variables
outFC = "{0}_3D.shp".format(desc.basename)
method = "BILINEAR"
# Execute InterpolateShape
arcpy.ddd.InterpolateShape(surface, fc, outFC,
10, 1, method, True)
else:
print "{0} is not a 2D feature.".format(fc)
else:
print "No feature classes were found in {0}.".format(env.workspace)
arcpy.CheckInExtension('3D')
except arcpy.ExecuteError:
print arcpy.GetMessages()
except:
# Get the traceback object
tb = sys.exc_info()[2]
tbinfo = traceback.format_tb(tb)[0]
# Concatenate error information into message string
pymsg = 'PYTHON ERRORS:\nTraceback info:\n{0}\nError Info:\n{1}'\
.format(tbinfo, str(sys.exc_info()[1]))
msgs = 'ArcPy ERRORS:\n {0}\n'.format(arcpy.GetMessages(2))
# Return python error messages for script tool or Python Window
arcpy.AddError(pymsg)
arcpy.AddError(msgs)
Environments
Licensing information
- ArcGIS Desktop Basic: Requires 3D Analyst
- ArcGIS Desktop Standard: Requires 3D Analyst
- ArcGIS Desktop Advanced: Requires 3D Analyst