Available with Spatial Analyst license.
Summary
Calculates, for each cell, its least-cost source based on the least accumulative cost over a cost surface.
Illustration
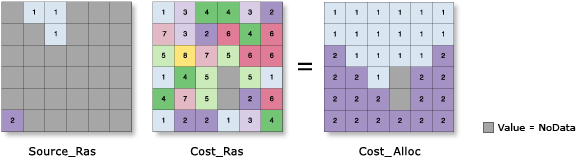
Usage
The input source data can be a feature class or raster.
When the input source data is a raster, the set of source cells consists of all cells in the source raster that have valid values. Cells that have NoData values are not included in the source set. The value 0 is considered a legitimate source. A source raster can be easily created using the extraction tools.
When the input source data is a feature class, the source locations are converted internally to a raster before performing the analysis. The resolution of the raster can be controlled with the Cell Size environment. By default, the resolution will be set to the resolution of the input cost raster.
When using polygon feature data for the input source data, care must be taken with how the output cell size is handled when it is coarse, relative to the detail present in the input. The internal rasterization process employs the same default Cell assignment type as the Polygon to Raster tool, which is the cell center method. This means that data not located at the center of the cell will not be included in the intermediate rasterized source output, so it will not be represented in the distance calculations. For example, if your sources are a series of small polygons (such as building footprints) that are small relative to the output cell size, it is possible that only a few will fall under the centers of the output raster cells, seemingly causing most of the others to be lost in the analysis.
To avoid this situation, as an intermediate step, you could rasterize the input features directly with the Polygon to Raster tool and set a Priority field. Then use the resulting output as input to the particular distance tool you want to use. Alternatively, you could select a small cell size to capture the appropriate amount of detail from the input features.
To calculate allocation, source locations can have an associated value, which can be specified by the Source field parameter. If the input source is an integer raster, the default field is VALUE. If it is a feature, it will be the first integer field in the attribute table. If the input source data is a floating-point raster, an integer value raster parameter must be specified.
When the source input is a feature, by default, the first valid available field will be used. If no valid fields exist, the ObjectID field (for example, OID or FID, depending on the type of feature input) will be used.
Cell locations with NoData in the Input cost raster act as barriers in the cost surface tools. Any cell location that is assigned NoData on the input cost surface will receive NoData on all output rasters (cost distance, allocation, and backlink).
The Input value raster is useful when alternative values or zones are to be used or if source was derived from an operation that results in a binary result of either 0 or 1, losing the original zone values that are associated with these locations. The value raster can restore these values or allow for analysis on additional combinations of zone values within the source locations.
If the value raster is used, it may change the configuration and results of the cost allocation output; it will not affect the optional cost distance or the back link results.
The Maximum distance is specified in the same cost units as those on the cost raster.
For the output distance raster, the least-cost distance (or minimum accumulative cost distance) of a cell from or to a set of source locations is the lower bound of the least-cost distances from the cell to all source locations.
The characteristics of the source, or the movers from or to a source, can be controlled by specific parameters. The Source cost multiplier parameter determines the mode of travel or magnitude at the source, Source start cost sets the starting cost before the movement begins, Source resistance rate is a dynamic adjustment accounting for the impact of accumulated cost, for example, simulating how much a hiker is getting fatigued, and Source capacity sets how much cost a source can assimilate before reaching its limit. The Travel direction identifies if the mover is starting at a source and moving to non-source locations, or is starting at non-source locations and moving back to a source.
If any of the source characteristics parameters are specified using a field, the source characteristic will be applied on a source-by-source basis, according to the information in the given field for the source data. When a keyword or a constant value is given, it will be applied to all sources.
If Source start cost is specified and the Travel direction is Travel from source, the source locations on the output cost distance surface will be set to the value of Source start cost; otherwise, the source locations on the output cost distance surface will be set to zero.
This tool supports parallel processing. If your computer has multiple processors or processors with multiple cores, better performance may be achieved, particularly on larger datasets. The Parallel processing with Spatial Analyst help topic has more details on this capability and how to configure it.
When using parallel processing, temporary data will be written to manage the data chunks being processed. The default temp folder location will be on your local C drive. You can control the location of this folder by setting up a system environment variable named TempFolders and specifying the path to a folder to use (for example, E:\RasterCache). If you have admin privileges on your machine, you can also use a registry key (for example, [HKEY_CURRENT_USER\SOFTWARE\ESRI\Desktop10.6\Raster]).
By default, this tool will use 50 percent of the available cores. If the input data is smaller than 5,000 by 5,000 cells in size, fewer cores may be used. You can control the number of cores the tool uses with the Parallel processing factor environment.
See Analysis environments and Spatial Analyst for additional details on the geoprocessing environments that apply to this tool.
Syntax
CostAllocation (in_source_data, in_cost_raster, {maximum_distance}, {in_value_raster}, {source_field}, {out_distance_raster}, {out_backlink_raster}, {source_cost_multiplier}, {source_start_cost}, {source_resistance_rate}, {source_capacity}, {source_direction})| Parameter | Explanation | Data Type |
in_source_data | The input source locations. This is a raster or feature dataset that identifies the cells or locations from or to which the least accumulated cost distance for every output cell location is calculated. For rasters, the input type can be integer or floating point. If the input source raster is floating point, the {in_value_raster} must be set, and it must be of integer type. The value raster will take precedence over any setting of the {source_field}. | Raster Layer; Feature Layer |
in_cost_raster | A raster defining the impedance or cost to move planimetrically through each cell. The value at each cell location represents the cost-per-unit distance for moving through the cell. Each cell location value is multiplied by the cell resolution while also compensating for diagonal movement to obtain the total cost of passing through the cell. The values of the cost raster can be integer or floating point, but they cannot be negative or zero (you cannot have a negative or zero cost). | Raster Layer |
maximum_distance (Optional) | Defines the threshold that the accumulative cost values cannot exceed. If an accumulative cost distance value exceeds this value, the output value for the cell location will be NoData. The maximum distance defines the extent for which the accumulative cost distances are calculated. The default distance is to the edge of the output raster. | Double |
in_value_raster (Optional) | The input integer raster that identifies the zone values that should be used for each input source location. For each source location (cell or feature), the value defined by the {in_value_raster} will be assigned to all cells allocated to the source location for the computation. The value raster will take precedence over any setting for the {source_field}. | Raster Layer |
source_field (Optional) | The field used to assign values to the source locations. It must be of integer type. If the {in_value_raster} has been set, the values in that input will have precedence over any setting for the {source_field}. | Field |
out_distance_raster (Optional) | The output cost distance raster. The cost distance raster identifies, for each cell, the least accumulative cost distance over a cost surface to the identified source locations. A source can be a cell, a set of cells, or one or more feature locations. The output raster is of floating-point type. | Raster Dataset |
out_backlink_raster (Optional) | The output cost backlink raster. The backlink raster contains values of 0 through 8, which define the direction or identify the next neighboring cell (the succeeding cell) along the least accumulative cost path from a cell to reach its least-cost source. If the path is to pass into the right neighbor, the cell will be assigned the value 1, 2 for the lower right diagonal cell, and continuing clockwise. The value 0 is reserved for source cells. 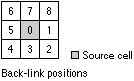 | Raster Dataset |
source_cost_multiplier (Optional) | Multiplier to apply to the cost values. Allows for control of the mode of travel or the magnitude at a source. The greater the multiplier, the greater the cost to move through each cell. The values must be greater than zero. The default is 1. | Double; Field |
source_start_cost (Optional) | The starting cost from which to begin the cost calculations. Allows for the specification of the fixed cost associated with a source. Instead of starting at a cost of zero, the cost algorithm will begin with the value set by source_start_cost. The values must be zero or greater. The default is 0. | Double; Field |
source_resistance_rate (Optional) | This parameter simulates the increase in the effort to overcome costs as the accumulative cost increases. It is used to model fatigue of the traveler. The growing accumulative cost to reach a cell is multiplied by the resistance rate and added to the cost to move into the subsequent cell. It is a modified version of a compound interest rate formula that is used to calculate the apparent cost of moving through a cell. As the value of the resistance rate increases, it increases the cost of the cells that are visited later. The greater the resistance rate, the more additional cost is added to reach the next cell, which is compounded for each subsequent movement. Since the resistance rate is similar to a compound rate and generally the accumulative cost values are very large, small resistance rates are suggested, such as 0.02, 0.005, or even smaller, depending on the accumulative cost values. The values must be zero or greater. The default is 0. | Double; Field |
source_capacity (Optional) | Defines the cost capacity for the traveler for a source. The cost calculations continue for each source until the specified capacity is reached. The values must be greater than zero. The default capacity is to the edge of the output raster. | Double; Field |
source_direction (Optional) | Defines the direction of the traveler when applying the source resistance rate and the source starting cost.
Either specify the FROM_SOURCE or TO_SOURCE keyword, which will be applied to all sources, or specify a field in the source data that contains the keywords to identify the direction of travel for each source. That field must contain the strings FROM_SOURCE or TO_SOURCE. | String; Field |
Return Value
| Name | Explanation | Data Type |
| out_allocation_raster | The output cost allocation raster. This raster identifies the zone of each source location (cell or feature) that could be reached with the least accumulative cost. The output raster is of integer type. | Raster |
Code sample
CostAllocation example 1 (Python window)
The following Python window script demonstrates how to use the CostAllocation tool.
import arcpy
from arcpy import env
from arcpy.sa import *
env.workspace = "C:/sapyexamples/data"
out = ()
costAllocOut = CostAllocation("observers.shp", "costraster", "", "elevation",
"FID", "c:/sapyexamples/output/distout",
"c:/sapyexamples/output/backlinkout", "Multiplier", "StartCost", "Resistance", 500000)
costAllocOut.save("c:/sapyexamples/output/costalloc")
CostAllocation example 2 (stand-alone script)
This script uses a cost raster, a feature layer of source points, and several optional parameter to calculate a raster of cells which contain the value of the nearest source.
# Name: CostAllocation_Ex_02.py
# Description: Calculates for each cell its nearest source
# based on the least accumulative cost over a
# cost surface.
# Requirements: Spatial Analyst Extension
# Import system modules
import arcpy
from arcpy import env
from arcpy.sa import *
# Set environment settings
env.workspace = "C:/sapyexamples/data"
# Set local variables
inFeature = "observers.shp"
costRaster = "costraster"
maxDist = ""
valRaster = "elevation"
featField = "FID"
outDistanceRaster = "c:/sapyexamples/output/distout"
outBacklink = "c:/sapyexamples/output/backlinkout"
multiplier = "Multiplier"
startCost = "StartCost"
resistance = "Resistance"
capacity = 500000
# Check out the ArcGIS Spatial Analyst extension license
arcpy.CheckOutExtension("Spatial")
# Execute CostAllocation
costAllocOut = CostAllocation(inFeature, costRaster, maxDist,
valRaster, featField, outDistanceRaster,
outBacklink, multiplier, startCost,
resistance, capacity)
# Save the output
costAllocOut.save("c:/sapyexamples/output/costalloc01")
Environments
Licensing information
- ArcGIS Desktop Basic: Requires Spatial Analyst
- ArcGIS Desktop Standard: Requires Spatial Analyst
- ArcGIS Desktop Advanced: Requires Spatial Analyst