Available with Spatial Analyst license.
Summary
Extracts the cells of a raster based on a logical query.
Illustration
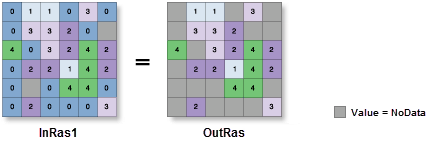
Usage
Additional attributes from the input raster, if any, will be carried over as-is to the output raster attribute table. Depending on the nature of the property being recorded, some of the attribute values may need to be recalculated.
When a multiband raster is specified as the Input Raster (in_raster in Python), all bands will be used.
To process a selection of bands from a multiband raster, first create a new raster dataset composed of those particular bands with the Composite Bands tool, and use the result as the Input Raster (in_raster in Python).
The default output format is a geodatabase raster. If an Esri Grid stack is specified as the output format, note that the name cannot start with a number, use spaces, or be more than nine characters in length.
If the Where clause evaluates to true, the original input value is returned for the cell location. If it evaluates to false, the cell location is assigned NoData.
The Where clause uses an SQL query. See the following topics for more details on creating queries in the Query Builder:
In order to use a {where_clause} in Python, it should be enclosed in quotes. For example, "Value > 5000".
You can consult the help for more information on specifying a query in Python.
If an item other than Value of input raster is specified in the query, the original input value is returned for the cell location.
If the input raster is integer, the output raster will be integer. If the input is floating point, the output will be floating point.
See Analysis environments and Spatial Analyst for additional details on the geoprocessing environments that apply to this tool.
Syntax
ExtractByAttributes (in_raster, where_clause)
| Parameter | Explanation | Data Type |
in_raster | The input raster from which cells will be extracted. | Raster Layer |
where_clause | A logical expression that selects a subset of raster cells. The expression follows the general form of an SQL expression. An example of a where_clause is "VALUE > 100". | SQL Expression |
Return Value
| Name | Explanation | Data Type |
| out_raster | The output raster containing the cell values extracted from the input raster. | Raster |
Code sample
ExtractByAttributes example 1 (Python window)
This example extracts cells from a raster based on a logical query, where elevation is greater than 1,000 meters.
import arcpy
from arcpy import env
from arcpy.sa import *
env.workspace = "C:/sapyexamples/data"
attExtract = ExtractByAttributes("elevation", "VALUE > 1000")
attExtract.save("c:/sapyexamples/output/attextract")
ExtractByAttributes example 2 (stand-alone script)
This example extracts cells from a raster based on a logical query, where elevation is greater than 1,000 meters.
# Name: ExtractByAttributes_Ex_02.py
# Description: Extracts the cells of a raster based on a logical query.
# Requirements: Spatial Analyst Extension
# Import system modules
import arcpy
from arcpy import env
from arcpy.sa import *
# Set environment settings
env.workspace = "C:/sapyexamples/data"
# Set local variables
inRaster = "elevation"
inSQLClause = "VALUE > 1000"
# Check out the ArcGIS Spatial Analyst extension license
arcpy.CheckOutExtension("Spatial")
# Execute ExtractByAttributes
attExtract = ExtractByAttributes(inRaster, inSQLClause)
# Save the output
attExtract.save("c:/sapyexamples/output/attextract02")
Environments
Licensing information
- ArcGIS Desktop Basic: Requires Spatial Analyst
- ArcGIS Desktop Standard: Requires Spatial Analyst
- ArcGIS Desktop Advanced: Requires Spatial Analyst