Available with Spatial Analyst license.
Summary
Determines on a cell-by-cell basis the position of the raster with the maximum value in a set of rasters.
Illustration
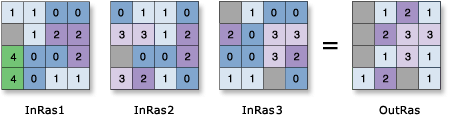
Usage
An arbitrary number of rasters can be specified in the input rasters list.
The order of the input rasters is relevant for this tool.
When a multiband raster is specified as one of the Input rasters or constant values (in_rasters_or_constants in Python), all the bands will be used.
To process a selection of bands from a multiband raster, you can first create a new raster dataset composed of those particular bands with the Composite Bands tool, and use the result in the list of the Input rasters or constant values (in_rasters_or_constants in Python).
If a cell location contains NoData on any of the input rasters, that location will be assigned NoData on the output.
The output raster is always of integer type.
If two or more input rasters contain the maximum value for a particular cell location, the position of the first one is returned on the output raster.
See Analysis environments and Spatial Analyst for additional details on the geoprocessing environments that apply to this tool.
Syntax
HighestPosition (in_rasters_or_constants)
| Parameter | Explanation | Data Type |
in_rasters_or_constants [in_raster_or_constant,...] | The list of input rasters for which the position of the input with the highest value will be determined. A number can be used as an input; however, the cell size and extent must first be set in the environment. | Raster Layer; Constant |
Return Value
| Name | Explanation | Data Type |
| out_raster | The output raster. For each cell in the output raster, the value represents the position of the raster with the highest value. | Raster |
Code sample
HighestPosition example 1 (Python window)
This example evaluates several input rasters and returns as an output value the position in the list of the raster with the maximum value.
import arcpy
from arcpy import env
from arcpy.sa import *
env.workspace = "C:/sapyexamples/data"
outHighestPosition = HighestPosition(["degs", "negs", "fourgrd"])
outHighestPosition.save("C:/sapyexamples/output/outhp.img")
HighestPosition example 2 (stand-alone script)
This example evaluates several input rasters and returns as an output value the position in the list of the raster with the maximum value.
# Name: HighestPosition_Ex_02.py
# Description: Determines the position of a raster with the maximum
# value in a set of rasters
# Requirements: Spatial Analyst Extension
# Import system modules
import arcpy
from arcpy import env
from arcpy.sa import *
# Set environment settings
env.workspace = "C:/sapyexamples/data"
# Set local variables
inRaster01 = "degs"
inRaster02 = "negs"
inRaster03 = "fourgrd"
# Check out the ArcGIS Spatial Analyst extension license
arcpy.CheckOutExtension("Spatial")
# Execute HighestPosition
outHighestPosition = HighestPosition([inRaster01, inRaster02, inRaster03])
# Save the output
outHighestPosition.save("C:/sapyexamples/output/outhp")
Environments
Licensing information
- ArcGIS Desktop Basic: Requires Spatial Analyst
- ArcGIS Desktop Standard: Requires Spatial Analyst
- ArcGIS Desktop Advanced: Requires Spatial Analyst