Available with Spatial Analyst license.
Available with 3D Analyst license.
Summary
Determines the raster surface locations visible to a set of observer features using geodesic methods
Illustration
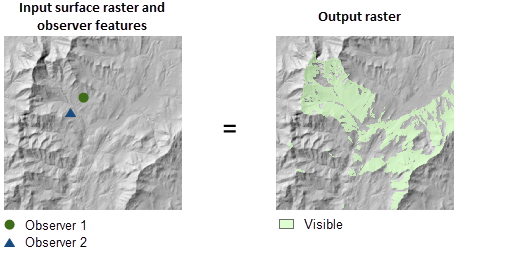
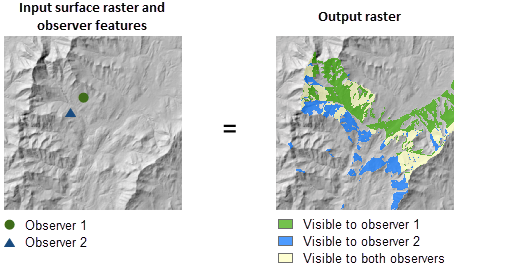
Usage
This tool performs two types of visibility analysis, Frequency and Observers, which can be set using the Analysis type parameter.
To ensure the accuracy of the output, assign a vertical coordinate system to the input raster, if it does not already have one.
Viewshed 2 does not require a z-factor parameter. It will compute a z-factor internally using the vertical (Z) unit and the map (XY) units from the spatial reference of the input raster.
Input rasters that contain noise, most commonly seen in high resolution data, may produce some unexpected results. Before running this tool, you can either correct the data in a pre-processing step, or smooth out the effect of the error by first using the Focal Statistics or the Filter tool before performing the viewshed operation.
When the input raster needs to be resampled, the bilinear technique will be used. An example of when an input raster may be resampled is when the output coordinate system, extent, or cell size is different from that of the input.
To enhance performance, you can explicitly set the Outer radius parameter to a value that represents the maximum viewing distance of interest for your analysis.
By default, the Analysis Method parameter uses the ALL_SIGHTLINES option, which gives the most accurate output. To improve the performance of the tool in terms of processing time, use the PERIMETER_SIGHTLINES option.
The observer parameters related to height, such as Surface offset, Observer elevation and Observer offset, can be specified as a linear unit or as a field. During the calculation, the linear unit value will be converted internally to the Z unit of the input raster. However, if the linear unit is unknown or a numeric field is specified, the value is assumed to be in the Z unit of the input raster.
The observer parameters related to viewing distances, such as the Inner radius and the Outer radius, can be specified as a linear unit or as a field. During the calculation, the linear unit value will be converted internally to the XY units of the input raster. However, if the linear unit is unknown or a numeric field is specified, the value is assumed to be in the XY unit of the input raster.
The field specified for an observer parameter, such as Surface offset or Observer offset, can be string type that contains a numerical value and a unit. For example, if field obs_height is specified for Observer offset, it can contain values like '6 Feet'.
In scripting, the observer parameters like observer_offset can be specified in various forms of strings. In each form, a value and a linear unit is parsed from the string. The following table list some example input strings and how the linear unit is determined for each case. For other parameters, you can follow the same pattern.
Example of input string for Observer offset Linear unit used ' ' or '#'
Default value and unit is used, which is 1 meter.
'6'
The Observer offset is 6 and since no unit is specified, the tool would use the default unit, meter.
'6 Feet'
The Observer offset is 6 Feet.
'6 Unknown'
The Observer offset is 6 and since no unit is specified, the tool would use the default unit, meter.
Examples of input strings and linear units This tool will automatically take advantage of a GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) for enhancing the performance of the tool, if it is available in your system and is configured correctly.
See the GPU processing with Spatial Analyst help topic for more information on how to configure your GPU device.
If you do not want the tool to take advantage of the available GPU devices installed in your system, create a system environment variable CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES, set its value to -1 and restart your application. The tool will then execute using the CPU only. To enable your tool to use a GPU device again, either delete the system environment variable CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES or set the value of this environment variable to the index value (0 for the first one, 1 for the second one and so on) of the GPU device you would like to use, and restart your application.
See Analysis environments and Spatial Analyst for additional details on the geoprocessing environments that apply to this tool.
Syntax
Viewshed2 (in_raster, in_observer_features, {out_agl_raster}, {analysis_type}, {vertical_error}, {out_observer_region_relationship_table}, {refractivity_coefficient}, {surface_offset}, {observer_elevation}, {observer_offset}, {inner_radius}, {inner_radius_is_3d}, {outer_radius}, {outer_radius_is_3d}, {horizontal_start_angle}, {horizontal_end_angle}, {vertical_upper_angle}, {vertical_lower_angle}, {analysis_method})| Parameter | Explanation | Data Type |
in_raster | The input surface raster. It can be an integer or a floating-point raster. The input raster is transformed into a 3D geocentric coordinate system during the visibility calculation. NoData cells on the input raster do not block the visibility determination. | Raster Layer |
in_observer_features | The input feature class that identifies the observer locations. It can be point, multipoint, or polyline features. The input feature class is transformed into a 3D geocentric coordinate system during the visibility calculation. Observers outside of the extent of the surface raster or located on NoData cells will be ignored in the calculation. | Feature Layer |
out_agl_raster (Optional) | The output above ground level (AGL) raster. The AGL result is a raster where each cell value is the minimum height that must be added to an otherwise nonvisible cell to make it visible by at least one observer. Cells that were already visible will be assigned 0 in this output raster. When the vertical error parameter is 0, the output AGL raster is a one-band raster. When vertical error is greater than 0, to account for the random effects from the input raster, the output AGL raster is created as a three-band raster. The first band represents the mean AGL values, the second band represents the minimum AGL values, and the third band represents the maximum AGL values. | Raster Dataset |
analysis_type (Optional) | Choose which type of visibility analysis you wish to perform, either determining how visible each cell is to the observers, or identifying for each surface location which observers are visible.
| String |
vertical_error (Optional) | The amount of uncertainty (the Root Mean Square error, or RMSE) in the surface elevation values. It is a floating-point value representing the expected error of the input elevation values. When this parameter is assigned a value greater than 0, the output visibility raster will be floating point. In this case, each cell value on the output visibility raster represents the sum of probabilities that the cell is visible to any of the observers. When the analysis type is OBSERVERS or the analysis method is PERIMETER_SIGHTLINES, this parameter is disabled. | Linear Unit |
out_observer_region_relationship_table (Optional) | The output table for identifying the regions that are visible to each observer. This table can be related to the input observer feature class and the output visibility raster for identifying the regions visible to given observers. This output is only created when the analysis type is OBSERVERS. | Table |
refractivity_coefficient (Optional) | Coefficient of the refraction of visible light in air. The default value is 0.13. | Double |
surface_offset (Optional) | This value indicates a vertical distance to be added to the z-value of each cell as it is considered for visibility. It should be a positive integer or floating-point value. You can select a field in the input observers dataset, or you can specify a numerical value. If this parameter is set to a value, that value will be applied to all the observers. To specify different values for each observer, set this parameter to a field in the input observer features dataset. The default value is 0. | Linear Unit; Field |
observer_elevation (Optional) | This value is used to define the surface elevations of the observer points or vertices. You can select a field in the input observers dataset, or you can specify a numerical value. If this parameter is not specified, the observer elevation will be obtained from the surface raster using bilinear interpolation. If this parameter is set to a value, that value will be applied to all the observers. To specify different values for each observer, set this parameter to a field in the input observer features dataset. | Linear Unit; Field |
observer_offset (Optional) | This value indicates a vertical distance to be added to the observer elevation. It should be a positive integer or floating-point value. You can select a field in the input observers dataset, or you can specify a numerical value. If this parameter is set to a value, that value will be applied to all the observers. To specify different values for each observer, set this parameter to a field in the input observer features dataset. The default value is 1 meter. | Linear Unit; Field |
inner_radius (Optional) | This value defines the start distance from which visibility is determined. Cells closer than this distance are not visible in the output but can still block visibility of the cells between inner radius and outer radius. You can select a field in the input observers dataset, or you can specify a numerical value. If this parameter is set to a value, that value will be applied to all the observers. To specify different values for each observer, set this parameter to a field in the input observer features dataset. The default value is 0. | Linear Unit; Field |
inner_radius_is_3d (Optional) | Type of distance for the inner radius parameter.
| Boolean |
outer_radius (Optional) | This value defines the maximum distance from which visibility is determined. Cells beyond this distance are excluded from the analysis. You can select a field in the input observers dataset, or you can specify a numerical value. If this parameter is set to a value, that value will be applied to all the observers. To specify different values for each observer, set this parameter to a field in the input observer features dataset. | Linear Unit; Field |
outer_radius_is_3d (Optional) | Type of distance for the outer radius parameter.
| Boolean |
horizontal_start_angle (Optional) | This value defines the start angle of the horizontal scan range. The value should be specified in degrees from 0 to 360, either as integer or floating point, with 0 oriented to north. The default value is 0. You can select a field in the input observers dataset, or you can specify a numerical value. If this parameter is set to a value, that value will be applied to all the observers. To specify different values for each observer, set this parameter to a field in the input observer features dataset. | Double; Field |
horizontal_end_angle (Optional) | This value defines the end angle of the horizontal scan range. The value should be specified in degrees from 0 to 360, either as integer or floating point, with 0 oriented to north. The default value is 360. You can select a field in the input observers dataset, or you can specify a numerical value. If this parameter is set to a value, that value will be applied to all the observers. To specify different values for each observer, set this parameter to a field in the input observer features dataset. | Double; Field |
vertical_upper_angle (Optional) | This value defines the upper vertical angle limit of the scan above a horizontal plane. The value should be specified in degrees from 0 to 90, which can be integer or floating point. If this parameter is set to a value, that value will be applied to all the observers. To specify different values for each observer, set this parameter to a field in the input observer features dataset. The default value is 90. | Double; Field |
vertical_lower_angle (Optional) | This value defines the lower vertical angle limit of the scan below a horizontal plane. The value should be specified in degrees from -90 to 0, which can be integer or floating point. You can select a field in the input observers dataset, or you can specify a numerical value. If this parameter is set to a value, that value will be applied to all the observers. To specify different values for each observer, set this parameter to a field in the input observer features dataset. The default value is -90. | Double; Field |
analysis_method (Optional) | Choose the method by which the visibility will be calculated. This option allows you to trade some accuracy for increased performance.
| String |
Return Value
| Name | Explanation | Data Type |
| out_raster | The output raster. For the FREQUENCY analysis type, when the vertical error parameter is 0 or not specified, the output raster records the number of times that each cell location in the input surface raster can be seen by the input observation points. When the vertical error parameter is greater than 0, each cell on the output raster records the sum of probabilities that the cell is visible to any of the observers. For the OBSERVERS analysis type, the output raster records the unique region IDs for the visible areas, which can be related back to the observer features through the output observer-region relationship table. | Raster |
Code sample
Viewshed2 example 1 (Python window)
This example determines the surface locations visible to a set of observers without using any observer parameters.
import arcpy
from arcpy import env
from arcpy.sa import *
env.workspace = "C:/sapyexamples/data"
outViewshed2 = Viewshed2("elevation", "obser1.shp", "", "OBSERVERS", "",
"C:/sapyexamples/output/obstable01.dbf",
analysis_method="ALL_SIGHTLINES")
outViewshed2.save("C:/sapyexamples/output/outvwshd2_01")
Viewshed2 example 2 (stand-alone script)
This example determines the surface locations visible to a set of observers using attributes in the input feature class as the observer parameters.
# Name: Viewshed2_Ex_02.py
# Description: Determines the raster surface locations visible to a set of
# observer features.
# Requirements: Spatial Analyst Extension
# Import system modules
import arcpy
from arcpy import env
from arcpy.sa import *
# Set environment settings
env.workspace = "C:/sapyexamples/data"
# Check out the ArcGIS Spatial Analyst extension license
arcpy.checkOutExtension("Spatial")
inRaster = "elevation"
inObservers = "obser2.shp"
outAGL = ""
analysisType = "OBSERVERS"
verticalError = ""
outAnalysisRelationTable = "C:/sapyexamples/output/obser_region2.dbf"
refractCoeff = ""
surfaceOffset = "offsetb"
observerElevation = "spot"
observerOffset = "offseta"
innerRadius = "radius1"
innerIs3D = "False"
outerRadius = "radius2"
outerIs3D = "True"
horizStartAngle = "azimuth1"
horizEndAngle = "azimuth2"
vertUpperAngle = "vert1"
vertLowerAngle = "vert2"
analysisMethod = "ALL_SIGHTLINES"
# Execute Viewshed2
outViewshed2 = Viewshed2(inRaster, inObservers, outAGL, analysisType,
verticalError, outAnalysisRelationTable, refractCoeff,
surfaceOffset, observerElevation, observerOffset,
innerRadius, innerIs3D, outerRadius, outerIs3D,
horizStartAngle, horizEndAngle, vertUpperAngle,
vertLowerAngle, analysisMethod)
# Save the output
outViewshed2.save("C:/sapyexamples/output/outvwshd2_02")
Environments
Licensing information
- ArcGIS Desktop Basic: Requires Spatial Analyst or 3D Analyst
- ArcGIS Desktop Standard: Requires Spatial Analyst or 3D Analyst
- ArcGIS Desktop Advanced: Requires Spatial Analyst or 3D Analyst