Available with Spatial Analyst license.
Summary
Calculates the specified geometry measure (area, perimeter, thickness, or the characteristics of ellipse) for each zone in a dataset.
Illustration
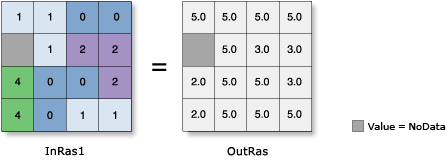
Usage
A zone is defined as all areas in the input that have the same value. The areas do not have to be contiguous. Both raster and feature can be used for the zone input.
If the Input raster or feature zone data (in_zone_data in Python) has overlapping polygons, the zonal analysis will not be performed for each individual polygon. Since the feature input is converted to a raster, each location can only have one value.
An alternative method is to process the zonal operation iteratively for each of the polygon zones and collate the results.
When specifying the Input raster or feature zone data (in_zone_data in Python), the default zone field will be the first available integer or text field. If no other valid fields exist, the ObjectID field (for example, OID or FID) will be the default.
The data type of the output raster for each of the geometry types will be floating point.
If a particular zone consists of only one cell or if the zone is a single square block of cells, the orientation of the ellipse (which, in this case, is a circle) is set to 90 degrees.
See Analysis environments and Spatial Analyst for additional details on the geoprocessing environments that apply to this tool.
Syntax
ZonalGeometry (in_zone_data, zone_field, {geometry_type}, {cell_size})| Parameter | Explanation | Data Type |
in_zone_data | Dataset that defines the zones. The zones can be defined by an integer raster or a feature layer. | Raster Layer; Feature Layer |
zone_field | Field that holds the values that define each zone. It must be an integer field of the zone dataset. | Field |
geometry_type (Optional) | Geometry type to be calculated.
| String |
cell_size (Optional) | The processing cell size for the zonal operation. This is the value in the environment if specifically set. If the environment is not set, the default for the cell size is determined by the type of the zone data as follows:
| Analysis Cell Size |
Return Value
| Name | Explanation | Data Type |
| out_raster | The output zonal geometry raster. | Raster |
Code sample
ZonalGeometry example 1 (Python window)
This example determines the area for each zone defined by the input polygon shape file.
import arcpy
from arcpy import env
from arcpy.sa import *
env.workspace = "C:/sapyexamples/data"
outZonalGeometry = ZonalGeometry("zones.shp", "Classes", "AREA", 0.2)
outZonalGeometry.save("C:/sapyexamples/output/zonegeomout3")
ZonalGeometry example 2 (stand-alone script)
This example determines the area for each zone defined by the input polygon shape file.
# Name: ZonalGeometry_Ex_02.py
# Description:Calculates for each zone in a dataset the specified geometry
# measure (area, perimeter, thickness, or the characteristics
# of ellipse).
# Requirements: Spatial Analyst Extension
# Import system modules
import arcpy
from arcpy import env
from arcpy.sa import *
# Set environment settings
env.workspace = "C:/sapyexamples/data"
# Set local variables
inZoneData = "zones.shp"
zoneField = "Classes"
cellSize = 0.2
# Check out the ArcGIS Spatial Analyst extension license
arcpy.CheckOutExtension("Spatial")
# Execute ZonalStatistics
outZonalGeometry = ZonalGeometry(inZoneData, zoneField, "AREA", cellSize)
# Save the output
outZonalGeometry.save("C:/sapyexamples/output/zonegeomout2")
Environments
Licensing information
- ArcGIS Desktop Basic: Requires Spatial Analyst
- ArcGIS Desktop Standard: Requires Spatial Analyst
- ArcGIS Desktop Advanced: Requires Spatial Analyst