The .esriaddin file is the key to sharing a Python add-in; all that other users need to do to execute the add-in is install the .esriaddin file on their machine or reference it using a network share.
Desktop add-ins are loaded by ArcGIS Desktop applications when the add-in file is discovered in one of several well-known add-in folders. Add-in files can be copied directly to one of these folders or to the appropriate folder automatically using ESRI ArcGIS Add-In Installation Utility.
ArcGIS Add-In Installation Utility
ESRI ArcGIS Add-In Installation Utility opens when an .esriaddin file is double-clicked. This utility is operational in Windows Explorer, through popular e-mail applications such as Outlook, and on web pages running on servers that have been configured to deploy add-in files (such as ArcGIS Online).
When ESRI ArcGIS Add-In Installation Utility is invoked, it analyzes the metadata of the selected add-in file and displays the author's name, a description of the add-in, and whether the add-in contains a trusted digital signature. See the following illustration:
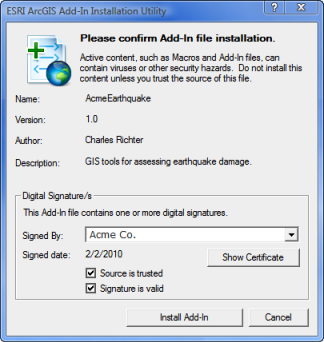
This information can be used to decide whether to install the add-in. If the user elects to install the add-in, the utility copies the add-in to the user's default add-in folder.
Add-ins are not backward compatible. Add-ins targeting 10.1, for example, will not work with 10.0 but will work with 10.2.
The installation utility copies the add-in file to a generated subfolder under the well-known add-in folder; the subfolder is automatically generated based on the globally unique identifier (GUID) specified in the add-in file metadata. This subfolder prevents file naming conflicts that might otherwise occur if several add-ins have the same file name.
Although add-ins can be manually copied to a default add-in folder, doing so bypasses the security and name conflict checks the add-in installation utility performs. For this reason, use the installation utility to install an add-in in ArcGIS Desktop applications.
Sharing add-ins on a network
Add-ins can also be distributed within a private network using a trusted network share. Add-in files can be copied to these locations and automatically picked up by clients who've added the network share to their add-in folder list. Additional add-in folders are added using Add-In Manager, as illustrated below.
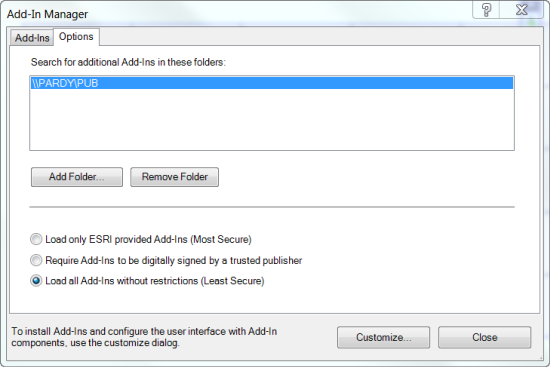
In this scenario, multiple users can benefit from add-ins managed in a central location. If an add-in needs an update, the newer version can be copied over the existing version (even if in use). Clients automatically get the updated version of the add-in the next time they restart the corresponding desktop application.
Determining add-in customizations
Once an add-in has been installed, Add-In Manager—accessed from the Customize menu—makes it easy to determine the customizations it contains. The following illustration shows an add-in with a toolbar and a tool:
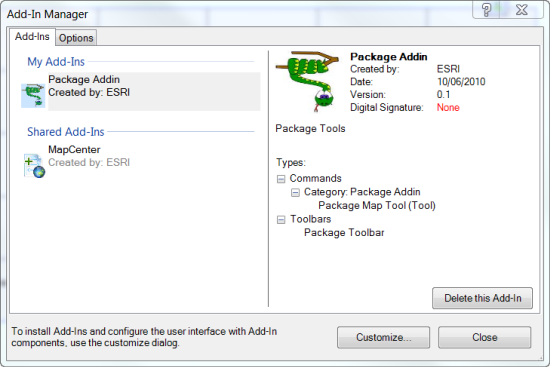
Uninstalling the add-in
You can uninstall the add-in just by deleting the .esriaddin file from the add-in folder. Alternatively, you can use the Delete this Add-In on Add-In Manager dialog to uninstall the add-in.