When working with lidar data in ArcGIS, there are several different configurations for managing and working with your data, depending on what you're doing. Some needs require specific data formats. For example, if you're editing LAS file classifications, then you'll use the LAS dataset; or to do analysis on massive collections of multipoint data that needs to be thinned, you'll use a terrain dataset; or if you're looking to manage all your collections, you'll use a mosaic dataset. The information below will help guide you in choosing the format that's appropriate for your needs and to show you how each works together.
Performing analysis in a 3D environment (using the ArcGIS 3D Analyst extension)
To analyze your lidar data you will add your LAS files to a LAS dataset or convert them to multipoint feature classes and add them to a terrain dataset. Both the LAS dataset and terrain dataset support surface constraints.
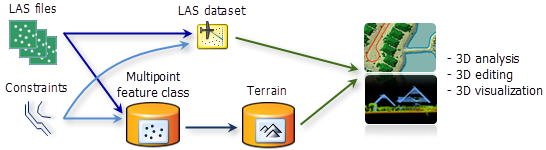
The LAS dataset is rendered as a surface of points or as a triangulated surface, whereas the terrain dataset is rendered as a triangulated surface. The terrain dataset offers z tolerance thinning, which can be used to conduct analysis on thinned representations of the surface data.
The tools and how you analyze the lidar data also depends on the licensing and extensions you have for ArcGIS. The LAS dataset allows you to build and analyze LAS files with ArcGIS Desktop Standard or Desktop Advanced. With the addition of the 3D Analyst extension you can build and analyze terrain datasets. This extension also provides additional analysis tools using ArcMap and ArcScene.
Learn more about the licensing requirements
Toolbars in ArcMap and ArcScene that provide tools to visualize and analyze data
| Application | Terrain dataset | LAS dataset |
|---|---|---|
ArcMap | 3D Analyst toolbar
| |
(not applicable) | LAS dataset toolbar
| |
ArcScene | 3D Analyst toolbar
| |
(not applicable) | LAS dataset toolbar
| |
There are several geoprocessing tools that work with both datasets, such as the Interpolate Shape tool and Line Of Sight tool. Currently, there are more of these analyzing tools for terrain datasets.
Performing raster analysis (using the ArcGIS Spatial Analyst extension or raster tools)
When using lidar data for analysis with tools that require a raster input, it is recommended that you use the mosaic dataset, rather than creating a raster dataset. A raster dataset requires you to write the entire raster dataset to disk, whereas a mosaic dataset only references the source files (such as the LAS dataset), thereby taking up much less space and being much faster to create. You can also modify the surface type in a mosaic dataset (such as bare earth or first return); however, a raster dataset can only be stored using one surface type that cannot be altered. Therefore, the mosaic dataset is much more versatile.
To create a mosaic dataset from LAS files you can add them directly, or if you need to apply constraints, you can create a LAS dataset or terrain dataset and add them to the mosaic dataset.
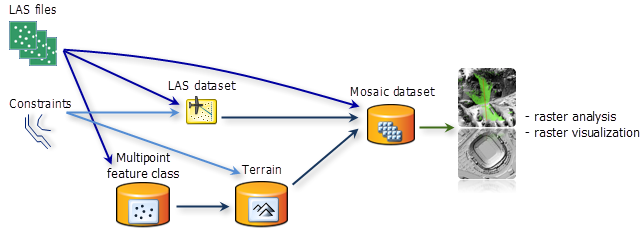
Managing multiple lidar collections
Often, lidar data is only used on a per-project basis and can be stored away in an organized or haphazard fashion. One way to catalog all your lidar collections and make them available is by using a mosaic dataset. In a mosaic dataset you can always view the footprints of every collection and even view the surface generated from them according to the surface type information you choose. Additionally, you can query the data held in a mosaic dataset to identify specific datasets you may want to work with, by information such as location and date.
To create a raster surface containing many formats
When you need to create a raster surface (representation) that contains multiple data sources you should create a mosaic dataset. A mosaic dataset can contain multiple raster datasets, LAS files, LAS datasets, and terrains. The mosaicked image will be generated using any of the surfaces to display a seamless, single dataset.
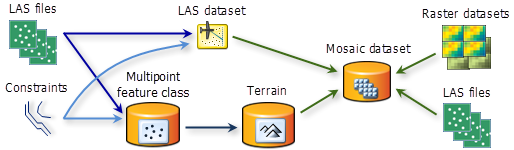
You can add LAS files directly, but if you need to enforce surface constraints you need to create LAS dataset (or terrain dataset), then add the dataset to the mosaic dataset.
To share as a service
In order to share lidar data using ArcGIS Server you can publish it as an image service. This means you must add the data to a mosaic dataset and publish the mosaic dataset as an image service. Alternatively, you could produce a single raster dataset and publish it as an image service.

When shared as an image service, users will view and access the data as an image; however, the image service can be set up to provide direct access to the source files using the download option. When a mosaic dataset is shared as an image service, users can make selections of the datasets in the image service and download the source LAS or raster dataset files to disk.