There are two basic types of lidar: airborne and terrestrial.
Airborne
With airborne lidar, the system is installed in either a fixed-wing aircraft or helicopter. The infrared laser light is emitted toward the ground and returned to the moving airborne lidar sensor. There are two types of airborne sensors: topographic and bathymetric.
Topographic lidar
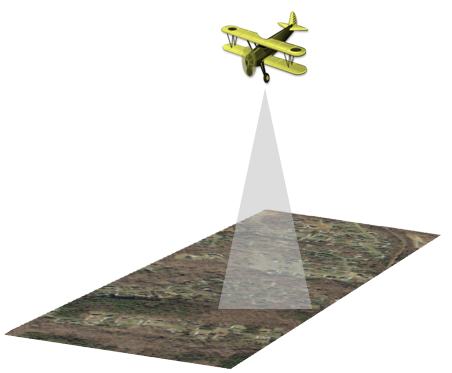
Topographic lidar can be used to derive surface models for use in many applications, such as forestry, hydrology, geomorphology, urban planning, landscape ecology, coastal engineering, survey assessments, and volumetric calculations.
Bathymetric lidar
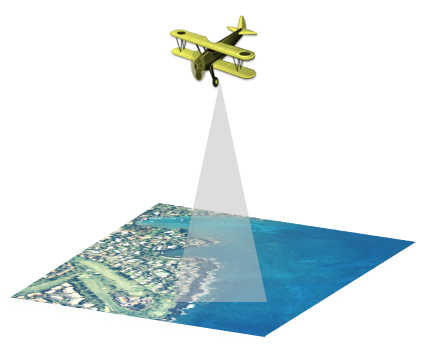
Bathymetric lidar is a type of airborne acquisition that is water penetrating. Most bathymetric lidar systems collect elevation and water depth simultaneously, which provides an airborne lidar survey of the land-water interface. With a bathymetric lidar survey, the infrared light (traditional laser system) is reflected back to the aircraft from the land and water surface, while the additional green laser travels through the water column. Analyses of the two distinct pulses are used to establish water depths and shoreline elevations. Bathymetric information is very important near coastlines, in harbors, and near shores and banks. Bathymetric information is also used to locate objects on the ocean floor.
Terrestrial lidar
There are two main types of terrestrial lidar: mobile and static. In the case of mobile acquisition, the lidar system is mounted on a moving vehicle. In the case of static acquisition, the lidar system is typically mounted on a tripod or stationary device. Both lidar sensors consist of eye-safe lasers.
Terrestrial lidar collects very dense and highly accurate points, which allows precise identification of objects. These dense point clouds can be used to manage facilities, conduct highway and rail surveys, and even create 3D city models for exterior and interior spaces, to name a few examples.
Mobile
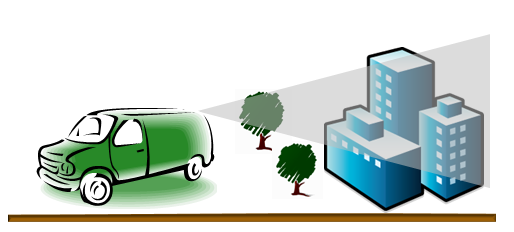
Mobile lidar is the collection of lidar point clouds from a moving platform. Mobile lidar systems can include any number of lidar sensors mounted on a moving vehicle. These systems can be mounted on vehicles, trains, and even boats. Mobile systems typically consist of a lidar sensor, cameras, GPS (Global Positioning System), and an INS (inertial navigation system), just as with airborne lidar systems.
Mobile lidar data can be used to analyze road infrastructure and locate encroaching overhead wires, light poles, and road signs near roadways or rail lines.
Static
Static lidar is the collection of lidar point clouds from a static location. Typically, the lidar sensor is mounted on a tripod mount and is a fully portable, laser-based ranging and imaging system. These systems can collect lidar point clouds inside buildings as well as exteriors. Common applications for this type of lidar are engineering, mining, surveying, and archaeology.