Available with 3D Analyst license.
To add polygons to an editable TIN, use the Add TIN Polygon interactive tool  from the TIN Editing toolbar.
from the TIN Editing toolbar.
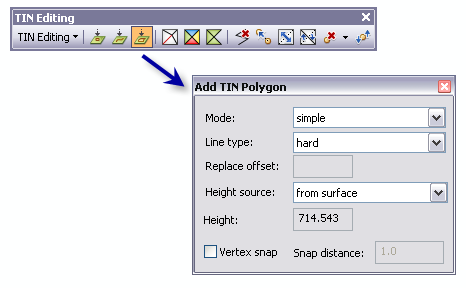
When the tool is clicked, the Add TIN Polygon dialog window appears, allowing you to specify properties for a polygon. These properties include the Mode, Line type, Replace offset, Height source, Height, and Vertex snap.
A single click will enter each vertex, then double-click to finish entering the polygon.
To add a polygon to a TIN interactively, follow the steps outlined below.
- Click the TIN Editing drop-down menu and click Start Editing TIN.
- Click the Add TIN Polygon tool from the TIN Editing toolbar. The Add TIN Polygon dialog box appears.
- Set the desired properties for the polygon to be created on the TIN surface in the Add TIN Polygon dialog box.
Mode—The type of polygon to be created. Choose from either replace, erase, clip, or simple.
Polygon type Description replace
Replace polygons set the boundary and all interior heights to the same value. A replace polygon could be used to model a lake or an area on a slope excavated to a level surface.
erase
Erase polygons define a boundary for interpolation. Input data that falls within the erase polygon is excluded from the interpolation and analysis operations.
clip
Clip polygons define a boundary for the TIN surface. Input data that falls outside the clip polygon is excluded from the interpolation and analysis operations.
simple
Adds a new polygon to the TIN.
Line type—The line type to use when adding the polygon can either be set to soft or hard. Hard breaklines represent a discontinuity in the slope of the surface. Soft breaklines allow you to add edges to a TIN to capture linear features that do not alter the local slope of a surface.
Replace offset— When the Replace Mode is used to add a polygon, the polygon you digitize will be added as a breakline, obtaining its heights from the surface. This polygon is used to hold the terrain along that boundary in place. The polygon is then buffered by the replace offset and inserted using the replace height. Therefore, there are two polygons created. The outer polygon always lies on the surface, while the inner polygon has a specified height value.
Height source—The height source to be used to generate the polygon on the TIN surface. Choose either from surface, max z on surface, min z on surface, or as specified.
Height source Description from surface The elevation of the digitized polygon is interpolated from the selected locations on the surface.
max z on surface The elevation of the digitized polygon is interpolated from the maximum height value that is encountered on the surface.
min z on surface The elevation of the digitized polygon is interpolated from the minimum height value that is encountered on the surface.
as specified The elevation of the digitized polygon is added to the surface at a constant specified elevation value set in the height field.
Height—Shows the elevation of the surface interactively while moving the cursor over the surface.
When as specified is set as the Height source, the elevation value is taken from the height added to the Height source window.
Vertex snap—If selected, the digitized polygon selection locations will snap to the closest node with a specified snap distance. Click to turn vertex snapping on/off.
Snap distance—The snap distance is the distance to use for vertex snapping. While adding the digitized points to the surface you will see a highlighted node to snap the selection point with. If you do not see a highlighted point on the TIN surface, then the closest node is farther away than the specified snap distance and no snapping occurs. Snap units are xy units of the TIN.
- Select the location on the TIN surface where the polygon will start; the first vertex is digitized on the surface. Continue to add each vertex to the polygon by a single click in the desired locations. Double-click to finish entering a new polygon.