In addition to data sources, such as a shapefile, you can add tabular data that contains geographic locations in the form of x,y coordinates to your map. If the table also contains z-coordinates, such as elevation values, you can add tabular data as 3D content into your globe or scene.
X,Y coordinates describe points on the earth's surface such as the location of fire hydrants in a city or the points where water samples were collected. You can easily collect x,y coordinate data using a GPS (also, frequently an elevation [z]-value).
To add a table of x,y coordinates to your map, globe, or scene, the table must contain two fields: one for the x-coordinate and one for the y-coordinate. The values in the fields may represent any coordinate system and units such as latitude and longitude or meters. A field for the z-coordinates that enables 3D geometry is optional.
The fields must be numeric. If the fields are not numeric, such as when the coordinate value is stored in degrees, minutes, and seconds (for example, -120 13 58), the coordinates will be converted and displayed as decimal degrees.
Once you have added the data to your map, globe, or scene, it becomes an x,y event layer and behaves like other point feature layers. For instance, you can decide whether you want to display it, symbolize it, set the visible scale, or display a subset of features that meet some criteria. In 3D, you can also change properties such as the layer's vertical exaggeration or its offset from an elevation surface.
Steps for adding x,y data as a layer
- Click File > Add Data > Add XY Data.
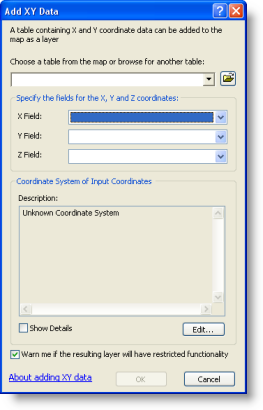
- Select the table that contains x,y coordinate data.
- Identify the columns that hold the x- and y-coordinates (and, optionally, the z-coordinate).
- Specify the coordinate system.
You can also add x,y data in tables as a new feature class using geoprocessing.
X,Y event layers and ObjectID fields
If the table on which an x,y event layer is based does not have an ObjectID field, you won't be able to perform certain tasks on the layer. Delimited text files or tables from OLE DB connections are some examples of tables without ObjectID fields.
Without an ObjectID field, you will not be able to do the following:
- Select features in the map layer.
- Perform operations that utilize the selection set such as navigating from the table to the map.
- Edit layer attributes. However, you can edit the table the layer is based on directly on disk such as in a text editor if the file is a .txt file—including changing the x-, y-, and z-coordinates of the point features. Your changes will be reflected the next time you refresh the view.
Note that you can start an edit session on an x,y event layer if the table it is based on has an ObjectID field and if the data source is editable. This will let you edit the layer's attributes in the table window—including editing the x-, y-, and z-coordinate fields manually to change the location of the points in the layer.
- Perform any interactive edits, such as select points in an edit session and move them around, delete them, and add new points, on any x,y event layer. This is true whether or not the table it is based on has an ObjectID field.
- Define a relate.
If you want to be able to perform these tasks, you can export the x,y layer to a feature class using the steps below or follow the steps above to use the Catalog window to create a feature class from an x,y table. Both of these procedures create a fully functional feature class with an ObjectID field.
Saving an x,y layer as a feature class
You can save the contents of an x,y layer as a feature class using the following steps:
- Right-click the x,y layer name and click Data > Export Data. The Export Data dialog box opens.
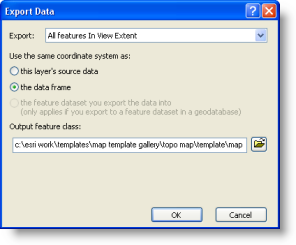
- Set the output coordinate system and specify the location and name of the new feature class.
- Click OK to save the new feature class.