Summary
Exports the nodes of a triangulated irregular network (TIN) dataset to a point feature class.
Illustration
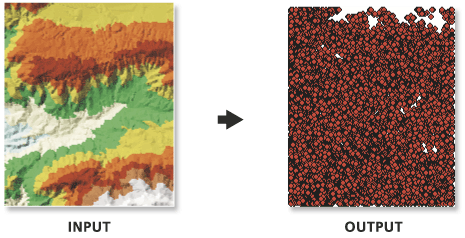
Usage
Populating a name for the Spot Field parameter results in the creation of 2D point feature class. Omitting the name creates 3D points.
- If the TIN has tag values assigned to its triangles, the points can be attributed with these values by specifying a name in the Tag Value Field parameter. Any nodes that do not have explicitly assigned tag values will assume a value of 0.
Syntax
TinNode(in_tin, out_feature_class, {spot_field}, {tag_field})| Parameter | Explanation | Data Type |
in_tin | The TIN dataset to process. | TIN Layer |
out_feature_class | The feature class that will be produced by this tool. | Feature Class |
spot_field (Optional) | The name of the elevation attribute field of the output feature class. If a name is given, the feature class will be 2D; otherwise, it will be 3D. No name is provided by default, which results in the creation of 3D point features. | String |
tag_field (Optional) | The name of the field storing the tag attribute in the output feature class. By default, no tag value field is created. | String |
Code sample
TinNode example 1 (Python window)
The following sample demonstrates the use of this tool in the Python window.
import arcpy
from arcpy import env
arcpy.CheckOutExtension('3D')
env.workspace = 'C:/data'
arcpy.TinNode_3d('tin', 'elevation_node.shp', '', 'Tag_Value')
TinNode example 2 (stand-alone script)
The following sample demonstrates the use of this tool in a stand-alone Python script.
"""****************************************************************************
Name: Create Terrain from TIN
Description: This script demonstrates how to create a terrain dataset using
features extracted from a TIN. It is particularly useful in
situations where the source data used in the TIN is not available,
and the amount of data stored in the TIN proves to be too large
for the TIN. The terrain's scalability will allow improved
display performance and faster analysis. The script is designed
to work as a script tool with 5 input arguments.
****************************************************************************"""
# Import system modules
import arcpy
import exceptions, sys, traceback
from arcpy import env
# Set local variables
tin = arcpy.GetParameterAsText(0) # TIN used to create terrain
gdbLocation = arcpy.GetParameterAsText(1) # Folder that will store terran GDB
gdbName = arcpy.GetParameterAsText(2) # Name of terrain GDB
fdName = arcpy.GetParameterAsText(3) # Name of feature dataset
terrainName = arcpy.GetParameterAsText(4) # Name of terrain
try:
arcpy.CheckOutExtension("3D")
# Create the file gdb that will store the feature dataset
arcpy.management.CreateFileGDB(gdbLocation, gdbName)
gdb = '{0}/{1}'.format(gdbLocation, gdbName)
# Obtain spatial reference from TIN
SR = arcpy.Describe(tin).spatialReference
# Create the feature dataset that will store the terrain
arcpy.management.CreateFeatureDataset(gdb, fdName, SR)
fd = '{0}/{1}'.format(gdb, fdName)
# Export TIN elements to feature classes for terrain
arcpy.AddMessage("Exporting TIN footprint to define terrain boundary...")
boundary = "{0}/boundary".format(fd)
# Execute TinDomain
arcpy.ddd.TinDomain(tin, tinDomain, 'POLYGON')
arcpy.AddMessage("Exporting TIN breaklines...")
breaklines = "{0}/breaklines".format(fd)
# Execute TinLine
arcpy.ddd.TinLine(tin, breaklines, "Code")
arcpy.AddMessage("Exporting TIN nodes...")
masspoints = "{0}/masspoints".format(fd)
# Execute TinNode
arcpy.ddd.TinNode(sourceTIN, TIN_nodes)
arcpy.AddMessage("Creating terrain dataset...")
terrain = "terrain_from_tin"
# Execute CreateTerrain
arcpy.ddd.CreateTerrain(fd, terrainName, 10, 50000, "",
"WINDOWSIZE", "ZMEAN", "NONE", 1)
arcpy.AddMessage("Adding terrain pyramid levels...")
terrain = "{0}/{1}".format(fd, terrainName)
pyramids = ["20 5000", "25 10000", "35 25000", "50 50000"]
# Execute AddTerrainPyramidLevel
arcpy.ddd.AddTerrainPyramidLevel(terrain, "", pyramids)
arcpy.AddMessage("Adding features to terrain...")
inFeatures = "{0} Shape softclip 1 0 10 true false boundary_embed <None> "\
"false; {1} Shape masspoints 1 0 50 true false points_embed "\
"<None> false; {2} Shape softline 1 0 25 false false lines_embed "\
"<None> false".format(boundary, masspoints, breaklines)
# Execute AddFeatureClassToTerrain
arcpy.ddd.AddFeatureClassToTerrain(terrain, inFeatures)
arcpy.AddMessage("Building terrain...")
# Execute BuildTerrain
arcpy.ddd.BuildTerrain(terrain, "NO_UPDATE_EXTENT")
arcpy.GetMessages()
except arcpy.ExecuteError:
print arcpy.GetMessages()
except:
# Get the traceback object
tb = sys.exc_info()[2]
tbinfo = traceback.format_tb(tb)[0]
# Concatenate error information into message string
pymsg = "PYTHON ERRORS:\nTraceback info:\n{0}\nError Info:\n{1}"\
.format(tbinfo, str(sys.exc_info()[1]))
msgs = "ArcPy ERRORS:\n {0}\n".format(arcpy.GetMessages(2))
# Return python error messages for script tool or Python Window
arcpy.AddError(pymsg)
arcpy.AddError(msgs)
finally:
arcpy.CheckInExtension("3D")
Environments
Licensing information
- Basic: Requires 3D Analyst
- Standard: Requires 3D Analyst
- Advanced: Requires 3D Analyst