Summary
Interpolates a raster using z-values from the input TIN.
Illustration
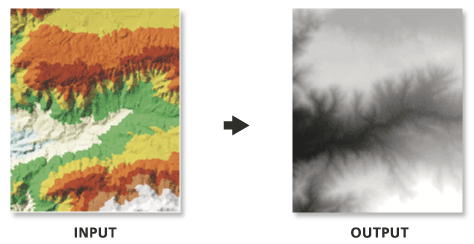
Usage
Because interpolation of the input TIN surface occurs at regular intervals, some loss of information in the output raster should be expected. How well the raster represents the TIN is dependent on the resolution of the raster and the degree and interval of TIN surface variation. Generally, as the resolution is increased, the output raster more closely represents the TIN surface. Because the raster is a cell structure, it cannot maintain the hard and soft breakline edges that may be present in the TIN.
-
When exporting a large raster, consider specifying the Output Data Type as an integer to save disk space if the accuracy requirements of your z-values are such that they can be represented by integer data.
Syntax
TinRaster(in_tin, out_raster, {data_type}, {method}, {sample_distance}, {z_factor})| Parameter | Explanation | Data Type |
in_tin | The TIN dataset to process. | TIN Layer |
out_raster | The location and name of the output raster. When storing a raster dataset in a geodatabase or in a folder such as an Esri Grid, no file extension should be added to the name of the raster dataset. A file extension can be provided to define the raster's format when storing it in a folder, such as .tif to generate a GeoTIFF or .img to generate an ERDAS IMAGINE format file. If the raster is stored as a TIFF file or in a geodatabase, its raster compression type and quality can be specified using geoprocessing environment settings. | Raster Dataset |
data_type (Optional) | Specifies the type of numeric values stored in the output raster.
| String |
method (Optional) | The interpolation method used to create the raster.
| String |
sample_distance sampling_method distance (Optional) | The sampling method and distance used to define the cell size of the output raster. | String |
z_factor (Optional) | The factor by which z-values will be multiplied. This is typically used to convert Z linear units to match XY linear units. The default is 1, which leaves elevation values unchanged. This parameter is disabled if the spatial reference of the input surface has a Z datum with a specified linear unit. | Double |
Code sample
TinRaster example 1 (Python window)
The following sample demonstrates the use of this tool in the Python window.
import arcpy
from arcpy import env
arcpy.CheckOutExtension("3D")
env.workspace = "C:/data"
arcpy.TinRaster_3d("tin", "raster.img", "INT", "LINEAR", "OBSERVATIONS 250", 1)
TinRaster example 2 (stand-alone script)
The following sample demonstrates the use of this tool in a stand-alone Python script.
'''******************************************************************
Name: TinRaster Example
Description: This script demonstrates how to use the
TinRaster tool to create rasters from
each TIN in the target workspace.
******************************************************************'''
# Import system modules
import arcpy
from arcpy import env
import exceptions, sys, traceback
try:
arcpy.CheckOutExtension("3D")
# Set environment setting
env.workspace = "C:/data"
# Set Local Variables
dataType = "INT"
method = "NATURAL_NEIGHBORS"
sampling = "CELLSIZE 10"
zfactor = "1"
# Create list of TINs
TINList = arcpy.ListDatasets("*", "Tin")
# Verify the presence of TINs in the list
if TINList:
# Iterate through the list of TINs
for dataset in TINList:
# Define the name of the output file
outRaster = "{0}_natural.img".format(dataset)
# Execute TinRaster
arcpy.ddd.TinRaster(dataset, outRaster, dataType,
method, sampling, zfactor)
print "Finished."
else:
print "There are no TIN(s) in {0}.".format(env.workspace)
arcpy.CheckInExtension("3D")
except arcpy.ExecuteError:
print arcpy.GetMessages()
except:
# Get the traceback object
tb = sys.exc_info()[2]
tbinfo = traceback.format_tb(tb)[0]
# Concatenate error information into message string
pymsg = 'PYTHON ERRORS:\nTraceback info:\n{0}\nError Info:\n{1}'\
.format(tbinfo, str(sys.exc_info()[1]))
msgs = 'ArcPy ERRORS:\n {0}\n'.format(arcpy.GetMessages(2))
# Return python error messages for script tool or Python Window
arcpy.AddError(pymsg)
arcpy.AddError(msgs)
Environments
Licensing information
- Basic: Requires 3D Analyst
- Standard: Requires 3D Analyst
- Advanced: Requires 3D Analyst