Summary
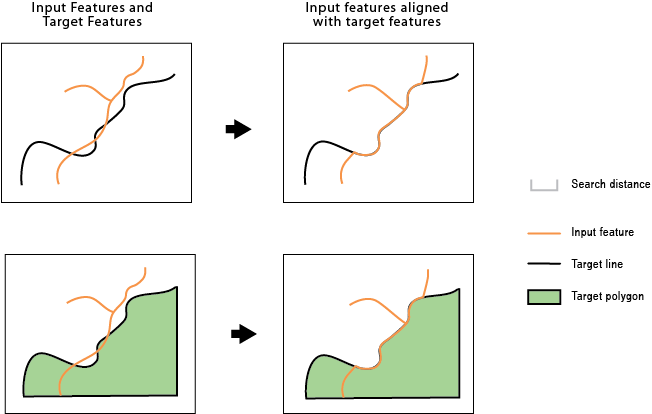
Identifies inconsistent portions of the input features against target features within a search distance and aligns them with the target features.
Illustration
Usage
The input features and target features can be line or polygon features. For example, you may have a county boundary as a line or a polygon, but a portion of it differs from the river centerline that is the border between it and the neighboring county. This tool can be used to align that portion of the county boundary with the river centerline so they are coincident.
An input feature or a portion of it becomes an alignment candidate when it is within the specified Search Distance to the target feature. The candidate shape has to be similar to the target shape; for example, an input road feature and a target road feature running in parallel are more similar than the two features crossing each other in a 90 degree angle.
If specified, Match Fields is used to determine if the alignment candidates are more likely the correct matching features to their targets. For example, if two input features are found within the search distance to a target feature and they both are similar in shape to the target, the one with a matching field value will be a stronger candidate.
The alignment preserves existing topological relationships among the input features. For example, if a line, with its endpoints connected with other lines, is moved due to the alignment, the endpoints of all the connecting lines are moved so that the lines remain connected.
A new field, AF_CONF, is added to the modified input. This field stores a value greater than 0 up to a maximum of 100, indicating the confidence level of the alignment for each feature. A value of 100 means no ambiguity in the candidate for the alignment. The value will decrease due to multiple potential candidates found, greater differences in shape, or unmatched attributes when Match Fields is specified. A value of -1 is given to unmodified features. Due to the possible complexity of the input and target features, unexpected alignment may occur; therefore, post inspection may be necessary, especially on features with relatively low AF_CONF values.
Syntax
AlignFeatures(in_features, target_features, search_distance, {match_fields})| Parameter | Explanation | Data Type |
in_features | Input line or polygon features to be adjusted. | Feature Layer |
target_features | Input lines or polygons as target features. | Feature Layer |
search_distance | The distance used to search for match candidates. A distance must be specified and it must be greater than zero. You can choose a preferred unit; the default is the feature unit. | Linear unit |
match_fields [[source_field, target_field],...] (Optional) | Fields from input and target features. If specified, each pair of fields are checked for match candidates to help determine the right match. | Value Table |
Derived Output
| Name | Explanation | Data Type |
| out_feature_class | The updated input features. | Feature Layer |
Code sample
AlignFeatures example 1 (Python window)
The following Python window script demonstrates how to use the AlignFeatures function in immediate mode.
import arcpy
arcpy.env.workspace = "C:/data/Countries.gdb"
arcpy.AlignFeatures_edit("countryA_border", "target_border", "25 Feet")
AlignFeatures example 2 (stand-alone script)
The following stand-alone script is an example of how to apply the AlignFeatures function in a scripting environment.
import arcpy
import os
# all input data are in country.gdb and output will also go to this gdb
arcpy.env.workspace = os.path.join(os.getcwd(), "country.gdb")
try:
in_features_orig = "common_border"
in_features_copy = "common_border1"
# Make a copy of the original data
arcpy.CopyFeatures_management(in_features_orig, in_features_copy)
# Features to which input will be aligned
target_features = "country1_border"
search_dist = "100 Meters"
match_fields = "A_field B_field"
arcpy.AlignFeatures_edit(in_features_copy, target_features, search_dist, match_fields)
except arcpy.ExecuteError as aex:
print(arcpy.GetMessages(2))
except Exception as ex:
print(ex.args[0])
Environments
Licensing information
- Basic: No
- Standard: No
- Advanced: Yes