 |
This document is archived and information here might be outdated. Recommended version. |
 |
This document is archived and information here might be outdated. Recommended version. |
| ArcObjects Help for .NET developers > ArcObjects namespaces > Geometry > ESRI.ArcGIS.Geometry > Interfaces > IE > IEnvelope Interface > IEnvelope.Expand Method (ArcObjects .NET 10.5 SDK) |
Moves the X and Y coordinates of the sides toward or away from each other.
[Visual Basic .NET] Public Sub Expand ( _ ByVal dx As Double, _ ByVal dy As Double, _ ByVal asRatio As Boolean _ )
[C#] public void Expand ( double dx, double dy, bool asRatio );
[C++]
HRESULT Expand(
double dx,
double dy,
VARIANT_BOOL asRatio
);
[C++]
Parameters dx dx is a parameter of type double dy dy is a parameter of type double asRatio asRatio is a parameter of type VARIANT_BOOL
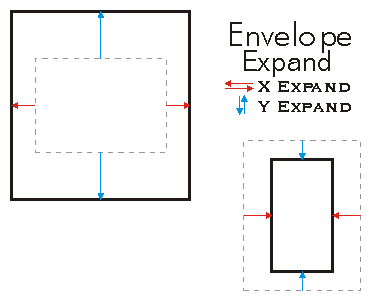
Expand scales the size of the Envelope. If asRatio=FALSE, the expansion is additive.
XMin=XMin - dx
YMin=YMin - dy
XMax=XMax + dx
YMax=YMax + dy
If asRatio=TRUE, the expansion is multiplicative. If the user wants to increase the envelope width by 10%, then dx=1.1. On the other hand, if the user intends to decrease the width by 10%, then dx=0.9. No negative number allowed when asRation is set to TRUE.
XMin=XMin - (dx-1)*Width/2
YMin=YMin - (dy-1)*Height/2
XMax=XMax + (dx-1)*Width/2
YMax=YMax + (dy-1)*Height/2
The Envelope remains centered at the same position.
// The example shows how to expand the Envelope by using a asRatio factor.
private void Expand()
{
IEnvelope envelope=new EnvelopeClass();
envelope.PutCoords(100, 100, 200, 200);
String report1="Envelope before expanding: \n" +
"LowerLeft X=" + envelope.LowerLeft.X + "\n" +
"LowerLeft Y=" + envelope.LowerLeft.Y + "\n\n" +
"LowerRight X = " + envelope.LowerRight.X + "\n" +
"LowerRight Y = " + envelope.LowerRight.Y + "\n\n" +
"UpperLeft X=" + envelope.UpperLeft.X + "\n" +
"UpperLeft Y=" + envelope.UpperLeft.Y + "\n\n" +
"UpperRight X = " + envelope.UpperRight.X + "\n" +
"UpperRight Y = " + envelope.UpperRight.Y;
System.Windows.Forms.MessageBox.Show(report1);
//expand
envelope.Expand(0.5, 0.5, true);
String report2="Envelope after expanding: \n" +
"LowerLeft X=" + envelope.LowerLeft.X + "\n" +
"LowerLeft Y=" + envelope.LowerLeft.Y + "\n\n" +
"LowerRight X = " + envelope.LowerRight.X + "\n" +
"LowerRight Y = " + envelope.LowerRight.Y + "\n\n" +
"UpperLeft X=" + envelope.UpperLeft.X + "\n" +
"UpperLeft Y=" + envelope.UpperLeft.Y + "\n\n" +
"UpperRight X = " + envelope.UpperRight.X + "\n" +
"UpperRight Y = " + envelope.UpperRight.Y;
System.Windows.Forms.MessageBox.Show(report2);
}
' The example shows how to expand the Envelope pEnv1 by using a
' asRatio factor. In this case the target Envelope is 50% of the
' original size.
Public Sub t_EnvExpand()
Dim pEnv1 As IEnvelope
pEnv1=New Envelope
pEnv1.PutCoords(100, 100, 200, 200)
pEnv1.Expand(0.5, 0.5, True)
Dim dXmin As Double, dYmin As Double, dXmax As Double, dYmax As Double
pEnv1.QueryCoords(dXmin, dYmin, dXmax, dYmax)
If pEnv1.IsEmpty Then
MsgBox("envelope is empty")
Else
MsgBox(dXmin & "," & dYmin & "," & dXmax & "," & dYmax)
End If
End Sub
IEnvelope Interface | IEnvelope.Union Method | IEnvelope.Offset Method | IEnvelope.Intersect Method | IEnvelope.CenterAt Method