 |
This document is archived and information here might be outdated. Recommended version. |
 |
This document is archived and information here might be outdated. Recommended version. |
| ArcObjects Help for .NET developers > ArcObjects namespaces > Geometry > ESRI.ArcGIS.Geometry > Interfaces > IT > ITopologicalOperator Interface > ITopologicalOperator.Buffer Method (ArcObjects .NET 10.5 SDK) |
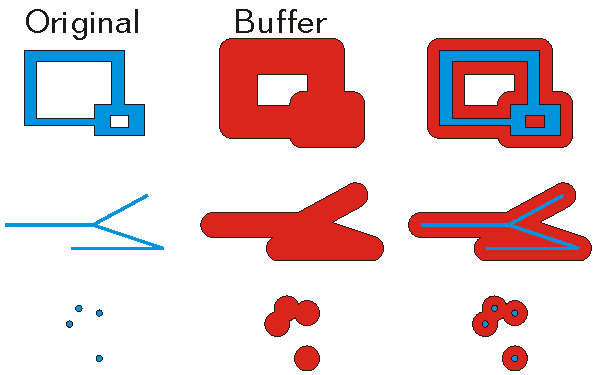
Constructs a polygon that is the locus of points at a distance less than or equal to a specified distance from this geometry.
[Visual Basic .NET] Public Function Buffer ( _ ByVal distance As Double _ ) As IGeometry
[C#] public IGeometry Buffer ( double distance );
[C++]
HRESULT Buffer(
double distance,
IGeometry** outBuffer
);
[C++]
Parameters distance distance is a parameter of type double outBuffer [out, retval]
outBuffer is a parameter of type IGeometry
The buffer distance is in the same units as the source shape that is being buffered.
A negative distance can be specified to produce a buffer inside the original polygon. This cannot be used with polyline. ITopologicalOperator methods must be applied on top-level geometries only. Top-Level geometries are point, multipoint, polyline and polygon. To use this method with segments (Line, Circular Arc, Elliptic Arc, Bézier Curve), paths or rings, they must be wrapped with a top-level type.
//The following code shows to wrap a line segment into a polyline in C#
//Assume a line (line1 as ILine) is already created
object obj=Type.Missing;
ISegmentCollection segCollection=new PolylineClass() as ISegmentCollection;
segCollection.AddSegment((ISegment)line1, ref obj, ref obj);
//Set the spatial reference on the new polyline
//The spatial reference is not transfered automatically from the segments
IGeometry geom=segCollection as IGeometry;
geom.SpatialReference=spatialRef;
//Can now be used with ITopologicalOperator methods
[C#]//This example demonstrates how to use ITopologicalOperator::Buffer
private void BufferArea()
{
IPoint[] points=new IPoint[5];
//The spatial reference should be set here using IGeometry::SpatialReference (Code skipped here)
for(int i=0; i < points.Length; i++)
{
points[i]=new PointClass();
}
points[0].PutCoords(0, 0);
points[1].PutCoords(0, 10);
points[2].PutCoords(10, 10);
points[3].PutCoords(10, 0);
points[4].PutCoords(0, 0);
IPointCollection4 pointCollection=new PolygonClass();
IGeometryBridge geometryBride=new GeometryEnvironmentClass();
geometryBride.AddPoints(pointCollection, ref points);
IArea area=pointCollection as IArea;
System.Windows.Forms.MessageBox.Show("Area original polygon : " + area.Area);
ITopologicalOperator topologicalOperator=pointCollection as ITopologicalOperator;
//Outside buffer
IPolygon polygon=topologicalOperator.Buffer(1) as IPolygon;
area=polygon as IArea;
System.Windows.Forms.MessageBox.Show( "Area polygon positive distance : " + area.Area);
//Inside buffer
polygon=topologicalOperator.Buffer(-1) as IPolygon;
area=polygon as IArea;
System.Windows.Forms.MessageBox.Show("Area polygon negative distance : " + area.Area);
}
Sub exampleITopologicalOperator_Buffer()
Dim ptc As ESRI.ArcGIS.Geometry.IPointCollection, i As Long, pa As ESRI.ArcGIS.Geometry.IArea, ptopo As ESRI.ArcGIS.Geometry.ITopologicalOperator
ptc=New ESRI.ArcGIS.Geometry.Polygon
Dim pt(4) As ESRI.ArcGIS.Geometry.IPoint, poutPoly As ESRI.ArcGIS.Geometry.IPolygon
'The spatial reference should be set here using IGeometry::SpatialReference (Code skipped here)
For i=0 To 4
pt(i)=New ESRI.ArcGIS.Geometry.Point
Next
pt(0).PutCoords(0, 0)
pt(1).PutCoords(0, 10)
pt(2).PutCoords(10, 10)
pt(3).PutCoords(10, 0)
pt(4).PutCoords(0, 0)
Dim geometryBride As ESRI.ArcGIS.Geometry.IGeometryBridge
geometryBride=New ESRI.ArcGIS.Geometry.GeometryEnvironmentClass()
geometryBride.AddPoints(ptc, pt)
pa=ptc
Debug.Print("Area original polygon : " & pa.Area)
ptopo=ptc
poutPoly=ptopo.Buffer(1) 'Outside buffer
pa=poutPoly
Debug.Print("Area polygon positive distance : " & pa.Area)
poutPoly=ptopo.Buffer(-1) 'Inside buffer
pa=poutPoly
Debug.Print("Area polygon negative distance : " & pa.Area)
End Sub