|
This document is archived and information here might be outdated. Recommended version. |
 |
This document is archived and information here might be outdated. Recommended version. |
Returns an array of geometries where each result geometry R[i] is (array1[i] intersect G2. If G2 is an Envelope, then this is clipping.
[Visual Basic .NET] Public Function Intersect ( _ ByVal pSR As ISpatialReference, _ ByVal pInGA1 As IGeometryArray, _ ByVal pInG2 As IGeometry _ ) As IGeometryArray
[C#] public IGeometryArray Intersect ( ISpatialReference pSR, IGeometryArray pInGA1, IGeometry pInG2 );
[C++]
HRESULT Intersect(
ISpatialReference* pSR,
IGeometryArray* pInGA1,
IGeometry* pInG2
);
[C++]
Parameters pSR
pSR is a parameter of type ISpatialReference* pInGA1
pInGA1 is a parameter of type IGeometryArray* pInG2
pInG2 is a parameter of type IGeometry*
This operation constructs the set-theoretic intersection between each element of the input array and InGeometry2. Each result is placed at the corresponding index in the output array – that is, Result[i]=InGeometryArray1[i] Intersect InGeometry2. If inGeometryArray1[i] and InGeometry2 disjoint, the output is an empty geometry of the type with the minimum dimension between inGeometryArray1[i] and InGeometry2.
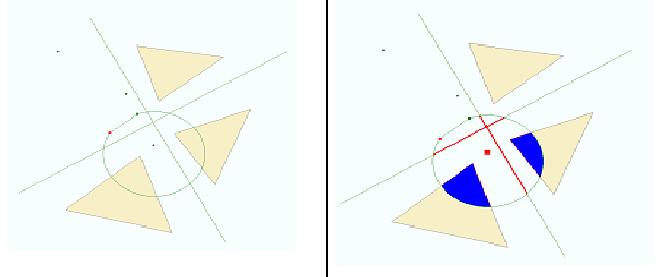
The figure below shows an example of the intersect operation. The input geometry array contains all geometries shown on the left of the figure with the exception of the central circular polygon. The output array contains the modified geometries shown in the right part of the figure. Note that two of the output points will be “empty” because their corresponding inputs are outside the circular polygon.