 |
This document is archived and information here might be outdated. Recommended version. |
 |
This document is archived and information here might be outdated. Recommended version. |
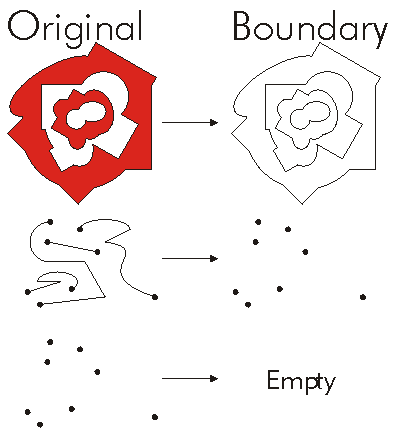
The boundary of this geometry. A polygon's boundary is a polyline. A polyline's boundary is a multipoint. A point or multipoint's boundary is an empty point or multipoint.
[Visual Basic .NET] Public ReadOnly Property Boundary As IGeometry
[C#] public IGeometry Boundary {get;}
[C++]
HRESULT get_Boundary(
IGeometry** outBoundary
);
[C++] Parameters outBoundary [out, retval]
outBoundary is a parameter of type IGeometry**
The Boundary of a Geometry is the part one the exterior of the Geometry. The Boundary is one Dimension lower than the Dimension of the original Geometry. The Boundary of a Polygon are the Polylines that form the Rings of the Polygon. The Boundary of a Polyline is a Multipoint corresponding to the endpoints of each Path in the Polyline. The Boundary of a Multipoint is an empty set.
ITopologicalOperator methods must be applied on high-level geometries only. High-Level geometries are point, multipoint, polyline and polygon. To use this method with low-level geometries such as segments (Line, Circular Arc, Elliptic Arc, Bézier Curve), paths or rings, they must be wrapped into high-level geometries types.
This method does not support GeometryBags.
//The following code shows to wrap a line segment into a polyline in C#
//Assume a line (line1 as ILine) is already created
object obj = Type.Missing;
ISegmentCollection segCollection = new PolylineClass() as ISegmentCollection;
segCollection.AddSegment((ISegment)line1, ref obj, ref obj);
//Set the spatial reference on the new polyline
//The spatial reference is not transfered automatically from the segments
IGeometry geom = segCollection as IGeometry;
geom.SpatialReference = spatialRef;
//Can now be used with ITopologicalOperator methods