 |
This document is archived and information here might be outdated. Recommended version. |
 |
This document is archived and information here might be outdated. Recommended version. |
Constructs the geometry that is the set-theoretic union of the input geometries.
[Visual Basic .NET] Public Function Union ( _ ByVal other As IGeometry _ ) As IGeometry
[C#] public IGeometry Union ( IGeometry other );
[C++]
HRESULT Union(
IGeometry* other
);
[C++] Parameters other
other is a parameter of type IGeometry*
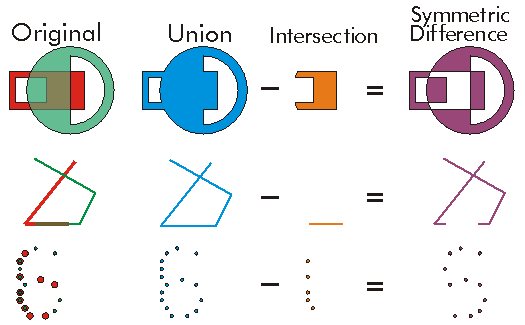
The Union of two Geometries of the same Dimension is a single Geometry corresponding to the combination of both Geometries such that anything within either of the original geometries is also part of the unioned geometry, but anything common to both geometries only exists once in the unioned geometry.
The Union is basically an OR between the input geometries.
ITopologicalOperator methods must be applied on high-level geometries only. High-Level geometries are point, multipoint, polyline and polygon. To use this method with low-level geometries such as segments (Line, Circular Arc, Elliptic Arc, Bézier Curve), paths or rings, they must be wrapped into high-level geometries types.
This method does not support GeometryBags.
//The following code shows to wrap a line segment into a polyline in C#
//Assume a line (line1 as ILine) is already created
object obj = Type.Missing;
ISegmentCollection segCollection = new PolylineClass() as ISegmentCollection;
segCollection.AddSegment((ISegment)line1, ref obj, ref obj);
//Set the spatial reference on the new polyline
//The spatial reference is not transfered automatically from the segments
IGeometry geom = segCollection as IGeometry;
geom.SpatialReference = spatialRef;
//Can now be used with ITopologicalOperator methods