Disponible con una licencia de Spatial Analyst.
Resumen
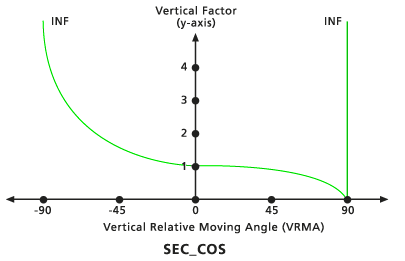
Defines the relationship between the vertical cost factor and the vertical relative moving angle (VRMA) through a secant/cosine function. If the VRMA is negative the vertical factor is defined by a secant function, and if the VRMA is nonnegative the vertical factor is defined by a cosine function.
Ilustración
Debate
The VfSecCos object is used in the Spatial Analyst tools Path Distance, Path Distance Allocation, and Path Distance Back Link.
The vertical factor (VF) object defines the relationship between the vertical cost factor and the vertical relative moving angle (VRMA).
VF defines the vertical difficulty encountered in moving from one cell to the next.
VRMA identifies the slope angle between the FROM or processing cell and the TO cell.
When the VRMA is a negative degree value, the VF is determined by the cosine function of the VRMA. If the VRMA is a positive degree value, the VF is determined by the secant function of the VRMA.
Sintaxis
VfSecCos ({lowCutAngle}, {highCutAngle}, {secPower}, {cosPower})| Parámetro | Explicación | Tipo de datos |
lowCutAngle | The VRMA degree defining the lower threshold, below which (less than) the VFs are set to infinity (El valor predeterminado es -90.0) | Double |
highCutAngle | The VRMA degree defining the upper threshold, beyond which (larger than) the VFs are set to infinity. (El valor predeterminado es 90.0) | Double |
secPower | The power to which the values in the secant VRMA function will be raised. The VF is determined by:
(El valor predeterminado es 1.0) | Double |
cosPower | The power to which the values in the cosine VRMA function will be raised. The VF is determined by:
(El valor predeterminado es 1.0) | Double |
Propiedades
| Propiedad | Explicación | Tipo de datos |
| lowCutAngle (Lectura y escritura) | The VRMA degree defining the lower threshold, below which (less than) the VFs are set to infinity. | Double |
| highCutAngle (Lectura y escritura) | The VRMA degree defining the upper threshold, beyond which (larger than) the VFs are set to infinity. | Double |
| secPower (Lectura y escritura) | The power to which the values in the secant VRMA function will be raised. The VF is determined by: | Double |
| cosPower (Lectura y escritura) | The power to which the values in the cosine VRMA function will be raised. The VF is determined by: | Double |
Ejemplo de código
VfSecCos example 1 (Python window)
Demonstrates how to create a VfSecCos class and use it in the PathDistance tool within the Python window.
import arcpy
from arcpy import env
from arcpy.sa import *
env.workspace = "C:/sapyexamples/data"
myVerticalFactor = VfSecCos(-90, 90, 1, 1)
outPathDist = PathDistance("source.shp", "costraster", "", "", "", "",
myVerticalFactor)
outPathDist.save("C:/sapyexamples/output/pathdistvfsc")
VfSecCos example 2 (stand-alone script)
Performs a PathDistance analysis using the VfSecCos class.
# Name: VfSecCos_Ex_02.py
# Description: Uses the VfSecCos object to execute the PathDistance tool.
# Requirements: Spatial Analyst Extension
# Import system modules
import arcpy
from arcpy import env
from arcpy.sa import *
# Set environment settings
env.workspace = "C:/sapyexamples/data"
# Set local variables
inSourceData = "source.shp"
inCostRaster = "costraster"
# Create the VfSecCos Object
lowCutAngle = -90
highCutAngle = 90
secPower = 1
cosPower = 1
myVerticalFactor = VfSecCos(lowCutAngle, highCutAngle, secPower, cosPower)
# Check out the ArcGIS Spatial Analyst extension license
arcpy.CheckOutExtension("Spatial")
# Execute PathDistance
outPathDist = PathDistance(inSourceData, inCostRaster, "", "", "", "",
myVerticalFactor)
# Save the output
outPathDist.save("C:/sapyexamples/output/pathdistvfsc2")