Calculated representation specification rules contain descriptive information to identify the rule as well as the Structured Query Language (SQL) statements and Visual Basic Scripting Edition (VBScript) expressions that define the symbolization for the statement. The SQL statements allow you to choose the attributes you want to use from both feature layers and stand-alone tables. For example, you can construct a query in which you include features where the Name field in a feature class is equal to the Full_Name field in a stand-alone table.
- Start ArcMap.
- On the main menu, click Customize > Toolbars > Production Cartography.
- If necessary, load data in the map.
- Right-click the layer for which you want to define the calculated representations and click Properties.
The Layer Properties dialog box appears.
- Click the Calculated Representations tab.
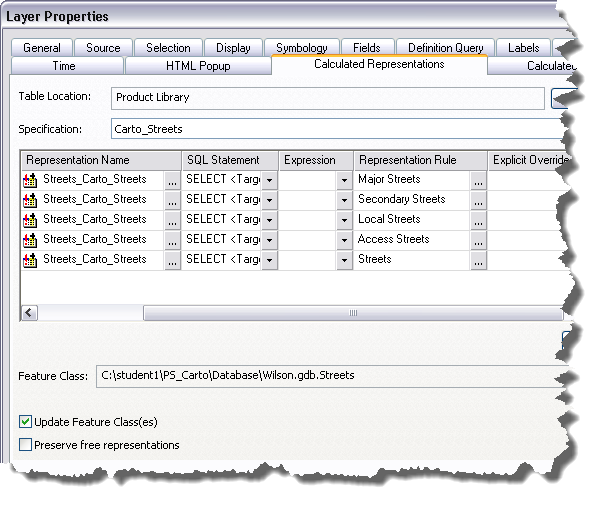
- Click the Specification drop-down arrow and choose the specification for which you want to create the rule.
- Click Options > New Rule.
A new row appears in the rule table.
- Double-click the Rule Description field and type a name for the rule.
- Click the ellipsis (...) in the Representation Name cell.
The Representation properties dialog box appears.
- Check the Edit Options check box.
The following items become available:
- ID Field text box
- Override Field text box
- Store change to geometry as representation override option
- Change the geometry of the supporting feature option
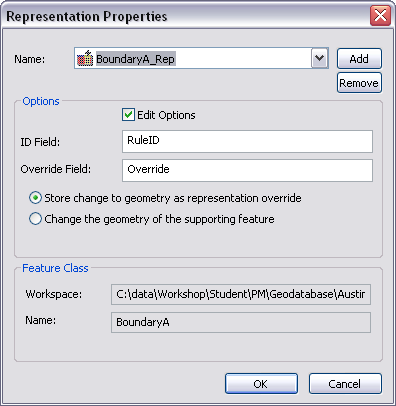
- Click Add to change the name in the Name text box.
The New Representation Name dialog box appears.
- If necessary, type a new name for the representation rule in the text box.
- Click OK.
- If necessary, type the name of a different field to use for storing the RuleIDs in the ID Field text box.
- If necessary, type the name of a different field to use for storing override information in the Override Field text box.
- Choose an option for geometry editing behavior.
- Store change to geometry as representation override—Any changes made to feature geometry during an edit session are stored as representation overrides. The original shape is copied, modified, and stored in the override field. This allows you to maintain the original feature's spatial integrity and use the representation override for display. This is the default.
- Change the geometry of the supporting feature—Any changes made to feature geometry during an edit session are stored in the shape, as a standard geometry edit. You can use this option for display only databases.
- Click OK.
The Calculated Representations tab appears.
- Click the SQL Statement drop-down arrow and click Edit SQL statement.
The Query Builder dialog box appears.
- Define a statement that includes the features you want to symbolize.
- Click OK.
- If necessary, click the Expression drop-down arrow and click Edit Expression.
The Expression Parser dialog box appears.
- Define the expression that refines the symbolization of the results of the SQL statement.
- Click OK.
- Click the ellipsis (...) in the Representation Rule field.
The Representation Rule Selector dialog box appears for the geometry type that matches the layer for which you are creating the representation rule.
- Choose the representation you want to use from an available style.
- Click OK.
The Calculated Representations tab appears.
At this point, you can either finish the rule creation process or define fields that allow you to override the default symbol.
- To finish the rule creation process, proceed to step 27.
- To define fields that allow you to override the default symbol, proceed to Defining override conditions for representations.
- To ensure that the feature class is updated with the rule information, verify that the Update Feature Class(es) check box is checked.
- Check the Preserve Free Representations check box to prevent the tool from overwriting any free representations in the feature class.
- Click OK.
Temas relacionados
- Creating a new specification
- Creating a calculated field specification rule
- Adding a specification rule
- Configuring calculated representation rule properties
- Preserving free representations
- ¿Qué son las representaciones?
- Comprender las reglas de representación
- SQL statements and visual specifications
- Defining a SQL statement
- Loading a SQL statement
- VBScript and visual specifications
- Creating VBScript expressions for calculated representations
- Creating VBScript expressions for calculated fields
- Saving a VBScript expression for later use
- Loading a VBScript expression