Disponible con una licencia de Data Interoperability.
GIS workflows often rely on data generated by outside sources in a variety of formats. The Extensión de ArcGIS Data Interoperability for Desktop gives you the ability to integrate nonnative data into your GIS and share it with others who do not use ArcGIS.
This topic gives you a high-level look at the Extensión de ArcGIS Data Interoperability for Desktop toolset, its capabilities, and basic workflow.
Direct-read formats
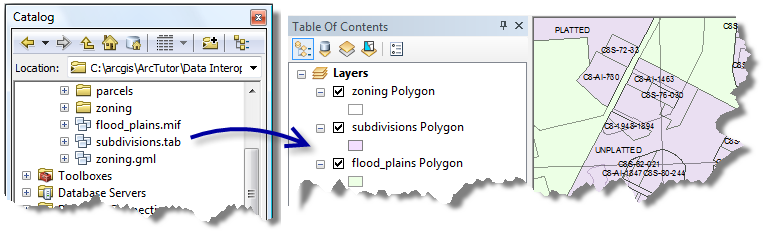
Direct-read formats are used directly from the Catalog tree as read-only datasets. When you add them to ArcMap, ArcScene, or ArcGlobe, all standard map functions are enabled, including attribute tables and labeling functions.
The Extensión de ArcGIS Data Interoperability for Desktop reads more than 110 spatial data formats including GML, XML, WFS, Autodesk DWG/DXF, MicroStation DGN, MapInfo MID/MIF and TAB, Oracle and Oracle Spatial, and Intergraph GeoMedia Warehouse.
Adding data
Using a direct-read feature class inArcMap is similar to working with other geodatabase feature classes. You can snap to geometry, substitute symbology, query attributes, and use it with all geoprocessing tools that accept feature classes or layers as input.
Interoperability connections
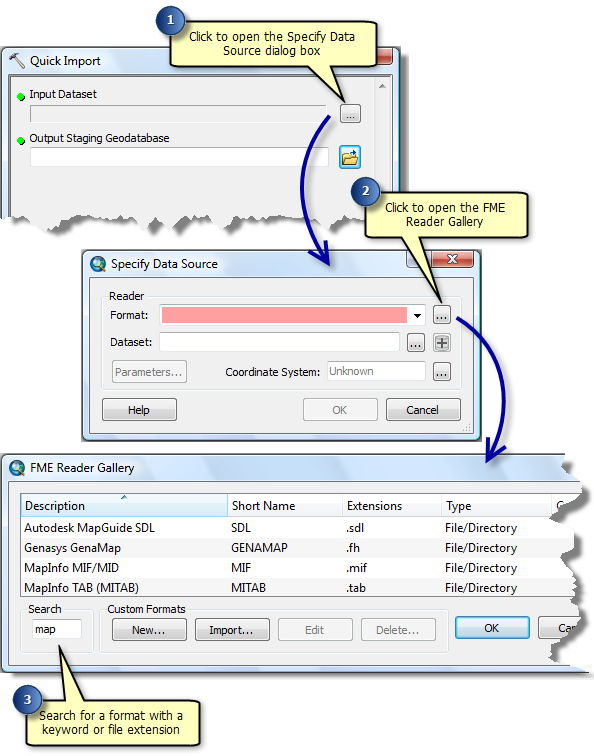
An interoperability connection is a user-created link to one or more data sources that is managed in the Catalog tree as a single direct-read dataset. The connection specifies the data source and the FME reader and any parameters supported by the chosen format.
Interoperability connections can be used to aggregate files, perform translations on the fly, define a coordinate system, and store format-specific parameters such as database connections and passwords. All interoperability connections are saved in the Interoperability Connections folder.
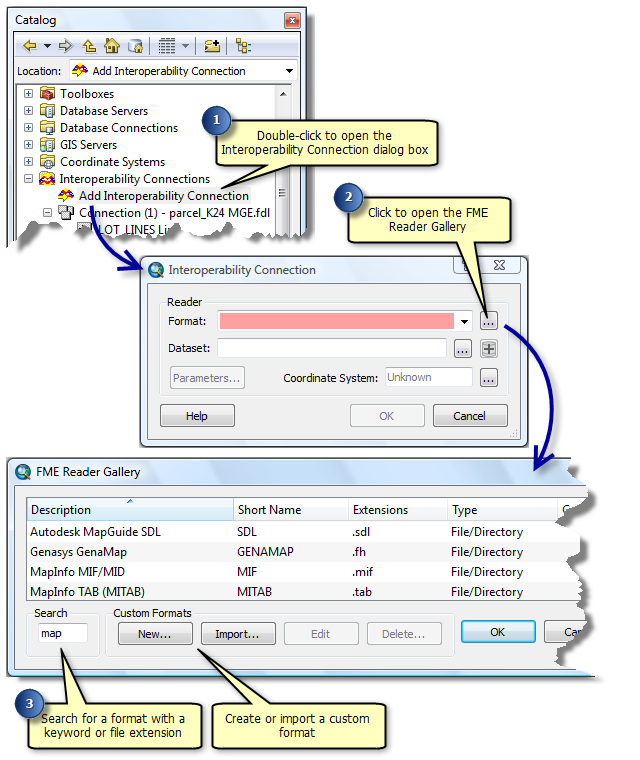
Custom formats
A custom format is a translation workspace that is exported from FME Workbench as a format and utilized in the FME reader gallery. It is saved to an external .fds file and can be imported to reader galleries on other desktops.
There are two ways to create a custom format:
- In FME Workbench , click File > Export as Custom Format on the main menu.
- In FME Reader Gallery, click the New button and use Create Custom Format Wizard.
Creating a custom format adds the format to the FME reader gallery. Once created, subsequent uses of the gallery allow you to edit the format in FME Workbench or delete it from the list. Deleting a custom format removes the .fds file from your desktop.
Data Interoperability toolbox
The Data Interoperability toolbox contains out-of-the-box geoprocessing conversion tools that import and export data between geodatabase and nonnative formats using FME readers and writers.
These tools are ideal when you need to convert data quickly. They can be used as stand-alone geoprocessing tools, used in ModelBuilder, executed in a Python window or script, or published with models in toolboxes as geoprocessing services using ArcGIS Server.
Quick conversion tools perform simple one-to-one translations and do not modify feature geometry or schemas during conversion. If your work requires schema changes, consider using spatial ETL tools.
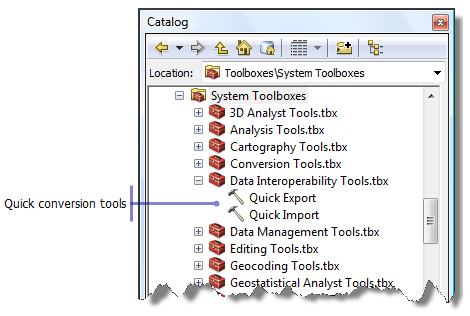
Quick Import
The Quick Import tool imports one or more external datasets into a geodatabase as feature classes. The input parameters include the data source and the FME reader and any parameters supported by the chosen format. The output staging geodatabase can be used directly or for further processing.
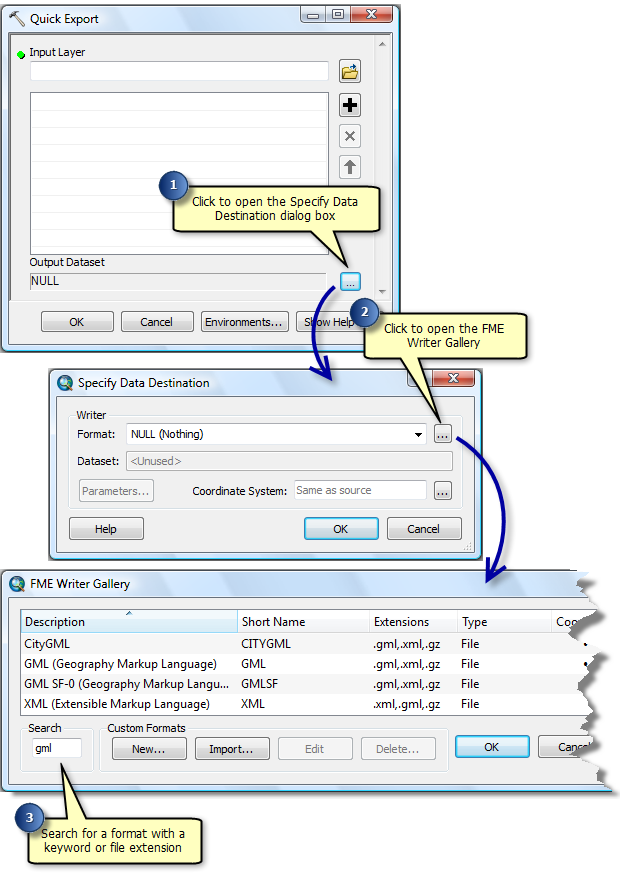
Quick Export
The Quick Export tool exports one or more geodatabase feature classes or feature layers to an external dataset. The input parameters include the data source and the FME writer and any parameters supported by the chosen format.
Spatial ETL tools
Spatial ETL tools are user-created geoprocessing tools that can transform data between different data models and different file formats. You create them with FME Workbench in a translation workspace and save them in a toolbox.
Spatial ETL tools are capable of a wide range of processes and dataflows from simple format translations to complex transformations that restructure geometry and attributes. They can be used as stand-alone geoprocessing tools, published in toolboxes as geoprocessing services  using ArcGIS Server, or exported as custom formats and utilized in the FME reader gallery.
using ArcGIS Server, or exported as custom formats and utilized in the FME reader gallery.
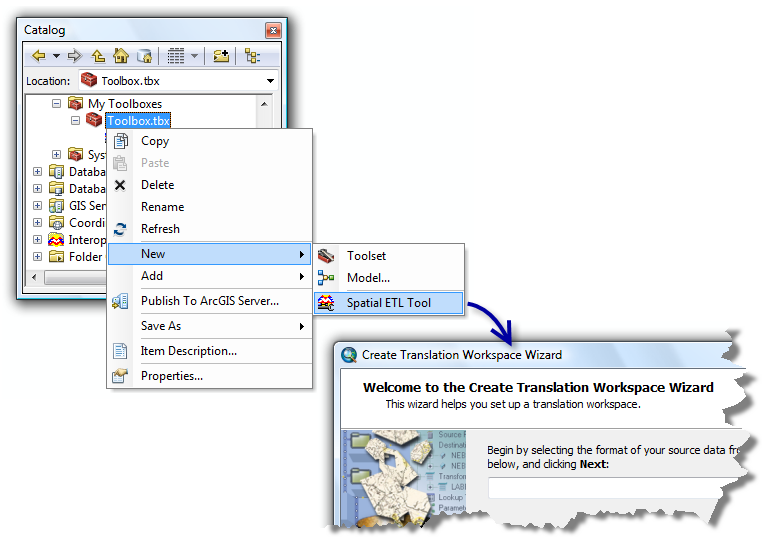
Initiating creation of a new spatial ETL tool opens the Create Translation Workspace Wizard. The wizard prompts you for information about the data source and data destination, then starts FME Workbench with a diagram of your dataflow. You can customize the default dataflow by adding or deleting connectors, inserting transformers, and editing parameters.
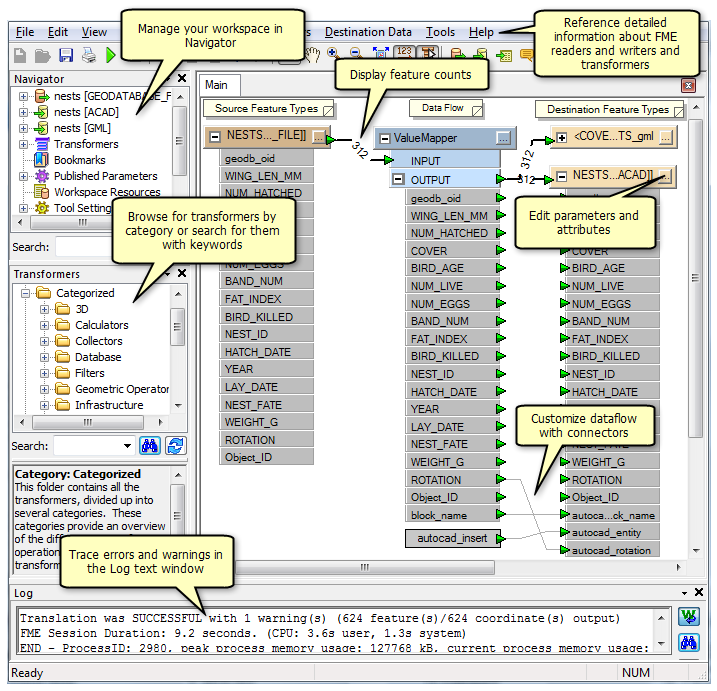
FME Workbench
FME Workbench is a visual workflow editor used for developing data transformation tools. When the Data Interoperability extension is enabled, you can use it to create spatial ETL tools and custom formats.
There are three ways to start FME Workbench:
- Right-click a toolbox
 and click New > Spatial ETL Tool.
and click New > Spatial ETL Tool. - Right-click an existing spatial ETL tool and click Edit from the shortcut menu.
- Double-click Add Interoperability Connection on the Catalog window and create a new custom format.
FME Workbench uses specialized explorer windows and dialog boxes that provide information and visual cues about your workspace.