Disponible con una licencia de Geostatistical Analyst.
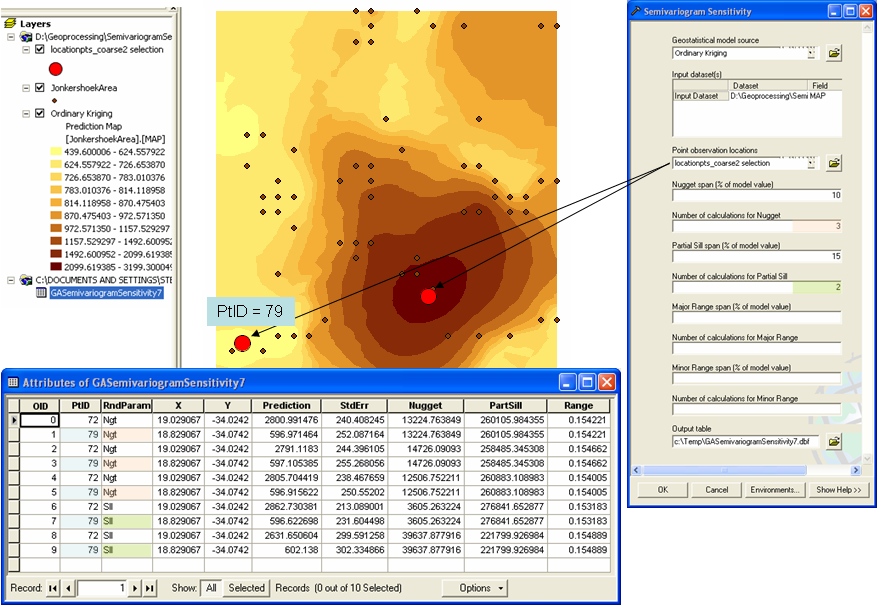
The Semivariogram Sensitivity tool performs a sensitivity analysis on the predicted values and associated standard errors by changing the model's parameters (the nugget, partial sill, and major and minor range) within a percentage of the original values. The tool's output is a table indicating which parameter values were used and what the resulting predicted and standard error values were, as illustrated in the following example. If there are large fluctuations in the output with small changes in the model's parameter values, then you cannot have much confidence in the output. On the other hand, if changes in the output are small, then you can be confident in the model's predictions and make decisions based on its output.
In the output table, PtID corresponds to the OID value in the Point observation locations feature class, and the RndParam field identifies which of the semivariogram parameters were randomly changed.
In this example, the parameter values for nugget and partial sill from the input Geostatistical model source (input geostatistical layer) are 13525.978688186458 and 259690.74619300355, respectively.
Three random nugget values are found that are within 10 percent of the model nugget (see these nugget values at OID=1, 3, 5 in the table below). Likewise, two partial sill values will be found that are within 15 percent of the model partial sill value (see these partial sill values at OID=7, 9 in the table below).
When the first nugget value is used, the partial sill and range parameters are automatically recalculated, and the prediction and the standard error of prediction values are determined. Then, when the first partial sill value is used, the nugget and range values are automatically recalculated, and the prediction and the standard error of prediction values are determined.
The Summary Statistics tool, for example, can now be used to summarize and further analyze the data in the output table.