Disponible avec une licence Geostatistical Analyst.
The standard search neighborhood is defined by the Ellipse parameters: Angle, Major Semiaxis, and Minor Semiaxis. The Smooth Interpolation option, however, creates an outer ellipse and an inner ellipse at distances which depend on the smoothing factor and the semiaxis lengths.
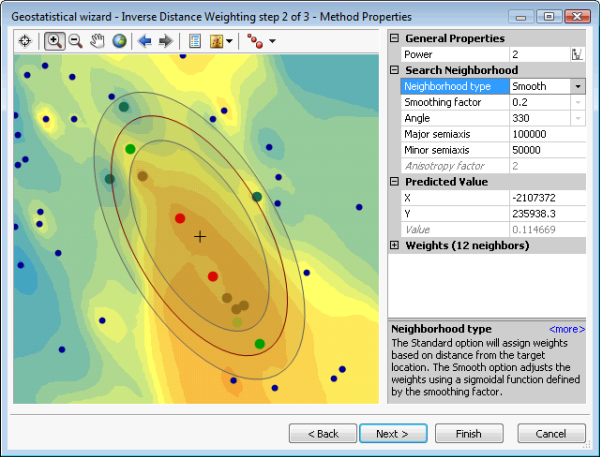
All the points within these three ellipses are used in the interpolation. The points that fall outside the inner ellipse but inside the outer ellipse are weighted using a sigmoidal function with a value between 0 and 1.
There are many methods for local smoothing. Spline algorithms are usually used to create a continuous map, because they minimize curvature of the surface. Geostatistical models are commonly used for optimal spatial prediction and mapping in many scientific disciplines, but classical kriging models produce noncontinuous surfaces when local neighborhood is used. Consider prediction at two nearby points, represented as centers of two circles.
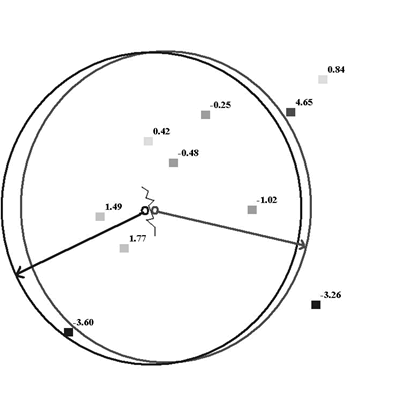
Prediction to each point uses data inside each corresponding circle. In the example above, the only difference between local neighborhoods is whether the location with value -3.60 is included. Generally speaking, kriging cannot produce continuous surfaces with local neighborhoods, but breaks are clearly seen if the data has significantly different values in nearby local neighborhoods.
A more detailed discussion can be found in the following article:
- A. Gribov and K. Krivoruchko, "Geostatistical Mapping with Continuous Moving Neighborhood."
 Mathematical Geology, Volume36, Number 2, February 2004.
Mathematical Geology, Volume36, Number 2, February 2004.