サマリ
指定されたラバーシート リンクを使用してラバーシート処理を行い、空間的に調整することによって、入力ライン フィーチャを変更します。それによって入力ライン フィーチャは、目的のターゲット フィーチャとより正確に一致するようになります。
図
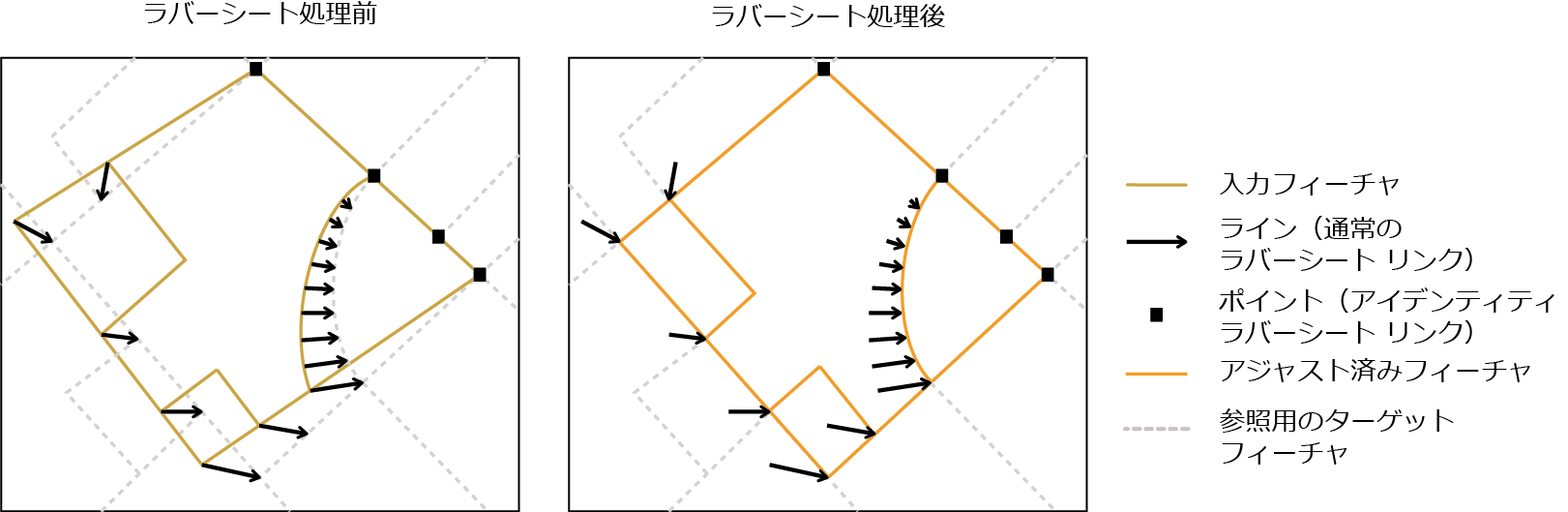
使用法
このツールは、[ラバーシート リンクの生成 (Generate Rubbersheet Links)] ツールの実行後に使用することを目的としています。ラバーシート処理は、指定されたラバーシート リンクに基づいて、入力フィーチャの位置とターゲット フィーチャの位置がより正確に一致するように、空間的に調整します。入力リンク フィーチャは、標準のリンクを表します。入力ポイント フィーチャは、ラバーシート処理の実行中にソースの位置を固定する固定リンクを表します。入力リンク フィーチャと固定リンク フィーチャの両方に、SRC_FID フィールドと TGT_FID フィールドが存在する必要があります。
[方法] パラメーターでは、ラバーシートでテンポラリ TIN の作成に使用される内挿法を指定します。詳細については、「アジャストのラバーシートについて」をご参照ください。
- LINEAR - この方法は、簡易 TIN サーフェスを作成しますが、近傍を考慮に入れません。この方法は、他の方法よりもわずかに高速であり、調整対象のデータに多くのラバーシート リンクが一様に拡散している場合に効果的です。
- NATURAL_NEIGHBOR - この方法は、他の方法よりも低速ですが、ラバーシート リンクの数が少なく、データセット全体に拡散している場合、より正確になります。この場合、リニア内挿法を使用すると、結果の精度が低下します。
構文
RubbersheetFeatures_edit (in_features, in_link_features, {in_identity_links}, {method})| パラメータ | 説明 | データ タイプ |
in_features | 調整対象の入力ライン フィーチャ。 | Feature Layer |
in_link_features | ラバーシートの標準のリンクを表す入力ライン フィーチャ。 | Feature Layer |
in_identity_links (オプション) | ラバーシート処理の固定リンクを表す入力ポイント フィーチャ。 | Feature Layer |
method (オプション) | フィーチャの調整に使用されるラバーシート方法。
| String |
コードのサンプル
RubbersheetFeatures (フィーチャのラバーシート) の例 1 (Python ウィンドウ)
次の Python ウィンドウ スクリプトで、RubbersheetFeatures (フィーチャのラバーシート) 関数をイミディエイト モードで使用する方法を示します。
import arcpy
arcpy.env.workspace = "C:/data"
arcpy.RubbersheetFeatures_edit("source_Roads.shp","rubbersheet_Links.shp",
"rubbersheet_Links_pnt.shp", "LINEAR")
RubbersheetFeatures (フィーチャのラバーシート) の例 2 (スタンドアロン Python スクリプト)
次のスタンドアロン Python スクリプトは、RubbersheetFeatures (フィーチャのラバーシート) 関数をスクリプティング環境に適用する例を示しています。
# Name: RubbersheetFeatures_example_script2.py
# Description: Performs rubbersheeting spatial adjustment using links produced by
# GenerateRubbersheetLinks, assuming newly updated roads are more
# accurate than existing base roads. The links go from base road data
# to corresponding newly updated road data. The links are then
# analyzed for potential errors; they are finally used to adjust the
# base roads (a copy is made) to better align with the updated roads.
# Author: Esri
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------
# Import system modules
import arcpy
from arcpy import env
# Set environment settings
env.overwriteOutput = True
env.workspace = r"D:\conflationTools\ScriptExamples\data.gdb"
# Set local variables
sourceFeatures = "baseRoads"
targetFeatures = "updateRoads"
grlOutput = "grlinks_out"
grlOutputPts = "grlinks_out_pnt"
search_distance = "300 Feet"
match_fields = "FULLNAME RD_NAME"
qaLocations = "qa_locations"
# Generate rubbersheet links
arcpy.GenerateRubbersheetLinks_edit(sourceFeatures, targetFeatures, grlOutput, search_distance, match_fields)
# ====================================================================================
# Note 1: The result of GenerateRubbersheetLinks may contain errors; see tool reference.
# Inspection and editing may be necessary to ensure correct links before using
# them for rubbersheeting.
#
# One of the common errors are intersecting or touching links. Their locations
# can be found by the process below.
# ====================================================================================
# Find locations where links intersect or touch; the result contains coincident points
arcpy.Intersect_analysis(grlOutput, qaLocations, "", "", "POINT")
# Delete coincident points
arcpy.DeleteIdentical_management(qaLocations, "Shape")
# ====================================================================================
# Note 2: At this point you can manually inspect locations in qaLocations; delete or
# modify links as needed.
# ====================================================================================
# Make a copy of the sourceFeatures for rubbersheeting
arcpy.CopyFeatures_management(sourceFeatures, "sourceFeatures_Copy")
# Use the links for rubbersheeting
arcpy.RubbersheetFeatures_edit("sourceFeatures_Copy", grlOutput, grlOutputPts, "LINEAR")
環境
ライセンス情報
- ArcGIS for Desktop Basic: ×
- ArcGIS for Desktop Standard: ×
- ArcGIS for Desktop Advanced: ○