Доступно с лицензией Data Interoperability.
Spatial ETL tools are capable of a wide range of processes and dataflows from simple format translations to complex transformations that restructure geometry and attributes.
In this exercise, you create a spatial ETL tool that extracts Intergraph Modular GIS Environment (MGE) parcel data and loads it into a geodatabase.
The MGE format uses standard MicroStation DGN files to store and edit the graphic elements of geographic data. The nongraphic elements, such as feature attributes, are stored in external database tables and linked to the graphic elements via pairs of entity and mslink numbers.
Begin by using Create Translation Workspace Wizard to perform the following tasks:
- Choose the FME reader and specify multiple data sources.
- Specify the reader parameters for the external database.
- Choose the FME writer and start FME Workbench.
Using FME Workbench, perform the following tasks:
- Reduce the workspace so it only processes the point and line features.
- Edit the destination parameter so the path defaults to the tutorial folder.
- Save the workspace and close Workbench.
- Open and run the spatial ETL tool from the Catalog window.
After running the tool and generating the data, add the dataset to ArcMap to verify your results.
Create a toolbox
Предварительное условие:
The Data Interoperability extension must be enabled.
In this exercise we will be creating a spatial ETL tool that will read MGE parcel data and load it into a geodatabase.
- Start ArcMap.
- Click Catalog
 on the Standard toolbar.
on the Standard toolbar.
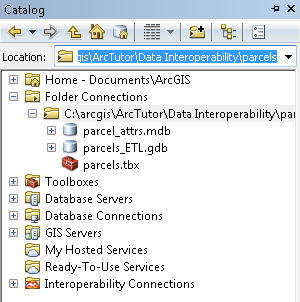
- Type C:\arcgis\ArcTutor\Data Interoperability\parcels\ in the Location text box and press ENTER.
The location is added to the Catalog tree under Folder Connections.
- Right-click the parcels folder and click New > Toolbox
 .
. - Right-click the toolbox, click
Rename, and name it parcels.
Create the translation workspace
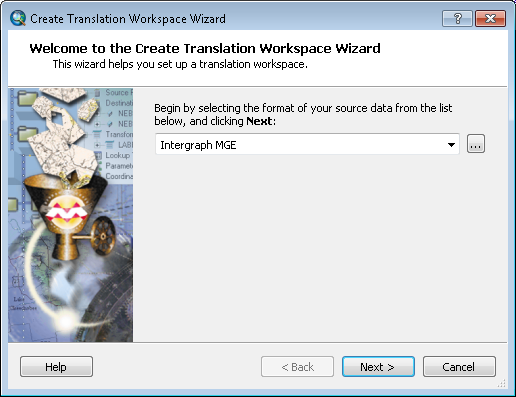
Starting the Create Translation Workspace Wizard
- Right-click the parcels toolbox and click New > Spatial ETL Tool.Create Translation Workspace Wizard opens.
Choosing the FME reader
- Click the Format browse button.
The FME Reader Gallery dialog box opens.
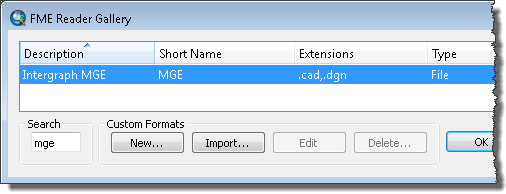
- Type mge in the Search text box.
- Click the row listing the Intergraph MGE format and click OK.
The FME Reader Gallery dialog box closes.
- Click Next.
Specifying the data source
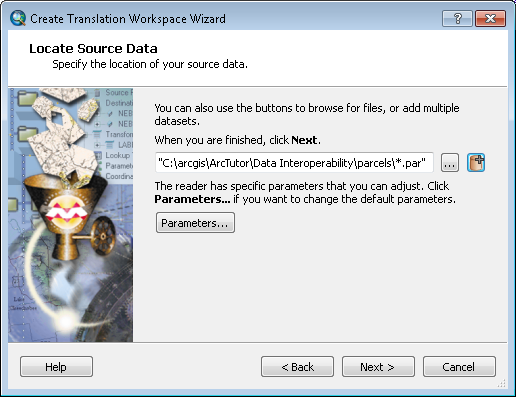
- Click the Add (+) button.
The Select File dialog box opens.
- Click the Add Directories button.
A second window opens.
- Browse to C:\arcgis\ArcTutor\Data Interoperability\parcels\ and click Select Folder.
The Select File dialog box is populated with the path and the standard (.dgn and .cad) file extensions defined for the Intergraph MGE format by FME Reader Gallery.
Specifying the file filter parameters
The next three steps edit the default File/Filter parameters to select the MicroStation DGN (.par) drawing files used in this exercise.
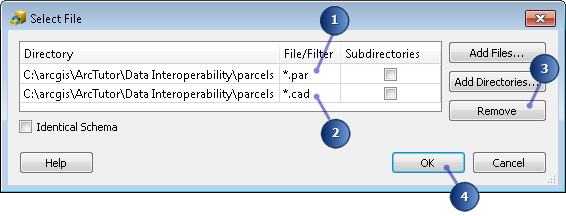
- Double-click the File/Filter field containing *.dgn and replace the contents with *.par.
- Click the row specifying *.cad.
- Click Remove.
- Click OK.
The Select Multiple Datasets dialog box closes.
Specifying the reader parameters
Specify the external database that contains the attribute tables.
- Click the Parameters button.
The Intergraph MGE Parameters dialog box opens.
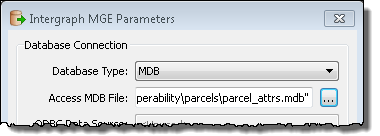
- Click the Database Type drop-down arrow and choose MDB.
- Click the Access MDB File browse button.
- Browse to C:\arcgis\ArcTutor\Data Interoperability\parcels\parcel_attrs.mdb and click Open.
- Click OK.
The Intergraph MGE Parameters dialog box closes.
- Click Next.
Choosing the FME writer
- Click the Format browse button.
The FME Writer Gallery dialog box opens.
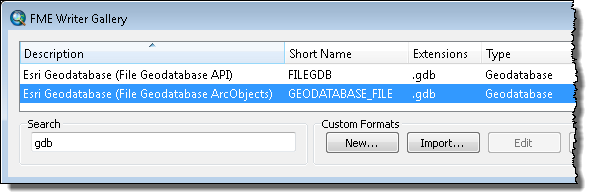
- Type gdb in the Search text box.
- Click the row listing Esri Geodatabase (File-Geodatabase ArcObjects) and click OK.
The FME Writer Gallery dialog box closes.
- Click Next.
Specifying the writer parameters
Accept the default parameters for the geodatabase and click Next.
Specifying the workflow options
Accept the default static schema and click Next.
- Click Next.
Creating the workspace
- Click Finish.
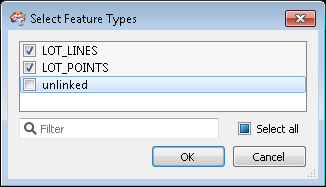
The wizard processes the information and starts Workbench. The Select Feature Types dialog box opens.
- Uncheck the unlinked feature type and click OK.
Prepare the tool
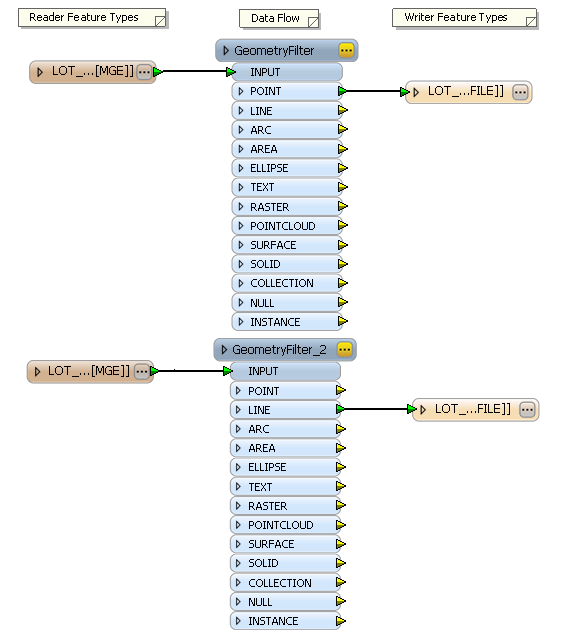
Workbench opens the workspace with an ETL model of the information you provided. Reduce the workspace so that it only processes point and line features.
Modifying the model
- Click and drag to create a selection box around the orphaned unlinked destination feature types, right-click the selection, and click Delete from the context menu.
- Delete all destination feature types except for source feature types LOT_LINES_line and LOT_POINTS_point.
The LOT_LINES source feature type LINE attribute is mapped to the LOT_LINES_line destination feature type, and the LOT_POINTS source feature type POINT attribute is mapped to the LOT_POINTS_point destination feature type.
Editing the destination parameter
Specify the default output geodatabase path and file.
- Confirm that Navigator is available.
To open the Navigator window from the main menu, click View > Windows > Navigator.
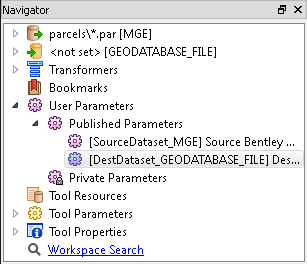
- Expand User Parameters > Published Parameters.
- Double-click DestDataset_GEODATABASE_FILE] Destination Esri File Geodatabase.The Edit Published Parameter dialog box opens.
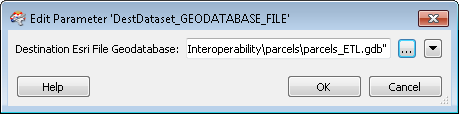
- Click the browse button.
The Select Destination Esri File Geodatabase dialog box opens.
- Browse to C:\arcgis\ArcTutor\Data Interoperability\parcels.
- Type parcels_ETL.gdb in the Geodatabase text box to complete the path and click Select .gdb Folder.
- Click OK.
The Edit Published Parameter dialog box closes.
Save and rename the tool
- Click File > Save to save the tool.
- Click File > Exit to exit Workbench.
- Right-click the new spatial ETL tool in the Catalog window, click Rename, and type Import MGE Parcels.
Open and run the tool
- In the Catalog window, expand the Parcels toolbox
 .
. - Double-click the Import MGE Parcels tool.
The spatial ETL tool Import MGE Parcels dialog box opens.
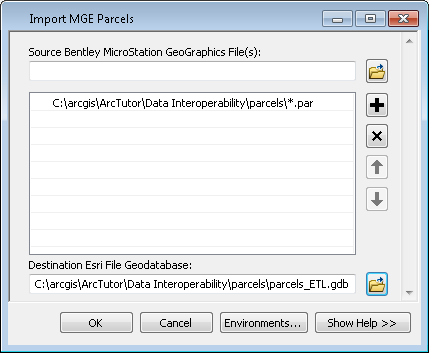
- Click OK.
The tool executes the conversion in the background. A progress bar at the bottom of your map displays the name of the tool. When the tool is finished, a pop-up notification appears in the system tray. You can examine the details of the conversion in the Results window.
Add the data to ArcMap
- In the Catalog window, expand the parcels_ETL geodatabase and drag the feature classes LOT_POINTS_point and LOT_LINES_line into ArcMap and verify your results.
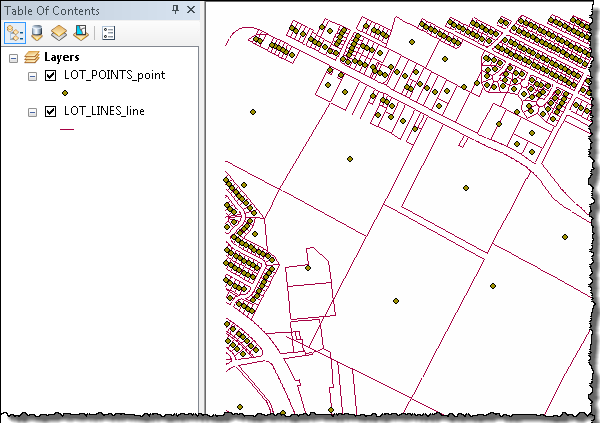
This completes the exercise.
Continue to the next exercise: Exercise 3b: Transforming data and using Data Inspector.