摘要
可计算输入要素与其他图层或要素类中的最近要素之间的距离和其他邻近性信息。
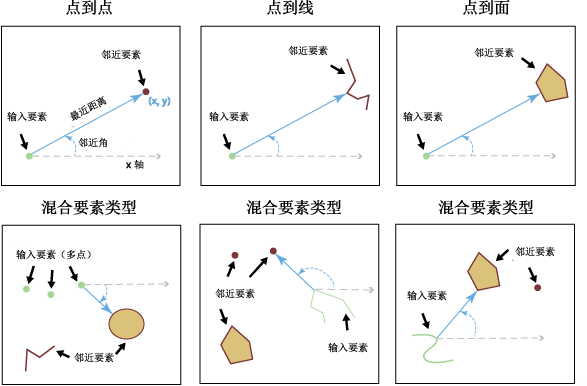
插图
用法
将以下字段添加到输入中。如果字段已存在,则更新字段值。
字段名 描述 NEAR_FID 最近的邻近要素的对象 ID。如果未发现邻近要素,则该值为 -1。
NEAR_DIST 输入要素与邻近要素之间的距离。该值采用输入要素坐标系的线性单位,如果将 Method 参数设置为 GEODESIC 且输入位于地理坐标系中,则该值将采用“米”作为单位。如果未发现邻近要素,则该值为 -1。
NEAR_FC 包含邻近要素的要素类的目录路径。仅在指定了多个邻近要素时,才会将此字段添加到输出表中。如果未发现邻近要素,则该值为空字符串或为空。
如果选中 Location 参数(在 Python 中 location 参数设置为 LOCATION),则以下字段将被添加到输入要素中。如果字段已存在,将更新字段值。字段值的单位取决于在 Method 参数中选择了什么方法。如果设置为 Planar,该值为输入要素坐标系的线性单位。如果设置为 Geodesic,该值则在与输入要素坐标系相关联的地理坐标系中。
字段名 描述 NEAR_X 邻近要素中距离输入要素最近位置的 x 坐标。如果未发现邻近要素,则该值为 -1。
NEAR_Y 邻近要素中距离输入要素最近位置的 y 坐标。如果未发现邻近要素,则该值为 -1。
如果选中 Angle 参数(在 Python 中 angle 参数设置为 ANGLE),则以下字段将被添加到输入要素中。如果字段已存在,将更新字段值。
字段 描述 NEAR_ANGLE 连接输入要素和邻近要素的位于 FROM_X 和 FROM_Y 位置的线的角度。如果未发现邻近要素或邻近要素与输入要素相交,则该值为 0。
如果在搜索半径内未找到任何要素,则 NEAR_FID 和 NEAR_DIST 的值都将为 -1。
输入要素和邻近要素均可为点、多点、线或面。
邻近要素可包括不同形状类型(点、多点、线或面)的一个或多个要素类。
同一要素类或图层可同时用作输入要素和邻近要素。这种情况下,所评估的输入要素将被排除在邻近要素候选项之外,以避免得出所有要素都与其自身最接近的结果。
输入要素可以是您已执行要素选择的图层。使用工具执行操作时将使用并更新所选要素。其余要素会将新建字段(例如 NEAR_FID 和 NEAR_DIST)的值设置为 -1。
如果有多个邻近要素与输入要素之间有相同的最短距离,则随机选择其中一个邻近要素作为最近要素。
使用 Method 参数的 Planar 选项时,输入要素应位于适合距离测量值的投影中,如等距投影。
要显示 FROM_X、FROM_Y、NEAR_X 和 NEAR_Y 位置,输出表可用作创建 XY 事件图层或 XY 转线工具的输入。
语法
Near_analysis (in_features, near_features, {search_radius}, {location}, {angle}, {method})| 参数 | 说明 | 数据类型 |
in_features | 输入要素可以是点、折线、面或多点类型。 | Feature Layer |
near_features [near_features,...] | 一个或多个包含邻近要素候选项的要素图层或要素类。邻近要素可以是点、折线、面或多点。如果指定了多个图层或要素类,则名为 NEAR_FC 的字段将被添加到输入表中,并将存储含有找到的最近要素的源要素类的路径。同一要素类或图层可同时用作输入要素和邻近要素。 | Feature Layer |
search_radius (可选) | 用于搜索邻近要素的半径。如果未指定任何值,则会考虑所有邻近要素。如果指定了距离,但没有指定任何单位或将单位设置为未知,则将使用输入要素的坐标系单位。如果使用了 Geodesic 选项,则应使用线性单位(如公里或英里)。 | Linear unit |
location (可选) | 指定是否将邻近要素最近位置的 x 和 y 坐标写入 NEAR_X 和 NEAR_Y 字段。
| Boolean |
angle (可选) | 指定是否计算邻近角并将其写入输出表的 NEAR_ANGLE 字段。邻近角测量与直线(该直线连接输入要素与其最近要素的最近位置)方向之间的夹角。在 method 参数中使用 PLANAR 方法时,角度在 -180° 到 -180° 的范围内,0° 代表东,90° 代表北,180°(或 -180°)代表西,-90° 代表南。使用 GEODESIC 方法时,角度在 -180° 到 180° 的范围内,0° 代表北,90° 代表东,180°(或 -180°)代表南,-90° 代表西。
| Boolean |
method (可选) | 确定是使用椭球体上的最短路径(测地线)还是使用地平(平面)方法。强烈建议将 Geodesic 方法用于在不适合进行距离测量的坐标系(例如 Web 墨卡托或任何地理坐标系)中存储的数据,以及任何地理区域跨度较大的分析。
| String |
代码示例
近邻分析示例 1(Python 窗口)
以下 Python 交互式窗口脚本演示了如何在即时模式下使用 Near 函数。
import arcpy
arcpy.env.workspace = "C:/data/city.gdb"
## find the nearest road from each house
arcpy.Near_analysis('houses', 'roads')
近邻分析示例 2(独立 Python 脚本)
以下 Python 脚本演示了如何在独立脚本中使用 Near 函数。
# Name: Near.py
# Description: Finds nearest features from input feature class to near feature class.
import arcpy
# Set workspace environment
arcpy.env.workspace = "C:/data/city.gdb"
try:
# set local variables
in_features = "houses"
near_features = "parks"
# find features only within search radius
search_radius = "5000 Meters"
# find location nearest features
location = "LOCATION"
# avoid getting angle of neares features
angle = "NO_ANGLE"
# execute the function
arcpy.Near_analysis(in_features, near_features, search_radius, location, angle)
# get geoprocessing messages
print(arcpy.GetMessages())
except arcpy.ExecuteError:
print(arcpy.GetMessages(2))
except Exception as err:
print(err.args[0])
近邻分析示例 3(独立 Python 脚本)
以下 Python 脚本演示了如何将邻近角转换为方位角。
# Name: near_angle_to_azimuth.py
import arcpy
# Near tool does not calculate angle in azimuths
# This script, using the output of the tool, converts the angles
# to azimuth angles.
in_table = r"C:/data/city.gdb/near_table"
angles = arcpy.da.SearchCursor(in_table, ["NEAR_ANGLE"])
azimuth_angles = []
with angles as rows:
for row in rows:
angle = row[0]
if angle <= 180 and angle > 90:
azimuth_angles.append(360.0 - (angle - 90))
else:
azimuth_angles.append(abs(angle - 90))
# Use these azimuth angles as necessary.
近邻分析示例 4(独立 Python 脚本)
演示使用邻近分析工具的派生输出进行后处理。脚本为每个邻近要素查找最接近的输入要素。
# Name: features_closest_to_input.py
"""
This script finds, for each input feature, a list of near feature it is closest to.
If near features 6, 7, 10 are closest to input feature 3 then the
resulting dictionary will have a list [6, 7, 10] as value for key 3
"""
import os
import arcpy
in_fc = r"C:\data\cities.gdb\cities_many"
# create a dictionary to hold the list of near ids for each input id
nearest_dict = dict()
with arcpy.da.SearchCursor(in_fc, ["OID@", "NEAR_FID"]) as rows:
for row in rows:
nearest_id = row[0] # get OID value for that row
input_id = row[1] # get NEAR_FID value
if input_id in nearest_dict:
# if a dict key already exists, append near id to value list for that key
nearest_dict[input_id].append(nearest_id)
else:
# if the key does not exist then create a new list with near id
# and add it to the dictionary
nearest_dict[input_id] = [nearest_id]
print(nearest_dict)
# output will look like:
# {1: [13, 28], 2: [2, 9, 14, 20, 22], 3: [11, 12, 24, 25]}
环境
许可信息
- ArcGIS Desktop Basic: 否
- ArcGIS Desktop Standard: 否
- ArcGIS Desktop Advanced: 是