摘要
提取与裁剪多边形或范围相交的 LAS 或 ZLAS 文件。
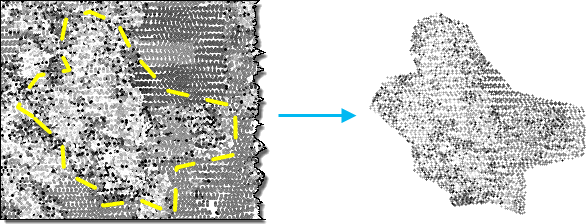
插图
用法
-
将 LAS 数据集指定为输入时,将处理它引用的 LAS 文件中的所有数据点。也可以按分类代码、分类标记和回波值来选择激光雷达数据的子集,方法是在 LAS 数据集图层中应用所需的 LAS 点过滤器。可通过图层属性对话或创建 LAS 数据集图层工具定义过滤器。
考虑使用此工具来提取在源激光雷达文件中捕获的激光雷达数据的子集。例如,如果仅需要在用面边界定义的区域中作业,则可将面用作边界要素来提取 LAS 文件。
要重新投影 LAS 文件,请在输出坐标系环境设置中指定所需的空间参考。
如果沿提取边界定义提取范围,将使用两者的交集来定义提取的 LAS 文件的 coverage。
LAS 点记录以不符合点空间聚类的二进制序列存储在 LAS 文件中并不罕见。查询此类数据分布时,访问代表 LAS 点的二进制记录的效率会有所降低。在生成的 LAS 文件中重新排列点可优化数据以供可视化及其他空间操作。启用重新排列选项后,将自动计算统计数据。如果您选择不重新排列 LAS 点,则可以选择启用或禁用计算统计数据。计算统计数据可优化空间查询并对 LAS 文件中存在的类代码和返回值提供汇总信息。但是,这也会增加工具的处理时间。如果不在 ArcGIS 中使用生成的 LAS 文件,则可以选择禁用计算统计数据,以便加快工具的执行速度。
语法
ExtractLas_3d (in_las_dataset, target_folder, {extent}, {boundary}, {process_entire_files}, {name_suffix}, {remove_vlr}, {rearrange_points}, {compute_stats}, {out_las_dataset})| 参数 | 说明 | 数据类型 |
in_las_dataset | 待处理的 LAS 数据集。 | LAS Dataset Layer |
target_folder | 将在其中写入 LAS 文件的文件夹。每个输出文件与输入文件的 LAS 文件版本和点记录格式都相同。 | Folder |
extent (可选) | 指定将由此工具进行评估的数据范围。 | Extent |
boundary (可选) | 定义将提取 LAS 文件的位置的面边界。 | Feature Layer |
process_entire_files (可选) | 指定处理范围的应用方式。
| Boolean |
name_suffix (可选) | 将追加到每个输出 LAS 文件名的文本。每个文件都将从其源文件继承其基本名称,后跟此参数中指定的后缀。 | String |
remove_vlr (可选) | 确定是移除附加变量长度记录,还是将其保留在 LAS 文件中。
| Boolean |
rearrange_points (可选) | 确定是否重新排列 LAS 文件中的点。
| Boolean |
compute_stats (可选) | 指定是否应计算 LAS 数据集引用的 LAS 文件的统计数据。统计数据允许 LAS 数据集图层使用过滤和符号系统选项,以便仅显示 LAS 文件中存在的 LAS 属性值。
| Boolean |
out_las_dataset (可选) | 输出的 LAS 数据集。 | LAS Dataset |
派生输出
| 名称 | 说明 | 数据类型 |
| out_folder | 将在其中写入 LAS 文件的文件夹。 |
代码示例
ExtractLas 示例 1(Python 窗口)
下面的示例演示了如何在 Python 窗口中使用此工具。
import arcpy
from arcpy import env
env.workspace = 'C:/data'
arcpy.ddd.ExtractLas('test.lasd', 'c:/lidar/subset', boundary='study_area.shp',
name_suffix='subset', remove_vlr=True,
rearrange_points='REARRANGE_POINTS',
out_las_dataset='extracted_lidar.lasd')
ExtractLas 示例 2(独立脚本)
下面的示例演示了如何在独立 Python 脚本中使用此工具。
'''****************************************************************************
Name: Split Large LAS File
Description: Divides a large LAS file whose point distribution covers the full
XY extent of the data into smaller files to optimize performance
when reading lidar data.
****************************************************************************'''
# Import system modules
import arcpy
import tempfile
import math
in_las_file = arcpy.GetParameterAsText(0)
tile_width = arcpy.GetParameter(1) # double in LAS file's XY linear unit
tile_height = arcpy.GetParameter(2) # double in LAS file's XY linear unit
out_folder = arcpy.GetParameterAsText(3) # folder for LAS files
out_name_suffix = arcpy.GetParameterAsText(4) # basename for output files
out_lasd = arcpy.GetParameterAsText(5) # output LAS dataset
try:
temp_lasd = arcpy.CreateUniqueName('temp.lasd', tempfile.gettempdir())
arcpy.management.CreateLasDataset(in_las_file, temp_lasd,
compute_stats='COMPUTE_STATS')
desc = arcpy.Describe(temp_lasd)
total_columns = int(math.ceil(desc.extent.width/tile_width))
total_rows = int(math.ceil(desc.extent.height/tile_height))
digits = int(math.log10(max(cols, rows))) + 1
for row in range(1, total_rows+1):
yMin = desc.extent.YMin + tile_height*(row-1)
yMax = desc.extent.YMin + tile_height*(row)
for col in range (1, total_columns+1):
xMin = desc.extent.XMin + tile_width*(col-1)
xMax = desc.extent.XMax + tile_width*(col)
name_suffix = '_{0}_{1}x{2}'.format(out_name_suffix,
str(row).zfill(digits),
str(col).zfill(digits))
arcpy.ddd.ExtractLas(temp_lasd, out_folder,
arcpy.Extent(xMin, yMin, xMax, yMax),
name_suffix=name_suffix,
rearrange_points='REARRANGE_POINTS',
compute_stats='COMPUTE_STATS')
arcpy.env.workspace = out_folder
arcpy.management.CreateLasDataset(arcpy.ListFiles('*{0}*.las'.format(out_name_suffix)),
out_lasd, compute_stats='COMPUTE_STATS',
relative_paths='RELATIVE_PATHS')
except arcpy.ExecuteError:
print(arcpy.GetMessages())
环境
许可信息
- ArcGIS Desktop Basic: 需要 3D Analyst
- ArcGIS Desktop Standard: 需要 3D Analyst
- ArcGIS Desktop Advanced: 需要 3D Analyst